Understanding Rational Exponents and Radicals: A Step-by-Step Guide
Rational exponents and radicals are important elements of algebra. Using them accurately and confidently can help you solve equations and perform other mathematical tasks with ease. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to understanding and working with rational exponents and radicals.
To begin, it is important to understand the definition of a rational exponent. A rational exponent is a fractional exponent, meaning it is an exponent that is a fraction. It is expressed as a fraction with a numerator that is greater than or equal to one and a denominator that is greater than one. For example, the expression x2/3 is a rational exponent.
The next step is to understand the definition of a radical. A radical is an expression that contains a square root. The square root can be of any number, but it is typically of a number that is not a perfect square. For example, the expression √5 is a radical.
[toc]
Now that the definitions of rational exponents and radicals are clear, let us move on to how they are used. Rational exponents are used to express roots as powers. For example, the expression x2/3 can be written as (x1/3)2. This is known as rationalizing the denominator.
Radicals can be used to express powers as roots. For example, the expression x2 can be written as √x4. This is known as taking the root of the power.
Rational exponents and radicals can also be used to simplify expressions. For example, the expression √25 can be written as 5√1. This is known as simplifying a radical.
Finally, rational exponents and radicals can be combined to form equations. For example, the equation x2/3 = 5 can be written as (x1/3)2 = 5. This is known as combining rational exponents and radicals.
This guide has provided a step-by-step approach to understanding and working with rational exponents and radicals. With practice and patience, you can use these mathematical tools with ease and confidence.
Examining the Different Types of Rational Exponents and Radicals
Rational exponents and radicals are essential components of algebraic equations. They are used to solve complex equations, and they are represented as superscripts and indices. Rational exponents and radicals have different properties that set them apart from one another.
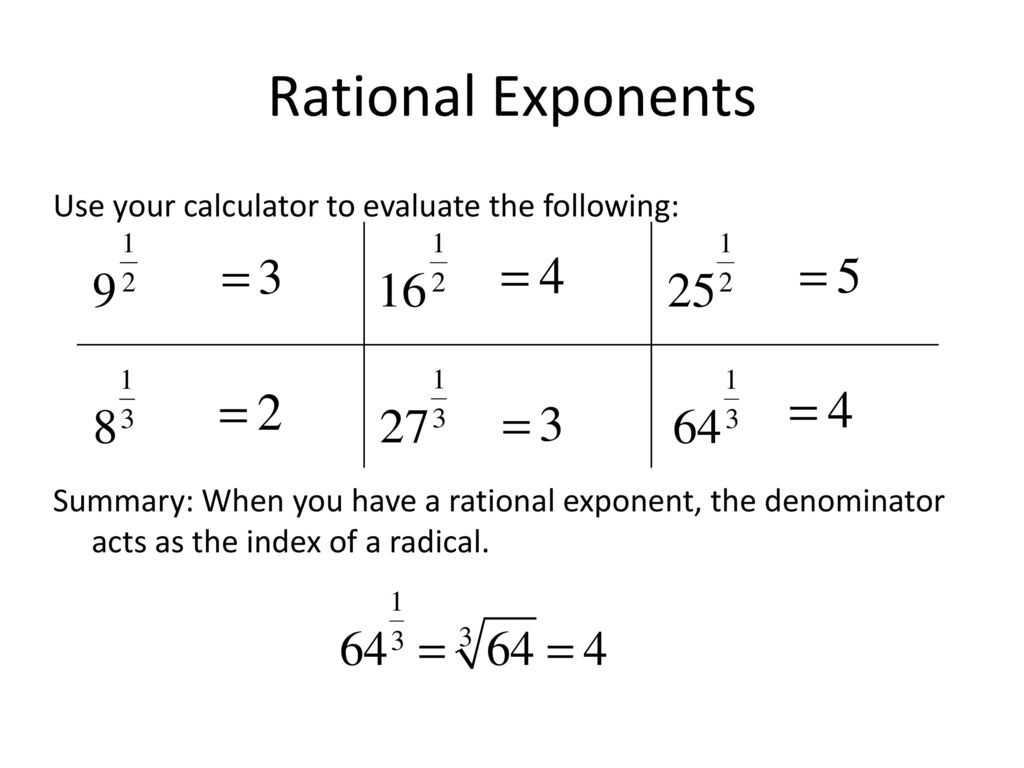
The first type of rational exponent is a power, which is denoted by a superscript number. For example, the power of two would be written as 2^2. This means that two is multiplied by itself twice, or squared. Powers can also be expressed in fractional form, such as 2^(1/2). This means that two is being divided by itself, or square rooted.
