Comparing Different Types of Waveforms: A Guide to Understanding the Waves Worksheet Answer Key
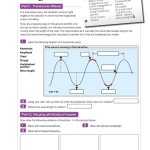
When it comes to comparing different types of waveforms, there are a few key parameters to consider. Waveforms are characterized by their amplitude, frequency, and phase. Amplitude is the maximum value of a signal, frequency is the number of cycles per second, and phase is the time relationship of the waveform to a reference point.
The most common types of waveforms are sine, cosine, square, and sawtooth.
Sine waves are characterized by their single-cycle, sinusoidal shape. They have an amplitude that oscillates between a maximum and a minimum value, and their frequency is constant throughout the waveform. Sine waves are often used in AC power, radio waves, and sound waves.
[toc]
Cosine waves are similar to sine waves, but the amplitude of a cosine wave varies with time. This type of waveform is often used for digital signals, and its frequency is also constant like a sine wave.
Square waves are created when the rise time and fall time of a signal are equal. They have a flat top and bottom, and they oscillate between a maximum and a minimum value. Square waves are often used in pulse-width modulation and digital timing circuits.
Sawtooth waves have a saw-shaped pattern. They have a rising slope that gradually decreases until it reaches a minimum value, followed by a sharp drop to a maximum value. Sawtooth waves are commonly used in audio synthesis, frequency modulation, and pulse-code modulation.
When comparing different types of waveforms, it is important to consider the shape of the wave, the amplitude, and the frequency. Understanding the differences between these waveforms can help you to make informed decisions when using them in electrical and electronic projects.
Exploring the Physics Behind Wave Interference: Using the Waves Worksheet Answer Key
Wave interference is a fascinating phenomenon of physics that occurs when two or more waves overlap in the same space. This interference can create a variety of effects, such as constructive interference, where two waves combine to produce a larger wave; or destructive interference, where two waves combine to produce a smaller wave. The effects of interference depend on the relative phases and amplitudes of the two waves.
The Waves Worksheet Answer Key provides a helpful guide to understanding wave interference. The worksheet includes diagrams of two waves that can be used to explore the effects of interference. By adjusting the relative phases of the two waves, the worksheet provides a visual representation of how wave interference works. It also highlights the difference between constructive and destructive interference.
The Waves Worksheet Answer Key is a useful tool for understanding wave interference. It provides an easy way to visualize the different effects that can occur when two waves interact. By manipulating the phases and amplitudes of the waves, students can observe the effects of interference and gain an appreciation for the importance of wave interference in physics. The worksheet is a great way to engage students in the exploration of wave interference and help them develop a better understanding of the physics behind it.
Wave Motion: A Comprehensive Analysis of the Waves Worksheet Answer Key
Wave Motion: A Comprehensive Analysis
The phenomenon of wave motion is one of the most important components of classical physics. Wave motion is a universal phenomenon that is present in nature in various forms, such as light, sound, and water. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of wave motion, examining the various types of waves, the properties of these waves, and their applications.
Types of Waves
Wave motion can be divided into two major categories: transverse and longitudinal waves. Transverse waves are those in which the displacement of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, while longitudinal waves are those in which the displacement of the medium is parallel to the direction of wave propagation. Examples of transverse waves include light, radio waves, and water waves, while examples of longitudinal waves include sound and seismic waves.
Properties of Waves
The properties of a wave can be determined by the wave equation. This equation states that the wave speed is equal to the product of the wave frequency and the wavelength. Additionally, the wave amplitude, or maximum displacement of the medium, can be determined by the wave equation as well.
Applications of Waves
Wave motion has a variety of applications. For example, sound waves are used in acoustic imaging and medical diagnosis. Radio waves are used in telecommunications and radar. Finally, light waves are used in optical communication and for imaging in astronomy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wave motion is an important component of classical physics and it is present in nature in various forms. Wave motion can be divided into transverse and longitudinal waves, and the properties of a wave can be determined by the wave equation. Additionally, wave motion has a variety of applications, such as sound waves in acoustic imaging and medical diagnosis, radio waves in telecommunications and radar, and light waves in optical communication and astronomy.
Conclusion
The Waves Worksheet Answer Key is a great resource for students and educators studying waves. It provides a comprehensive overview of the properties of waves, including their frequency, amplitude, and wavelength. It also provides answers to important questions about waves, such as how they move, how they interact with objects, and how they can be used in everyday life. By using the Waves Worksheet Answer Key, students can gain a greater understanding of this important part of physics, and can become more knowledgeable about the world around them.
[addtoany]