Exploring the Necessary Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System
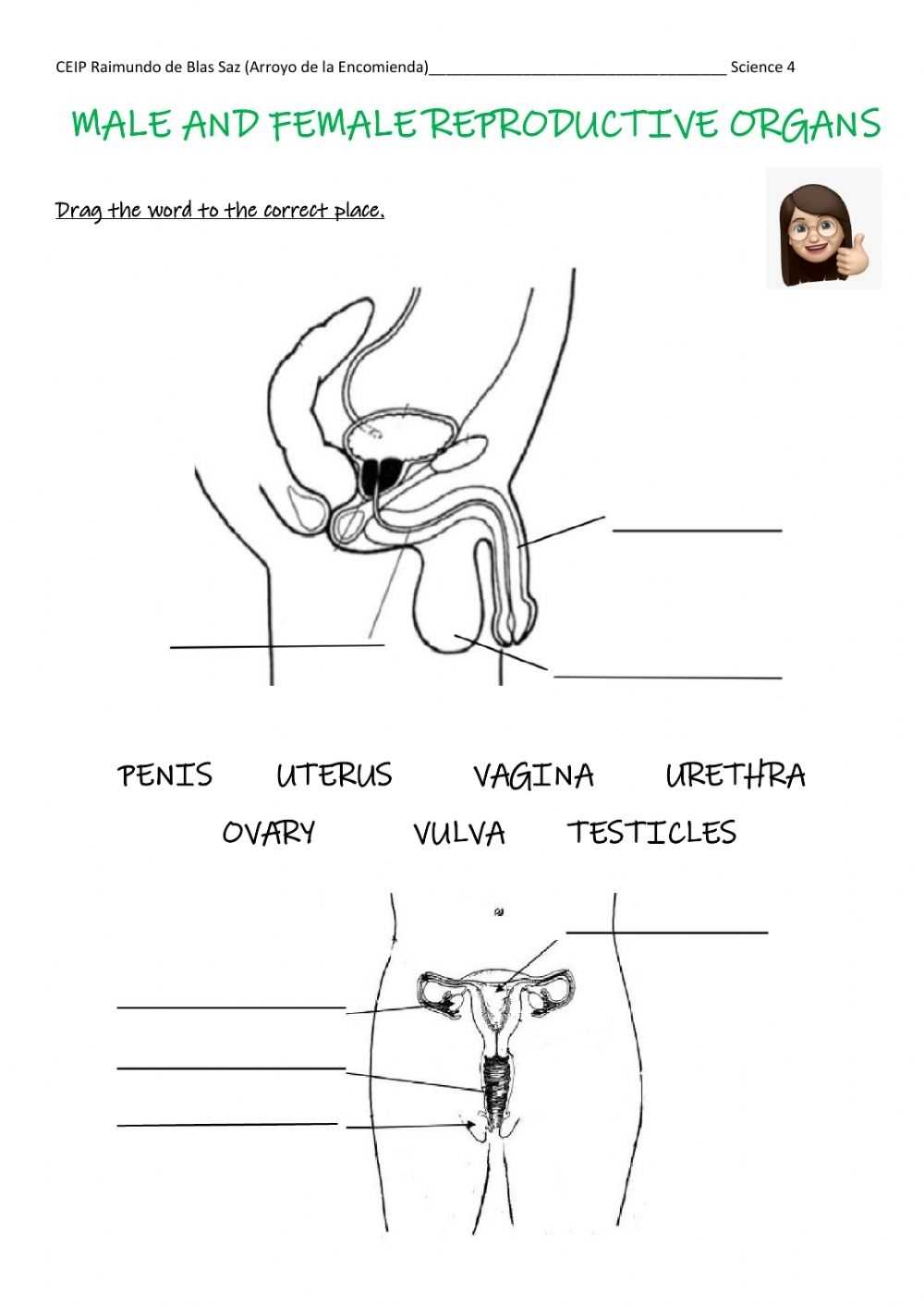
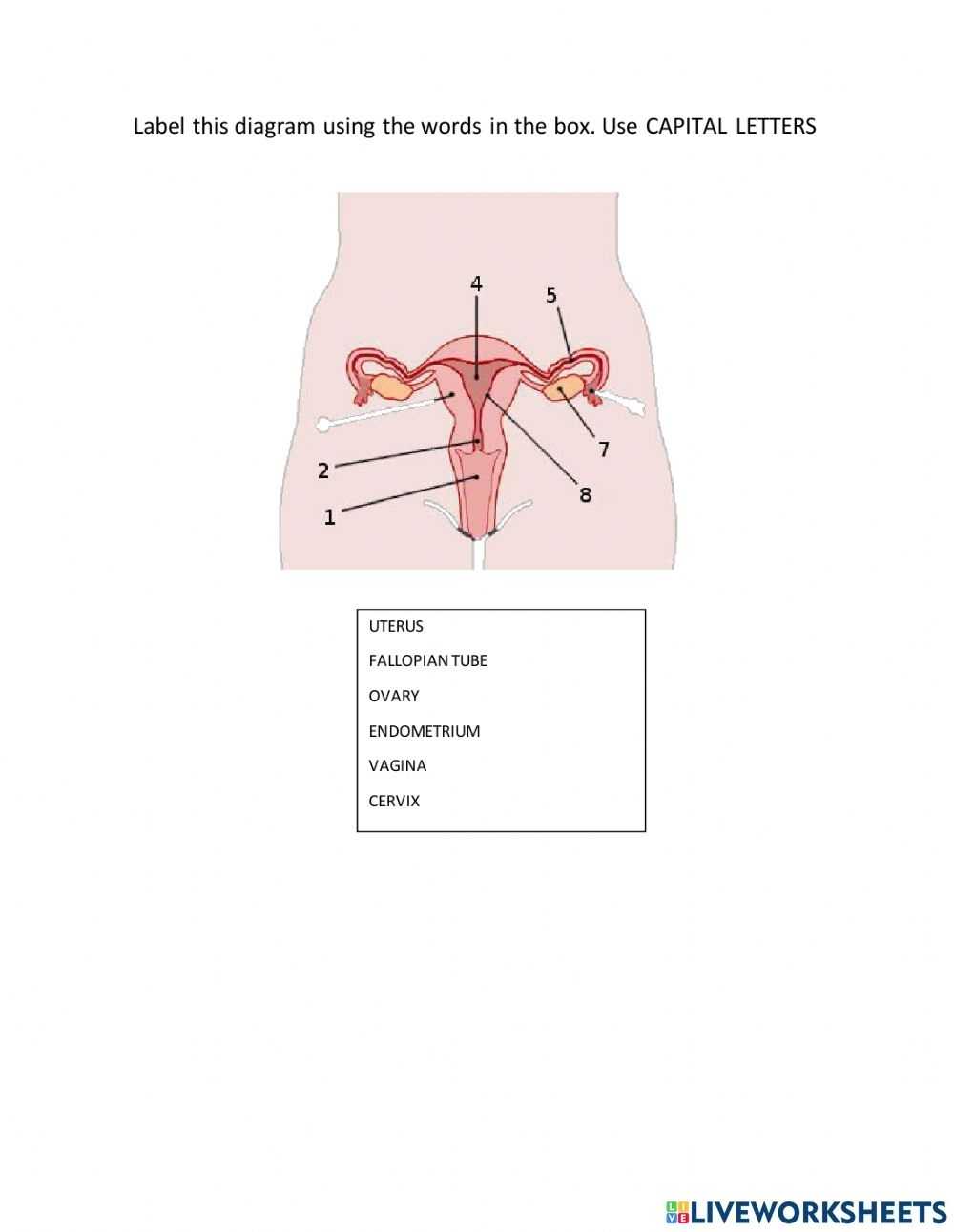
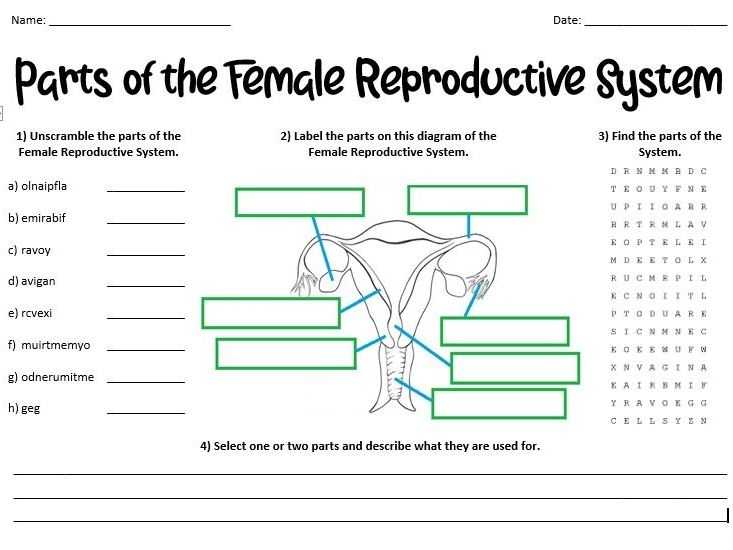
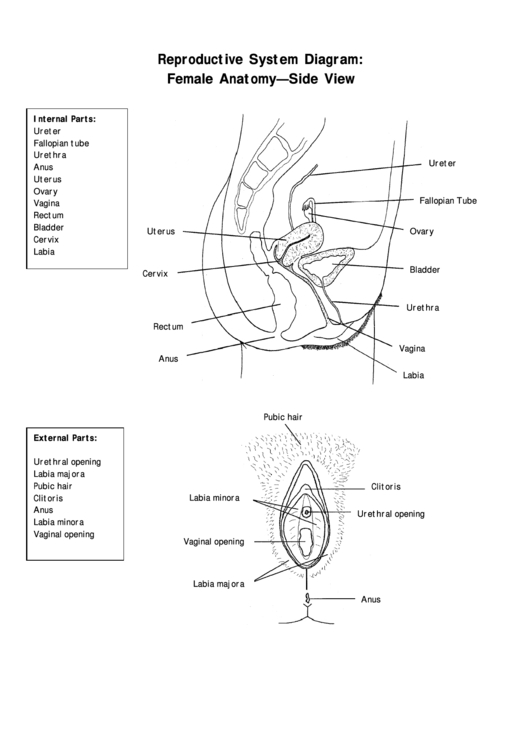
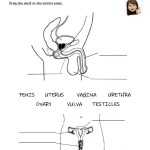
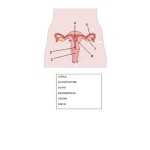
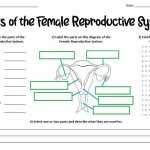
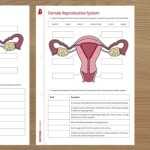
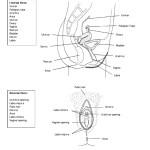
The female reproductive system is composed of several essential parts that work together to allow for fertilization and pregnancy. The main organs of the female reproductive system are the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
The vagina is a muscular passageway that connects the external parts of the female reproductive system to the internal organs. It has a lining of mucous membrane that produces secretions, which help to keep the area moist and to protect the body from infection. The vagina also serves as the birth canal during childbirth.
The uterus is a pear-shaped organ that lies in the pelvis between the bladder and the rectum. It is made up of three layers: the endometrium, myometrium, and perimetrium. The endometrium is the innermost layer and is responsible for the growth and shedding of the uterine lining in response to fluctuations in hormones during the menstrual cycle. The myometrium is the middle layer and helps to support the uterus. The perimetrium is the outermost layer and helps to protect the uterus from infection.
[toc]
The fallopian tubes are two narrow tubes that connect the uterus to the ovaries. They are lined with tiny, finger-like projections called fimbriae, which help to guide the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
The ovaries are two small, almond-shaped organs that sit on either side of the uterus. They produce and store eggs and secrete hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone. During ovulation, an egg is released from one of the ovaries and travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus.
The female reproductive system is an intricate and complex system that is necessary for reproduction. Its parts work together to allow for fertilization and pregnancy.
Understanding Menstruation: A Comprehensive Guide for Females
Menstruation is a natural process that affects most females during their reproductive years. It is a sign that the female body is functioning properly and is a part of the process of preparing to conceive a child. Understanding menstruation is important for every female so that she can better manage her body, her health, and her overall wellbeing.