The second type of rational exponent is a root. Roots are denoted by an index, which is a number in the bottom right corner of a radical sign. For example, the square root of two would be written as √2. This means that two is being divided by itself, or square rooted. Roots can also be expressed in fractional form, such as ∛8. This means that eight is being divided by itself three times, or cubed.
Rational exponents and radicals are important components of algebraic equations, and they are represented in different ways. Powers are denoted by superscripts, while roots are denoted by indices. Powers can also be expressed in fractional form, while roots can also be expressed in fractional form. Understanding the different types of rational exponents and radicals is essential for solving complex equations.
Exploring the Benefits of Using Rational Exponents and Radicals in Algebraic Equations
Rational exponents and radicals are important components of algebraic equations. They enable mathematicians to solve equations more efficiently and accurately. Rational exponents are the exponents of fractions or rational numbers, while radicals are the roots of numbers. When used together, rational exponents and radicals can help to simplify and solve complex algebraic equations.
The use of rational exponents and radicals in algebraic equations can be beneficial in several ways. Firstly, rational exponents can be used to represent repeated multiplication of a number or variable. For example, the expression x2 can be written as x1/2, making it easier to calculate the value of the expression. Similarly, radicals can be used to represent the root of a number or variable. This allows for the simplification of equations that involve square roots, cube roots, and more complex roots.
Not only does the use of rational exponents and radicals simplify equations, it can also help to make them more accurate. By using rational exponents and radicals, mathematicians can eliminate errors that may arise from rounding numbers. This is because the root of a number or variable will always yield the exact value.
Finally, rational exponents and radicals can be used to express equations in a more concise manner. In some cases, an equation containing radicals or exponential terms may be simpler and easier to understand than an equation that only contains variables and operators. This makes it easier for mathematicians to identify patterns, make predictions, and draw conclusions.
Overall, the use of rational exponents and radicals in algebraic equations can have many advantages. Not only can they help to simplify and solve equations, they can also make equations more accurate and concise. By utilizing these powerful tools, mathematicians can gain insight into the underlying structure of complex equations and make informed decisions about the best way to solve them.
Conclusion
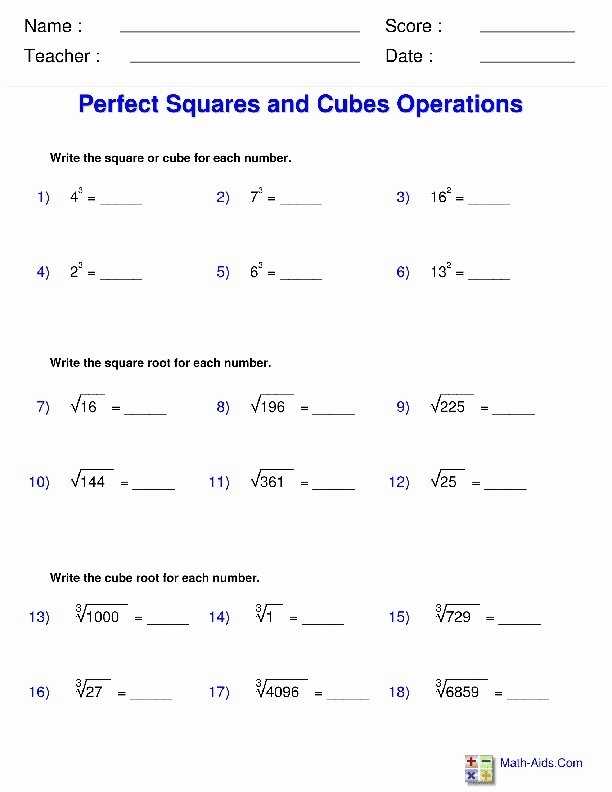
The Rational Exponents and Radicals Worksheet provides students with important practice in manipulating rational exponents and radicals. With this practice, students can understand the properties of radical and rational exponents and how to manipulate them to solve real-world problems. Additionally, the worksheet helps students develop a deeper understanding of the relationship between rational exponents and radicals. Furthermore, the worksheet can be used to strengthen students’ algebraic skills and develop the critical thinking skills necessary for success in higher level math.
[addtoany]