Exploring the Differences: Examining Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells with a Worksheet
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are two distinct types of cells found in nature. In order to better understand the differences between the two, it is important to examine their characteristics and structure. This worksheet is designed to explore the contrasts between the two types of cells in order to better comprehend their differences.
The most obvious difference between the two types of cells is their size. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells. They measure in the range of 0.2 to 2.0 microns in diameter, while eukaryotic cells range from 10 to 100 microns in diameter. This difference in size allows prokaryotic cells to fit in much smaller spaces than eukaryotic cells.
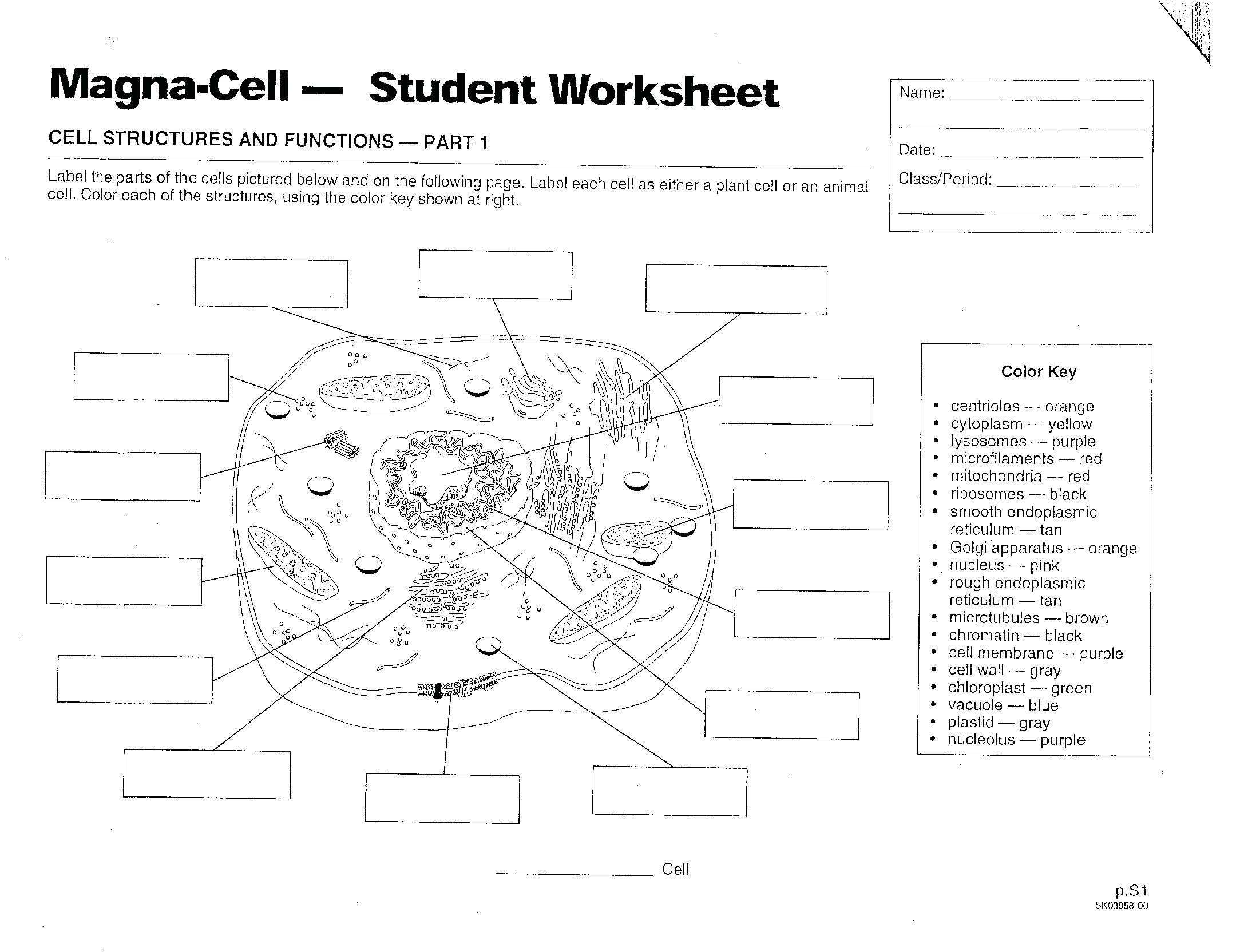
Another difference between the two types of cells is their structure. Prokaryotic cells contain no nucleus, whereas eukaryotic cells possess a membrane-bound nucleus. The nucleus of a eukaryotic cell houses the genetic material and the cell’s hereditary information. In addition, prokaryotic cells have no internal organelles, while eukaryotic cells contain various organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes. These organelles perform various cellular functions.
