Exploring the Role of Transport in Cell Biology: Examining the Answers in a Transport in Cells Worksheet
Transport in cells is an area of research that has become increasingly important in the field of cell biology. It is now known that cells rely on the movement of molecules and ions across their membrane in order to maintain homeostasis and allow for necessary functions to occur. This article will explore the role of transport in cell biology by examining the answers in a transport in cells worksheet.
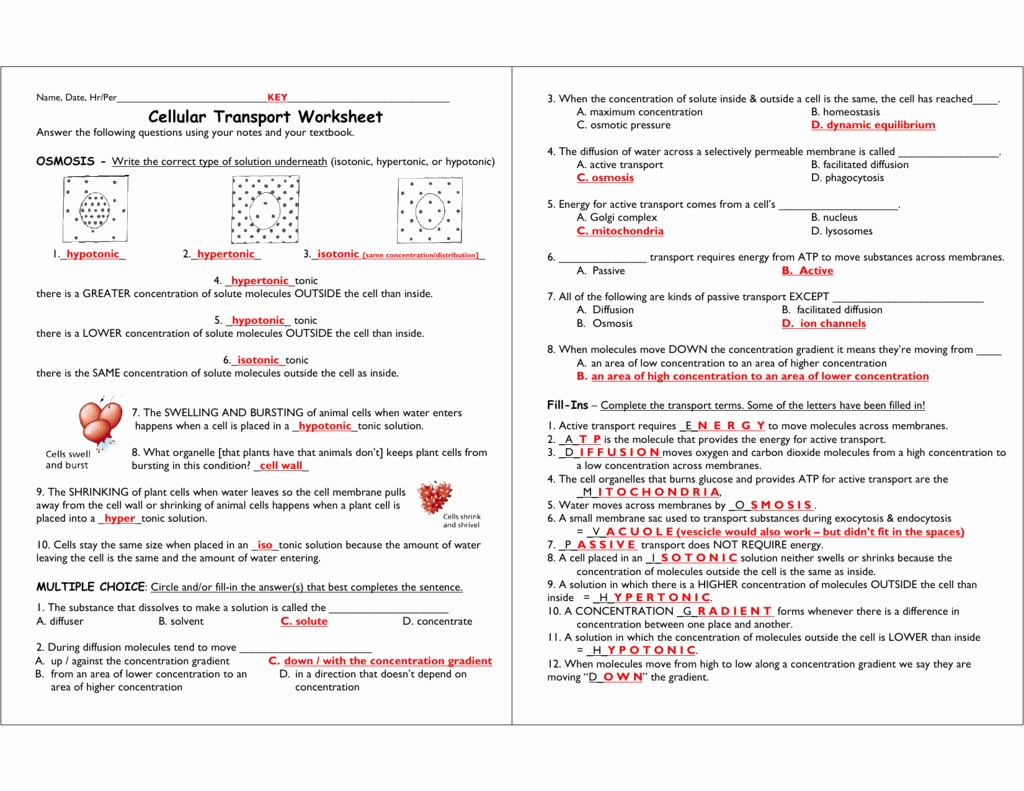
