Exploring the Basics of Cellular Transport: A Guide to Understanding the Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key
Cellular transport is an essential process for all cells. Without it, cells would be unable to receive the necessary nutrients and materials they need to survive and function. Understanding the basics of cellular transport is important for anyone studying biology, chemistry, or related fields.
This guide will help you understand the answers to the Cellular Transport Worksheet, which tests your knowledge of the different types of cellular transport.
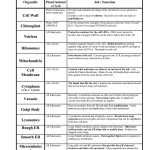
Diffusion: Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This type of transport is passive, meaning that it does not require energy. Diffusion is an important process in cells as it allows them to absorb molecules needed for functions like respiration and metabolism.
[toc]
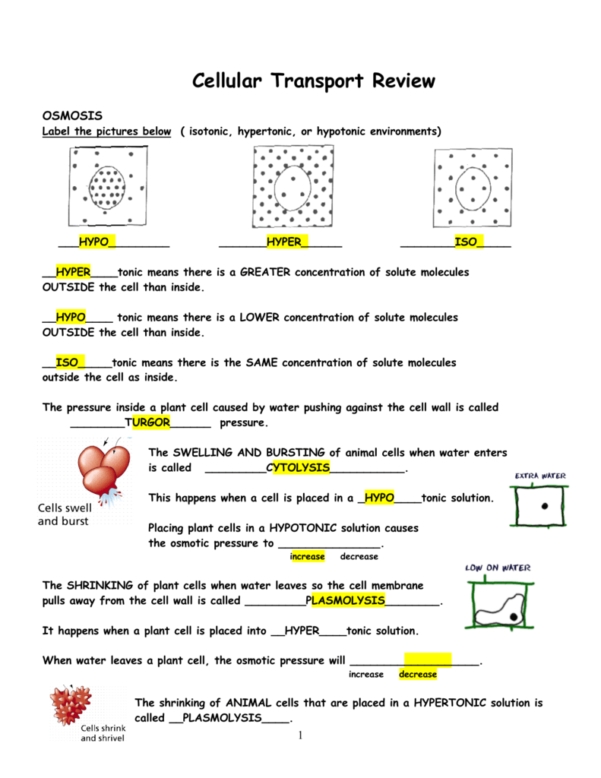
Osmosis: Osmosis is similar to diffusion, except it involves the movement of water molecules. When two solutions of different concentrations are separated by a semi-permeable membrane, water molecules will move from the area of higher concentration to the area of lower concentration. This type of transport is also passive and is important for maintaining the balance of water and other molecules within the cell.
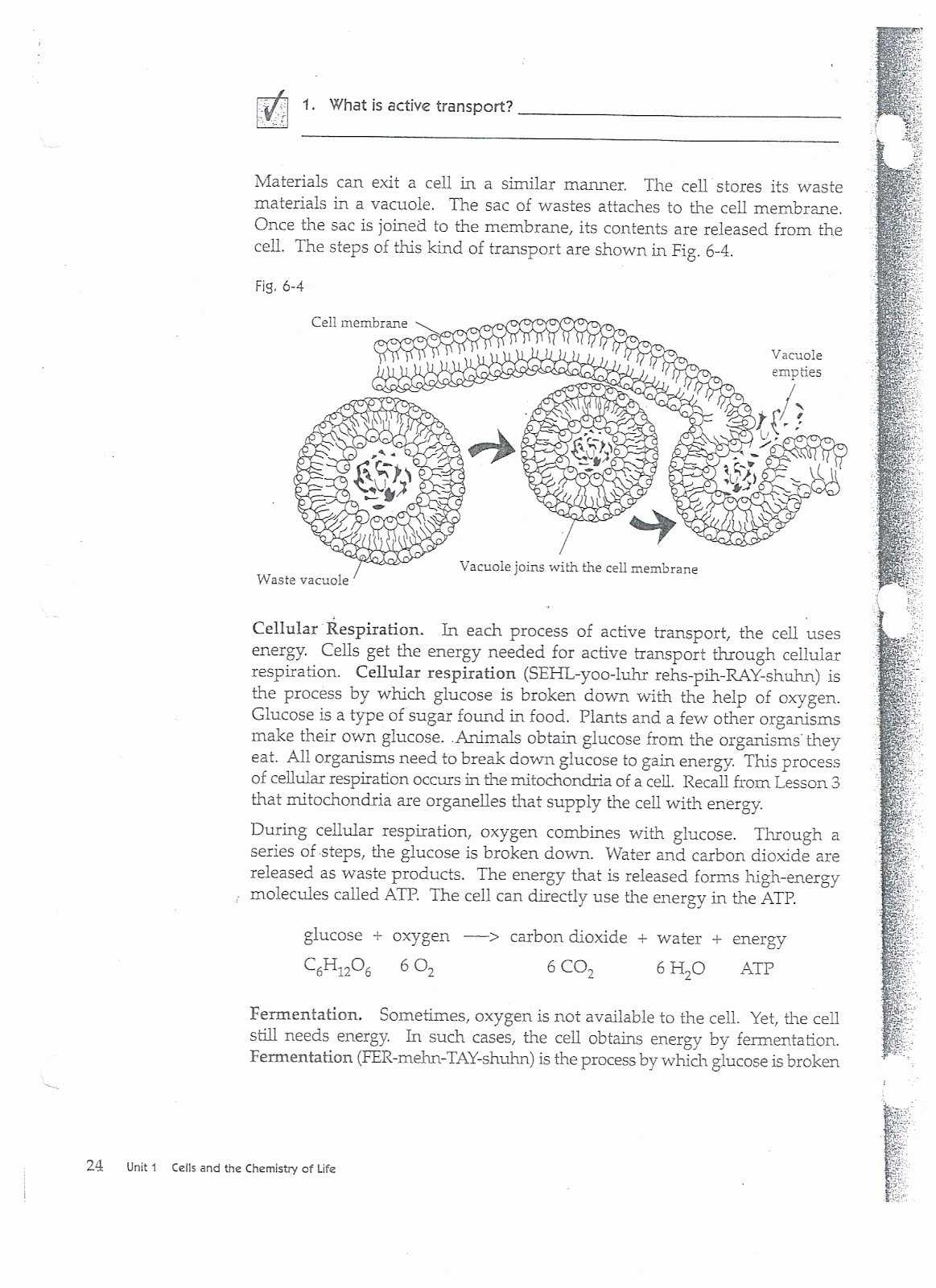
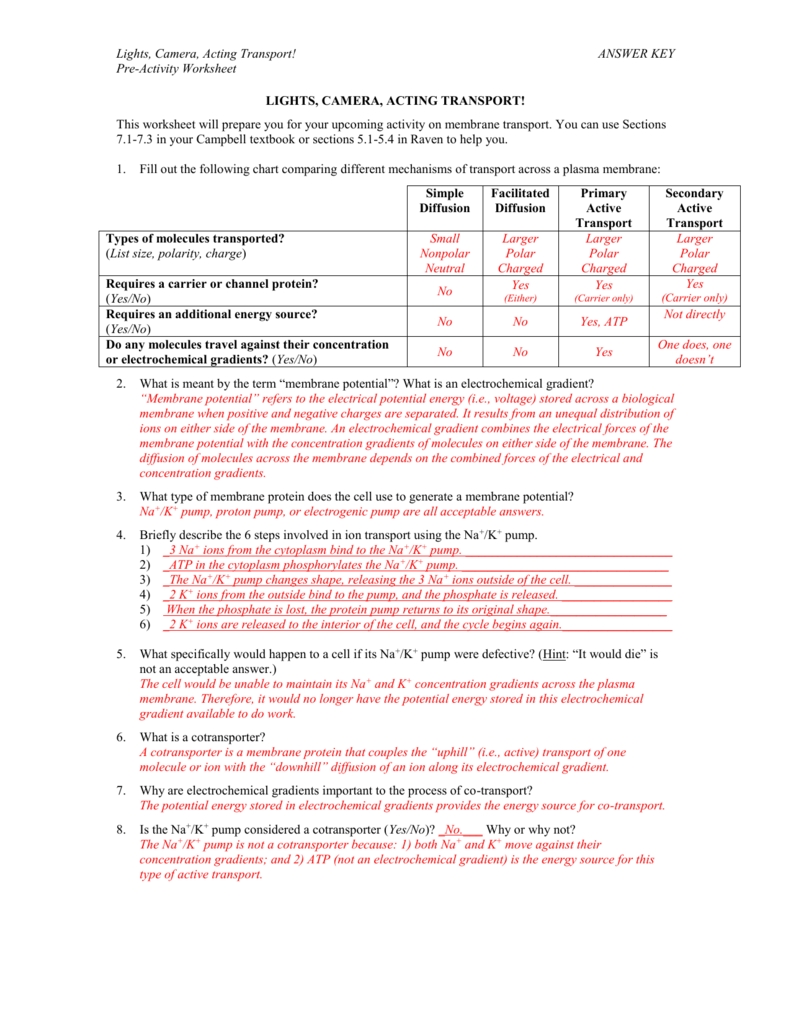
Active Transport: Active transport is the movement of molecules from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. This type of transport requires energy, usually in the form of ATP. Active transport is important for cells to obtain molecules that cannot pass through the cell membrane by diffusion or osmosis.
Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process by which cells take in large molecules or particles by engulfing them with the cell membrane. This type of transport is usually used to take in nutrients and other molecules that are too large to be absorbed by diffusion or osmosis.
Exocytosis: Exocytosis is the opposite of endocytosis and involves the release of molecules from within the cell. This type of transport is used to release molecules that are too large to pass through the cell membrane.
By understanding these different types of cellular transport, you can better understand the answers to the Cellular Transport Worksheet. Being familiar with the basics of cellular transport will give you a greater appreciation for this important process.
Unpacking the Science Behind Cellular Transport: A Look at the Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key
Cellular transport is a fundamental process in the life of every cell. It is the movement of molecules in and out of the cell, allowing for the exchange of necessary nutrients and waste products. The Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key helps students to understand the science behind how this process works.
The worksheet starts by introducing the basics of cellular transport, including active and passive transport, facilitated diffusion, and endocytosis and exocytosis. It also explains the role of membrane proteins in allowing molecules to move across the cell membrane. This helps students to understand the different types of cellular transport and how they work.
The worksheet then goes on to explain the role of energy in cellular transport. It explains how ATP is used to power the movement of molecules through the membrane. This helps students to understand why cellular transport requires energy, and how it is used.
The worksheet then goes on to discuss the different types of solutes and how they move across the membrane. It explains how solutes can be moved passively, or by active transport. It also discusses osmosis, diffusion, and how these processes are affected by the concentration gradient.
Finally, the worksheet explains how cells use energy to move molecules across the membrane. It explains the role of ATP and how it is used to power active transport. It also discusses how different types of molecules are moved across the membrane, and how specialized proteins can facilitate the movement of molecules. This helps students to understand the complexities of cellular transport and how it works.
Overall, the Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key provides a comprehensive look at the science behind cellular transport. It explains the basics of cellular transport, including active and passive transport, facilitated diffusion, and endocytosis and exocytosis. It also explains the role of energy in cellular transport, and how different types of solutes move across the membrane. Finally, it explains how cells use energy to move molecules across the membrane, and how specialized proteins can facilitate this movement. This helps students to gain a better understanding of the science behind cellular transport and how it works.
Investigating the Role of Cellular Transport in Structural Support: Examining the Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key
Cellular transport plays an important role in the structural support of cells. The Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key provides an in-depth examination of the mechanisms that are responsible for the movement of substances in and out of cells.
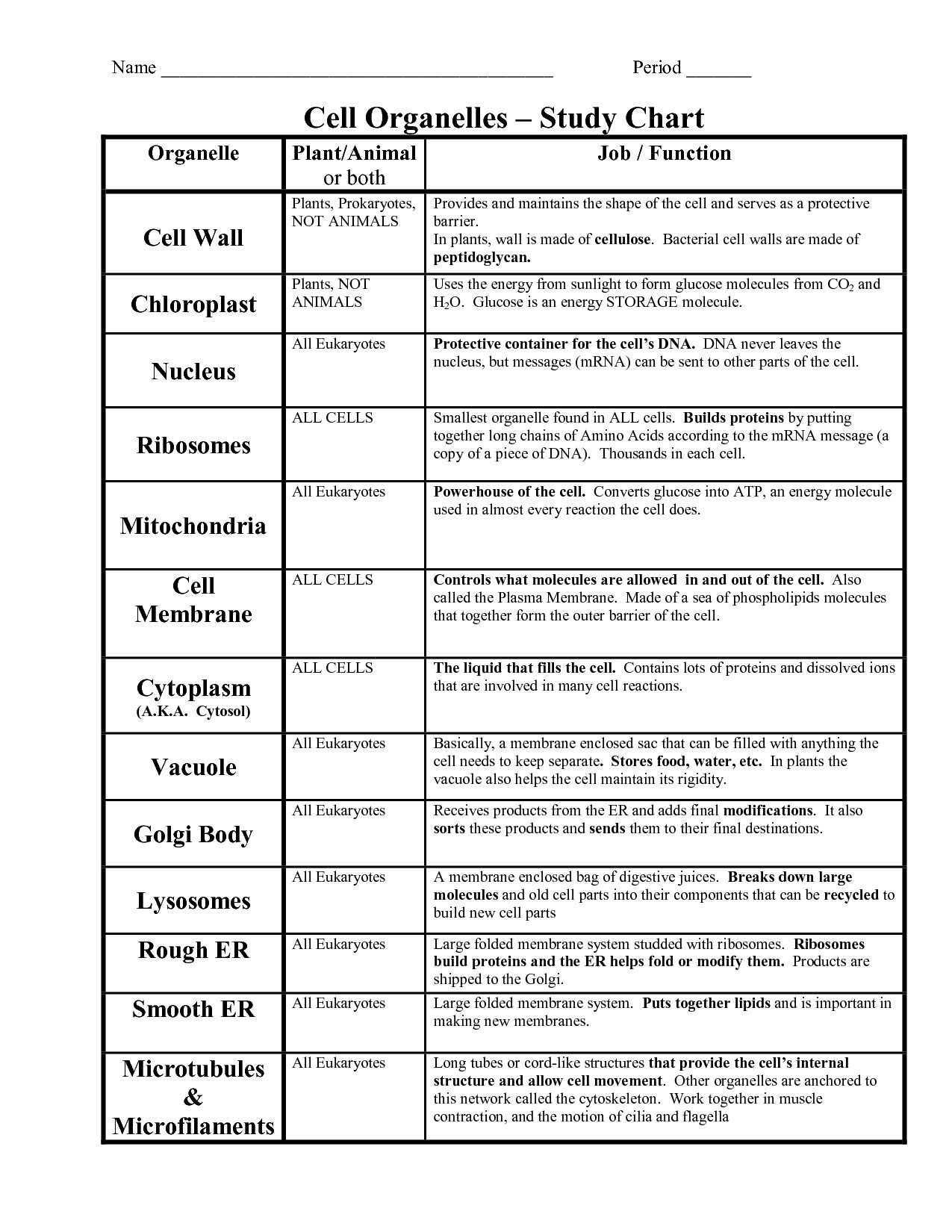
The Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key starts by introducing the main types of cellular transport: passive, active, and endocytosis. It explains how these forms of transport are used to move substances across cell membranes, and how they work together to maintain the balance of materials inside and outside of the cell. The answer key also describes the role of proteins in the process, such as channel proteins, carrier proteins, and receptors, as well as their function in transporting material.
Next, the Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key explains the importance of membrane composition in cellular transport. It covers topics such as the structure of the cell membrane, the role of lipids, and the role of proteins in determining the permeability of the membrane.
Finally, the Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key looks at the role of ions in the movement of materials. It explains how ions are transported through channels, how they interact with proteins, and how they affect the movement of substances across the cell membrane.
By examining the Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key, it is evident that cellular transport plays an integral role in the structural support of cells. It is essential for the movement of substances across the cell membrane, and for maintaining the balance of materials inside and outside of the cell. Understanding the process of cellular transport is essential for understanding how cells work and how they are able to maintain their structure.
Analyzing the Significance of Diffusion in Cellular Transport: Exploring the Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key
Diffusion plays a critical role in cellular transport, allowing for the movement of molecules, ions, and other materials across the cell membrane. Diffusion is a passive process, which means that it does not require energy or the assistance of specialized proteins. Instead, it relies on the natural tendency of molecules to move from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration. This process is known as concentration gradient, and it is an essential factor in the diffusion of molecules across a cell membrane.
The process of diffusion is made possible due to the presence of small pores in the cell membrane. These pores, known as ion channels, allow molecules to pass through the membrane without being hindered by it. This allows for the movement of substances such as oxygen, glucose, and amino acids across the membrane.
In addition to aiding in the movement of materials across the cell membrane, diffusion also helps to maintain the concentration gradient in the cell. When molecules move across the cell membrane, they create a concentration gradient that helps to maintain the balance of substances inside and outside the cell. This process is known as osmosis, and it is essential for the functioning of the cell.
Diffusion is also important for the regulation of cell volume. As molecules and ions move across the cell membrane, they create a gradient that helps to control the amount of water that is entering and exiting the cell. This helps to maintain the balance of fluids and solutes in the cell, allowing for the maintenance of cell volume.
In conclusion, diffusion plays a significant role in cellular transport, allowing for the movement of molecules, ions, and other materials across the cell membrane. It also helps to maintain the concentration gradient in the cell, as well as regulate cell volume. As such, diffusion is a critical process in the functioning of the cell.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key provides a comprehensive overview of the concepts and processes involved in cellular transport. It highlights the importance of understanding the different types of transport processes, as well as their respective roles in maintaining cell homeostasis. This information can be used to better understand cellular physiology and help students gain a better understanding of the various transport mechanisms at work in the cell.
[addtoany]