[toc]
The genetic material of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells also differs. Prokaryotic cells contain a single, circular DNA molecule that is not bound by a membrane. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, contain multiple linear DNA molecules bound by a nuclear membrane.
Finally, the reproduction process of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is distinct. Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually through a process called binary fission. During this process, the cell splits into two identical cells. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, reproduce sexually, with the fusion of two cellular components resulting in a new cell.
In conclusion, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are two distinct types of cells with distinct characteristics. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells and lack a nucleus and internal organelles. Furthermore, the genetic material of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ, as do their reproduction processes. By understanding these differences, one can better comprehend the complexity of the cellular world.
Uncovering the Mysteries of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells with an Interactive Worksheet
Cellular biology is an essential part of understanding life as we know it. In order to gain a better understanding of the structure and function of cells, it is important to explore the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. This worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and allows for an interactive exploration of the similarities and differences between them.
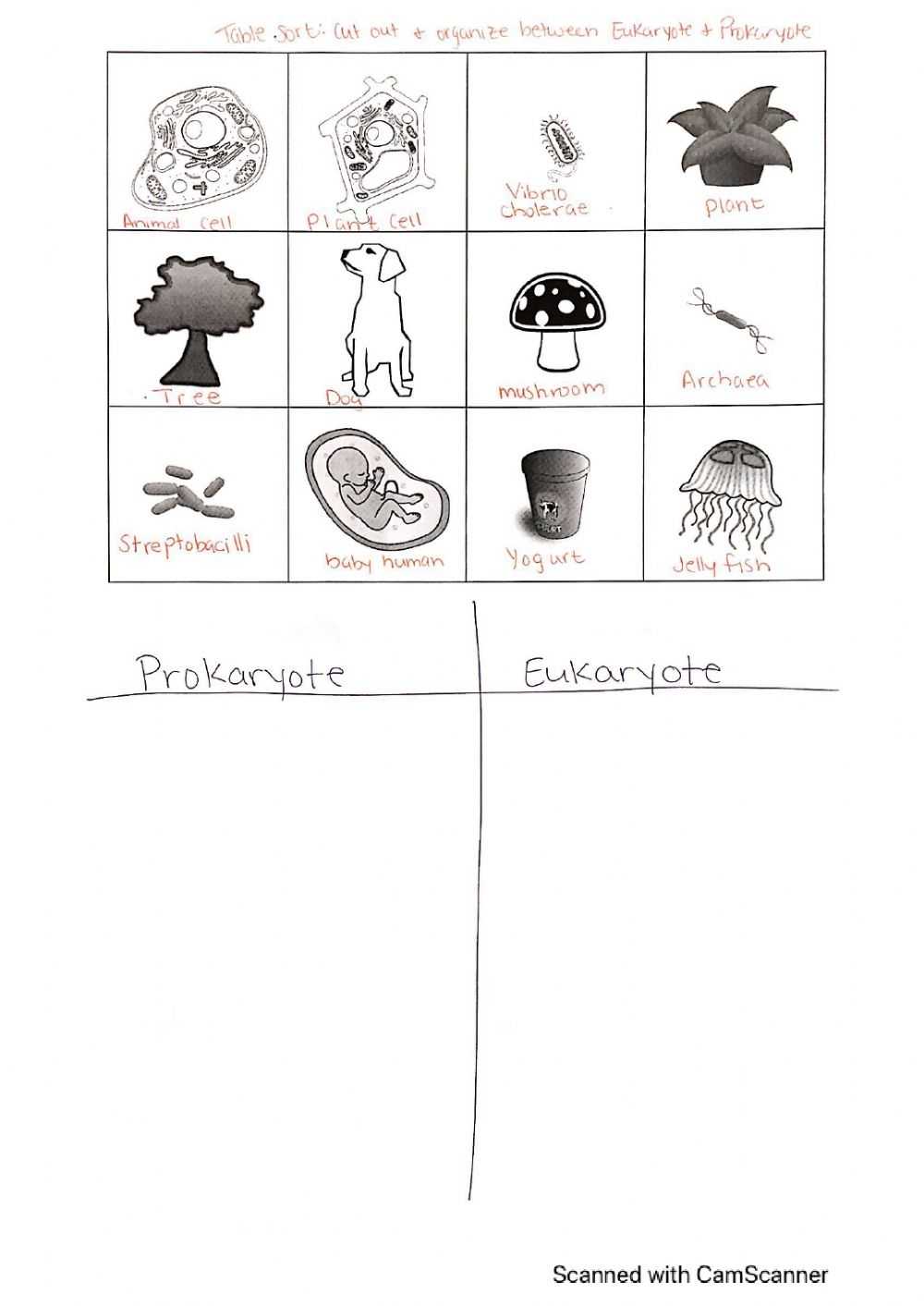
Studying prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is the first step towards understanding how life works. Prokaryotic cells are simple, single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus and other organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are more complex than prokaryotic cells, and contain a nucleus and various other organelles.
In this worksheet, students will be presented with a side-by-side comparison of the features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. This will allow them to discover the differences between the two cell types, including differences in their size, structure, and composition.
Students will also be given the opportunity to explore the similarities between the two cell types. By completing the interactive tasks provided, they will be able to identify the components of each cell type that are identical, such as the role of DNA, the presence of a cell membrane, and the role of ribosomes.