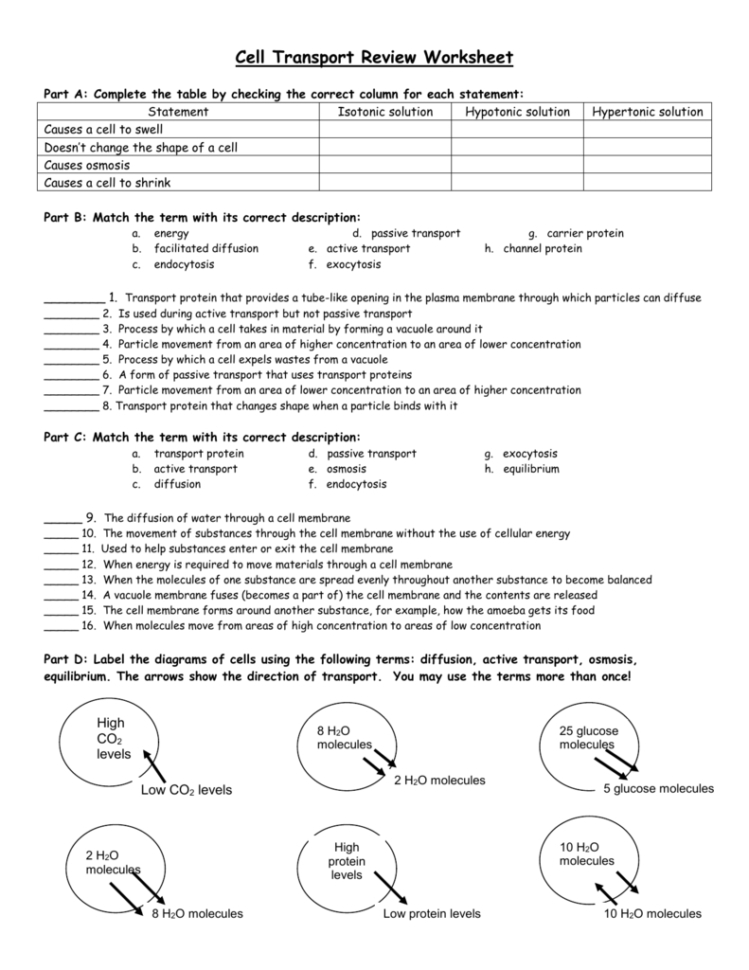
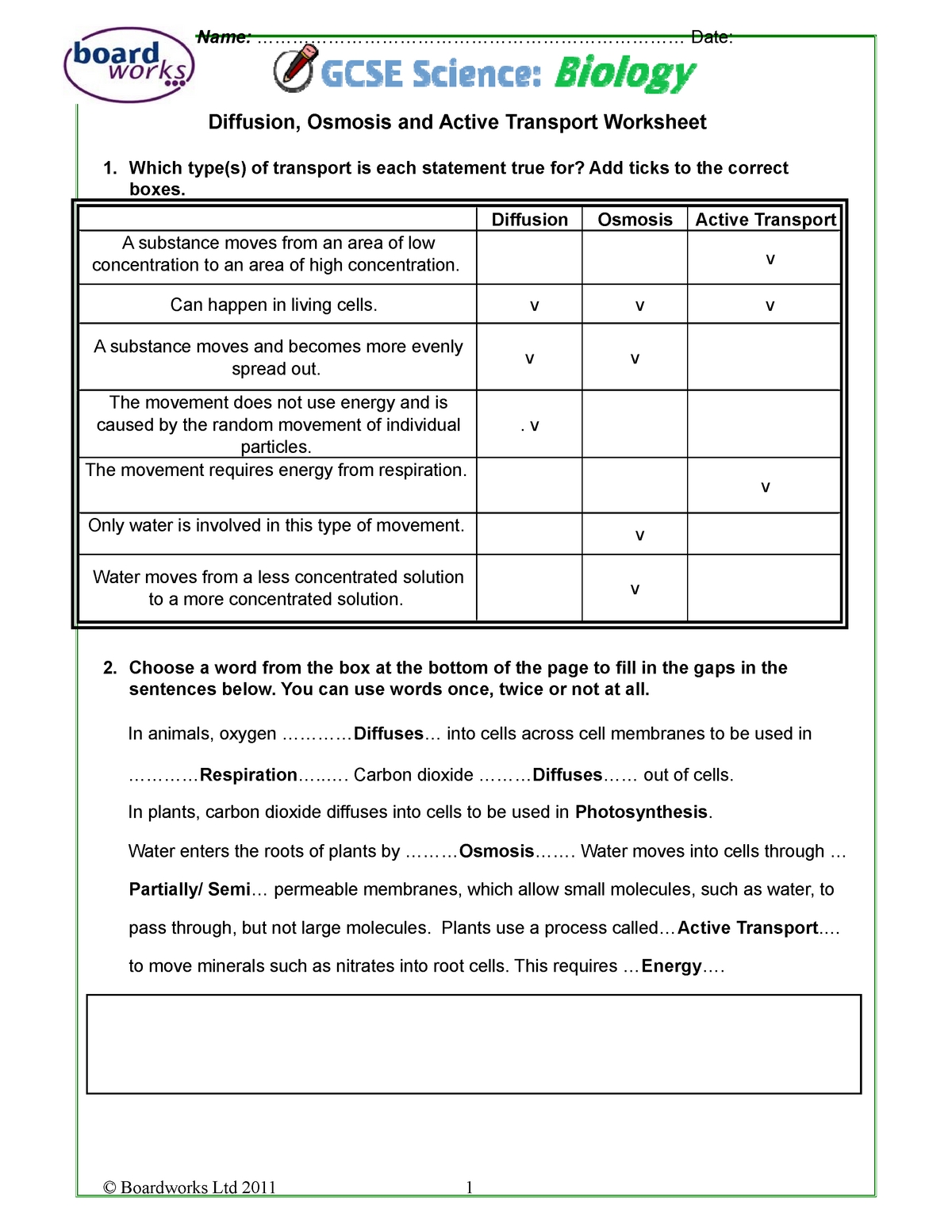
The worksheet begins by introducing students to the concept of transport in cells. It explains how molecules and ions are moved in and out of cells, and the importance of this process for cell function. The worksheet then goes on to discuss the two main types of transport: passive and active. Students are asked to identify the differences between these two forms of transport, as well as their respective roles in cell biology.
