Exploring the Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: A Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet
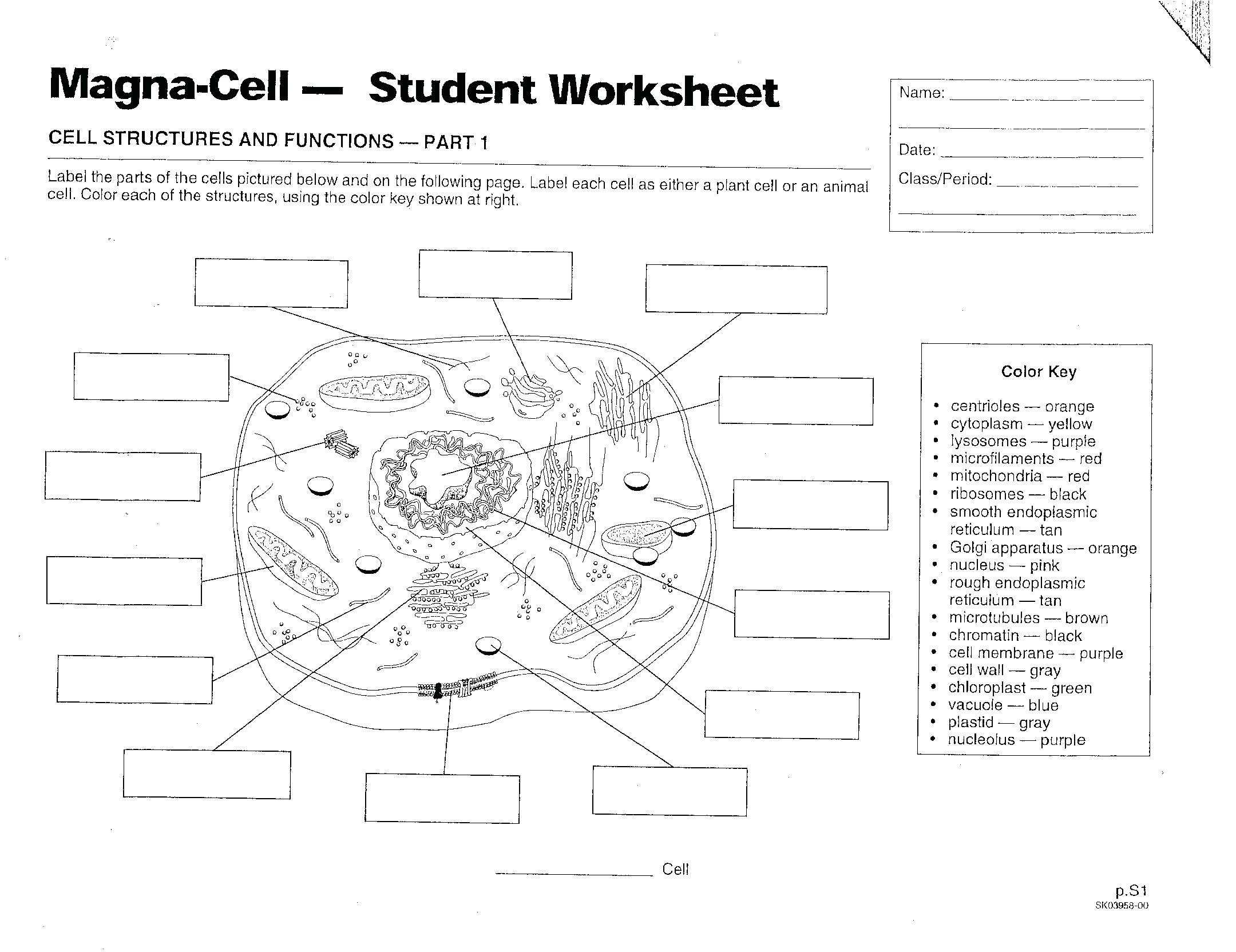
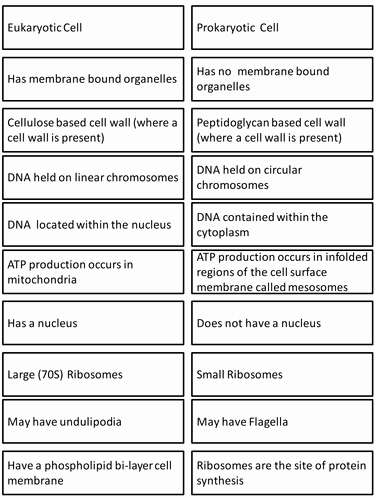
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are two distinct types of cells that differ in their structure and organization. Prokaryotic cells are the simplest type of cell and are found in all living organisms. They are often referred to as “primitive” cells, as they lack a nucleus and the other organelles found in eukaryotic cells. On the other hand, eukaryotic cells are much more complex and are found in higher life forms, such as plants and animals.
When comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, one of the most fundamental differences is the presence of a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus, and instead have their genetic material dispersed throughout the cell. Eukaryotic cells, however, contain a nucleus, which is surrounded by a nuclear membrane and contains the cell’s genetic material.
In addition to the presence of a nucleus, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells also differ in terms of the organelles they contain. Prokaryotic cells typically contain only a few organelles, such as ribosomes, a cell wall, and flagella. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, contain a variety of organelles, including the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts.
[toc]
The size of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is also different. Prokaryotic cells are generally much smaller than eukaryotic cells, ranging in size from 0.2 to 2.0 micrometers. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, can range in size from 10 to 100 micrometers.
Finally, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in terms of their method of reproduction. Prokaryotic cells reproduce by a process called binary fission, in which a single cell splits into two identical daughter cells. Eukaryotic cells reproduce through a process called mitosis, in which the cell’s genetic material is divided into two identical daughter cells.
In summary, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in a number of ways, including the presence of a nucleus, the number and types of organelles they contain, their size, and their method of reproduction. These differences are essential to understanding the structure and organization of living cells.
Unraveling the Mystery of Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells with a Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet
Prokaryote and eukaryote cells are the two fundamental types of cells found in nature. Prokaryote cells are simpler in structure and smaller than eukaryote cells. They have no nucleus or organelles, and their DNA is not bound by a membrane. Eukaryote cells, on the other hand, are more complex and much larger than prokaryote cells. They contain a nucleus, organelles, and their DNA is bound by a membrane.
This Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Worksheet will help students understand the major differences between these two types of cells. The worksheet begins by introducing the two types of cells and providing an overview of their structure and function. It then moves on to compare and contrast the two types of cells in detail, discussing their structure, organelles, DNA, and other important characteristics.
The worksheet then asks students to complete a number of questions related to the topic. These questions focus on the differences between the two types of cells and ask students to identify which type of cell contains a nucleus, organelles, and DNA. Finally, the worksheet provides an opportunity for students to interpret the information they have learned and draw their own conclusions about the differences between prokaryote and eukaryote cells.
By completing this Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Worksheet, students will gain a better understanding of the differences between these two types of cells. They will also be able to recognize and explain the structures and functions of each type of cell. This worksheet will provide an engaging way for students to explore the complex world of cellular biology.
Comparing and Contrasting Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells with a Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet
A comparison between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is often drawn in order to understand the differences between the two types of cells. Prokaryotic cells are simple cellular structures that lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles while eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and a variety of membrane-bound organelles. This prokaryote vs eukaryote worksheet explains the characteristics of each type of cell and contrasts the differences between them.
Prokaryotic cells are single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus and have a single circular DNA molecule. They also lack membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. These cells have a cell wall composed of peptidoglycan, which provides them with structure and protection. They also have a cell membrane that is responsible for regulating the movement of molecules into and out of the cell.
Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, contain a nucleus and a variety of membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains genetic material, such as DNA and RNA. The organelles are responsible for carrying out specific cellular functions. Eukaryotic cells also contain a cell wall composed of cellulose, which provides them with structure and protection. Additionally, they also contain a plasma membrane that is responsible for regulating the movement of molecules into and out of the cell.
The differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells can be summarized in the following way. Prokaryotic cells have a single circular DNA molecule, lack a nucleus, and do not contain membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus, a variety of membrane-bound organelles, and a cell wall composed of cellulose. By understanding these differences, we can gain an appreciation for the unique characteristics of each type of cell.
Using a Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet to Examine the Unique Characteristics of Each Cell Type
The prokaryote and eukaryote are two distinct types of cells that differ in their biological composition and structure. Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms and lack a nucleus, whereas eukaryotes are more complex and contain a nucleus. This article examines the unique characteristics of each cell type using a Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet.
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms, such as bacteria and archaea. They are characterized by the absence of a true nucleus, instead relying on a single loop of DNA to store genetic information. They also lack other organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, and have a much simpler cell structure than eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are able to reproduce quickly and are well adapted to their environment.
Eukaryotes, on the other hand, are more complex organisms that contain a nucleus, as well as other organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. Their DNA is also more complex, with multiple linear chromosomes that are organized within a membrane-bound nucleus. Eukaryotic cells are more efficient at harvesting energy from their environment than prokaryotic cells, and can reproduce more slowly.
In conclusion, the Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheet reveals the fundamental differences between these two types of cells. Prokaryotes lack a nucleus and other organelles, and are adapted for rapid reproduction, whereas eukaryotes are more complex and contain a nucleus, as well as other organelles. Eukaryotic cells also have a more complex DNA structure and are more efficient at harvesting energy.
Conclusion
The Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Worksheet has provided an overview of the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms without a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotes are multi-celled organisms that contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. By understanding the differences between these two types of organisms, it is possible to better understand the structure and function of cells.
[addtoany]