By completing this worksheet, students will gain a better understanding of the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and will be able to apply their knowledge to their studies of cellular biology.
Unlocking the Power of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells with an Engaging Worksheet
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are the building blocks of life, and understanding their differences and similarities is key to unlocking the secrets of biology. With this engaging worksheet, students will explore the complex functions of these two types of cells, and come to a better understanding of their individual roles in the body.
This worksheet begins by introducing the two types of cells and highlighting some of their most basic differences. For instance, prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells and lack a nucleus. Students will then be asked to name other differences between the two, such as the fact that eukaryotic cells contain organelles and prokaryotic cells do not.
Next, the worksheet focuses on how the two types of cells interact with each other. Students will be asked to identify the different organelles found in eukaryotic cells and explain their roles in the cell. They will also be asked to draw a diagram of a prokaryotic cell and label its components.
The worksheet also focuses on the differences between the two types of cells when it comes to metabolism. Students will be asked to explain how prokaryotic cells obtain energy, as well as how eukaryotic cells obtain energy.
Finally, the worksheet will ask students to identify the different types of cell division and explain their importance. Students will also be asked to give examples of how these processes are used in the body.
By completing this worksheet, students will gain a better understanding of the differences and similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. They will gain a greater appreciation for the complexity of the cell and how it functions in the body.
Using a Worksheet to Learn About the Unique Characteristics of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are two distinct forms of cells that compose the vast majority of life on Earth. While they share many similarities, they also have unique characteristics that set them apart. To better understand the differences between these two types of cells, it is important to explore the unique characteristics of each.