Next, the worksheet introduces students to the various types of transporters that are found in cells. These include channels, pumps, transporters, and carriers. Students are asked to identify the differences between these types of transporters, as well as their respective roles in cell biology. The worksheet also explains the mechanisms by which these transporters work, including the role of electrochemical gradients and concentration gradients.
[toc]
The worksheet then goes on to discuss the various types of cargo that can be transported across cell membranes. This includes proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Students are then asked to explain how these substances are moved in and out of cells. Finally, students are asked to identify the importance of transport in cells, and how it contributes to cell biology.
By examining the answers in this transport in cells worksheet, it is clear that transport plays a vital role in cell biology. It is responsible for the movement of molecules and ions across cell membranes, enabling cells to maintain homeostasis and carry out necessary functions. It is also responsible for the transport of various cargo substances, allowing them to move in and out of cells. Finally, it is responsible for the maintenance of electrochemical and concentration gradients, allowing cells to perform their necessary functions. Through this worksheet, students can gain a better understanding of the role of transport in cell biology, and how it contributes to the overall functioning of cells.
Analyzing the Impact of Membrane Transport on Cell Function: Decoding the Answers in a Transport in Cells Worksheet
Membrane transport plays an essential role in the functioning of cells. It is responsible for the movement of molecules, ions, and other substances across the cell membrane. This process is essential for the proper functioning of cells, as it allows for the exchange of nutrients, waste products, and other essential molecules.
The impact of membrane transport on cell function can be explored by completing a Transport in Cells Worksheet. This worksheet can be used to identify the transport processes involved in the movement of molecules and ions, as well as their impact on the cell. Additionally, the worksheet can help to identify the mechanisms by which molecules and ions are transported across the cell membrane, as well as how this process is regulated.
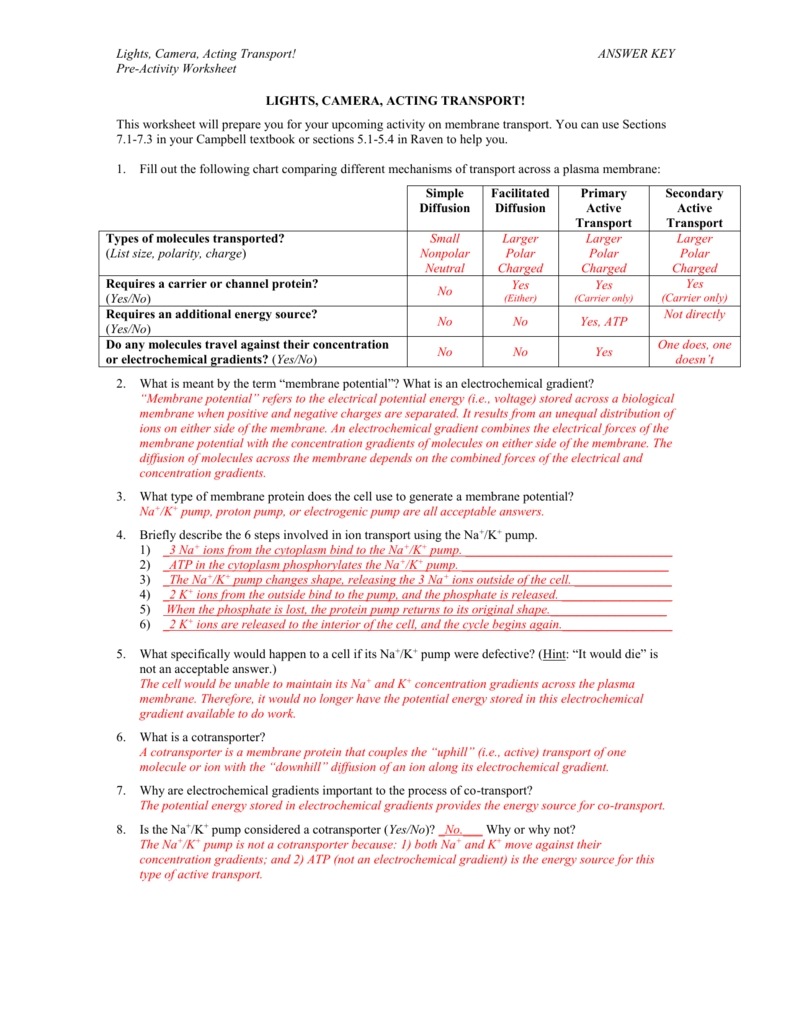
The first section of the worksheet focuses on active transport. This type of transport occurs when molecules, ions, or other substances are moved against a concentration gradient. This type of transport requires energy, and can be either primary, secondary, or facilitated. Primary active transport occurs when molecules, ions, or other substances are moved against a concentration gradient using a specific protein. Secondary active transport occurs when molecules, ions, or other substances are moved against a concentration gradient using an ATP-driven pump. Facilitated transport occurs when molecules, ions, or other substances are moved across the cell membrane using a carrier protein.