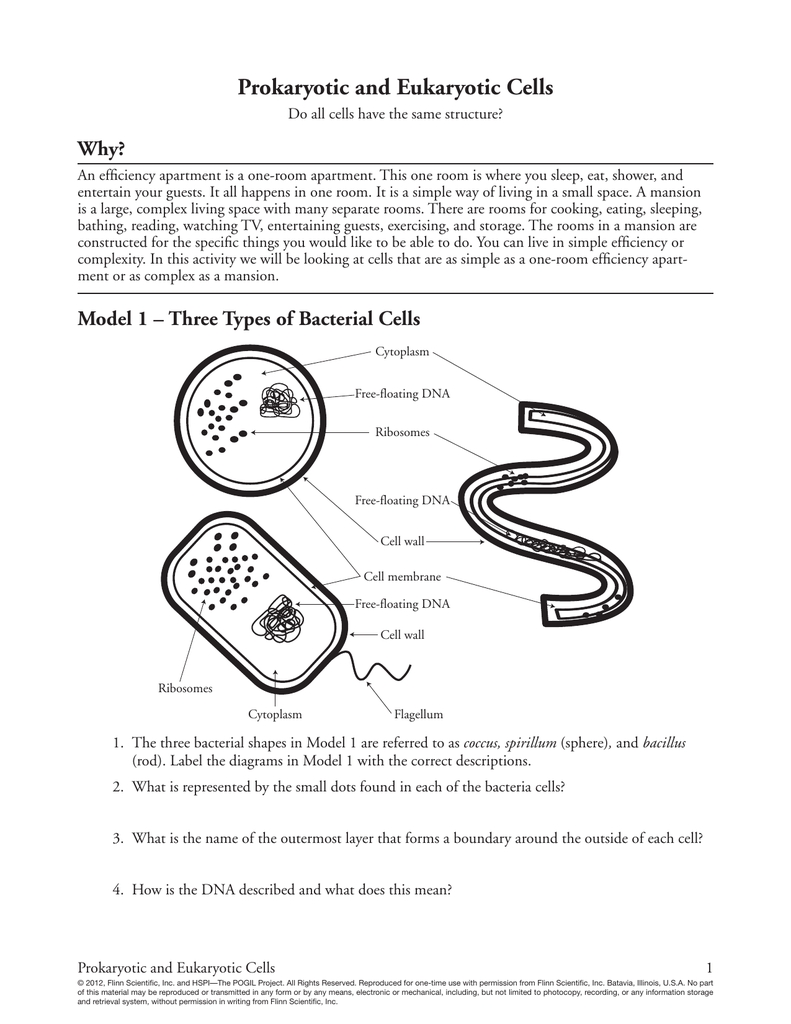
Prokaryotic cells are the simpler of the two cell types, and are typically found in single-celled organisms such as bacteria. They lack a nucleus, and their DNA is not contained within a membrane. Instead, the DNA is found in a region known as the nucleoid. Additionally, prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria or chloroplasts. Instead, the metabolic processes of these cells take place in the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are much more complex than prokaryotic cells. They contain a nucleus, which is a membrane-bound structure that houses the cell’s DNA. Additionally, eukaryotic cells contain other membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. These organelles play an important role in the metabolic processes of the cell, such as energy production and photosynthesis.
These two types of cells also differ in size. Prokaryotic cells are typically much smaller than eukaryotic cells, ranging from 0.1 – 10 micrometers in diameter. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, range from 10 – 100 micrometers in diameter.
In conclusion, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are two distinct forms of cells that have some similarities, but also unique characteristics that set them apart. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess both. Additionally, prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells. Understanding the unique characteristics of these two types of cells is an important part of understanding the biology of life on Earth.
Conclusion
The Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet has provided a good overview of the differences between the two types of cells. It has highlighted the major differences between the two, such as the presence of a nucleus in eukaryotic cells, and the lack of membrane-bound organelles in prokaryotic cells. While there are many similarities between the two, the differences are important to understand in order to appreciate the complexity and importance of cell structure and function.
[addtoany]