The second section of the worksheet focuses on passive transport. This type of transport occurs when molecules, ions, or other substances are moved down a concentration gradient without the use of energy. This type of transport can be either simple diffusion or facilitated diffusion. Simple diffusion occurs when molecules, ions, or other substances are moved down a concentration gradient without the assistance of a carrier protein. Facilitated diffusion occurs when molecules, ions, or other substances are moved down a concentration gradient using a carrier protein.
The Transport in Cells Worksheet can be used to gain a better understanding of the impact of membrane transport on cell function. Through this worksheet, we can explore how molecules, ions, and other substances are moved across the cell membrane, as well as how this process is regulated. Additionally, we can gain a better understanding of the mechanisms by which molecules, ions, and other substances are moved across the cell membrane. With this knowledge, we can gain a better understanding of how these processes affect the functioning of cells.
Understanding the Significance of Vesicular Transport in Cell Biology: A Guide to the Answers in a Transport in Cells Worksheet
Vesicular transport is a process that is essential for the functioning of cells. It involves the movement of molecules and particles from one area to another within the cell. In order to understand the importance of this process, it is important to have a basic knowledge of cell biology and the role of vesicular transport in it.
Vesicular transport is the process of transporting molecules and particles within the cell by vesicles, which are small, membrane-bound structures. Vesicles are formed from the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and plasma membrane, and they are responsible for transporting large molecules, such as proteins, within the cell. They can also be used to transport particles, such as ions and small molecules, from one area of the cell to another. This process is important for the functioning of the cell, as it allows the cell to move molecules and particles to where they are needed.
In addition, vesicular transport is important for the regulation of cell signals. Vesicles can carry a variety of signalling molecules and proteins that help the cell respond to its environment. By carrying these signalling molecules, vesicles can help the cell recognize and respond to changes in its environment. This is essential for the cell to be able to respond to stimuli, such as hormones and other external signals.
In order to understand the significance of vesicular transport in cell biology, it is important to look at how it is used in a transport in cells worksheet. In a transport in cells worksheet, vesicular transport is used to describe the movement of molecules and particles from one area of the cell to another. The worksheet typically includes diagrams that illustrate the movement of molecules and particles within the cell and how they are transported by vesicles.
In addition to diagrams, the worksheet usually includes questions related to the vesicular transport process. These questions can include questions about the structure of vesicles, how they are formed, and how they transport molecules and particles. By answering these questions, students can gain a better understanding of the importance of vesicular transport in cell biology.
Vesicular transport is an important process that is essential for the functioning of cells. By understanding the significance of this process, students can gain a better understanding of how cells function and how they respond to their environment. By answering questions related to vesicular transport in a transport in cells worksheet, students can gain a better understanding of the importance of this process in cell biology.
Investigating the Role of Active Transport in Cellular Processes: An Overview of Answers in a Transport in Cells Worksheet
Active transport is an essential process for the functioning of cells. It is the movement of molecules across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient, which is driven by ATP hydrolysis. This process is vital for the transport of nutrients, hormones, and other necessary molecules into the cell and for the removal of wastes from the cell.
Active transport is carried out by a variety of membrane proteins, such as ion channels, carriers, and pumps. Ion channels are pores in the membrane that allow ions to flow through, while carriers and pumps are integral membrane proteins that can bind to specific molecules and move them across the membrane.
The role of active transport in cellular processes is essential in order to maintain homeostasis in the cell. It allows cells to achieve a steady-state concentration of molecules inside and outside of the cell. Active transport is also necessary for the transport of molecules across the membrane that are too large to diffuse through the membrane. This process is also important for the secretion and absorption of hormones, as well as for the transport of toxins and wastes out of the cell.
Active transport is a highly regulated process, and the proteins involved in this process are regulated by several different mechanisms. These mechanisms include phosphorylation, allosteric regulation, and proteolytic cleavage. Each of these mechanisms can fine-tune the activity of the proteins, allowing them to respond to changes in the cell’s environment.
In summary, active transport is a vital process for the functioning of cells. It allows cells to maintain homeostasis, transport large molecules, and secrete and absorb hormones. This process is regulated by several different mechanisms, allowing the proteins involved to respond to changes in the cell’s environment.
Conclusion
The Transport in Cells Worksheet Answers provide a great overview of the different types of transport that can occur in a cell. It is important to understand how each type of transport works and how it can affect the cell’s function. With this knowledge, students can gain a better understanding of how cells function and what happens when something goes wrong. It is also important to remember that transport across a membrane is not always easy and that some molecules may require special proteins to move them from one side of the membrane to the other. With this understanding, students can gain a better appreciation for the complexity of the cell and its importance in maintaining life.
[addtoany]