Menstruation typically occurs once every 28 days, although this can vary from female to female. It begins with the shedding of the endometrium, the innermost layer of the uterus, which leads to bleeding from the vagina. This typically lasts between three and seven days. During this time, the female may experience a range of physical and emotional symptoms such as cramps, fatigue, bloating, and mood swings.
During the menstrual cycle, hormones such as estrogen and progesterone are released, which affect the body in different ways. Estrogen helps to regulate the menstrual cycle and prepare the uterine lining for implantation of a fertilized egg. Progesterone is involved in the production of new cells and helps to thicken the uterine lining, preparing it for pregnancy.
In addition to the physical changes that occur during the menstrual cycle, there are also certain hygiene practices that should be followed. These include changing tampons or pads regularly, washing the genital area before and after changing, and avoiding scented products or douches. In addition, it is important to get regular check-ups to ensure that the female is healthy and that any issues are addressed.
Understanding menstruation is important for every female. By being aware of the physical and emotional changes that occur during this time, she can better manage her body and her health. In addition, proper hygiene practices and regular check-ups can help ensure that any issues are addressed in a timely manner.
Debunking Common Myths about the Female Reproductive System
There are many misconceptions about the female reproductive system, and it is important to understand the truth behind these myths.
First, there is the myth that menstrual cycles are always 28 days long. While it is true that most women have 28 day cycles, they can range from 21 to 35 days. In addition, it is normal for the length of your cycle to vary from month to month.
Second, some women believe that they are infertile if they do not have regular menstrual cycles. This is not true; irregular cycles can be caused by many factors and do not necessarily mean that a woman is unable to conceive.
Third, some women believe that endometriosis is caused by having sex during menstruation. This is a myth; endometriosis is caused by a hormone imbalance and has nothing to do with sexual activity.
Fourth, many women think that the size of their uterus is a sign of fertility. This is also false; the size of the uterus has no effect on a woman’s reproductive capabilities.
Finally, it is a common misconception that the only way to prevent pregnancy is to use birth control. While birth control is an effective method of contraception, there are other options, such as natural family planning and barrier methods.
Understanding the truth behind these myths can help women make informed decisions about their reproductive health. With the right education and information, women can better understand their bodies and make informed choices.
10 Tips for Keeping Your Female Reproductive System Healthy and Balanced
1. Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can put you at risk for a number of reproductive issues, including infertility and polycystic ovary syndrome. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet will help keep your reproductive system in balance.
2. Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with your reproductive system and affect fertility. Therefore, it is important to limit or avoid smoking and drinking alcohol.
3. Take a multivitamin: A daily multivitamin can help ensure that your body gets all the necessary vitamins and minerals it needs to function properly.
4. Practice safe sex: Unprotected sex can put you at risk for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and other reproductive health issues. Always use condoms and practice safe sex.
5. Avoid douching: Douching can interfere with the normal balance of bacteria in your vagina, which can lead to infection. Therefore, it is best to avoid douching.
6. Wear cotton underwear: Cotton underwear is better for your reproductive system than synthetic materials as it is breathable and less likely to trap moisture and bacteria.
7. Get regular gynecological check-ups: Regular visits to your gynecologist can help you stay on top of any potential reproductive health issues.
8. Be aware of signs and symptoms of reproductive issues: Pay attention to any changes in your body and be aware of any signs or symptoms of reproductive issues, such as abnormal bleeding, pain during sex, or pelvic discomfort.
9. Don’t ignore irregular periods: Irregular periods could be a sign of a more serious reproductive issue. If your periods are irregular or you are experiencing any other symptoms, contact your doctor.
10. Practice stress management: Stress can have a negative impact on your reproductive health. Try to incorporate stress management techniques into your daily routine, such as yoga, meditation, or exercise.
Conclusion
The Female Reproductive System Worksheet is a great way to learn about the organs and processes of the female reproductive system. It provides an easy-to-understand overview of the anatomy and physiology of the system, as well as the roles of hormones and other factors in reproduction. It also serves as a great way to review and reflect on the material learned in a classroom setting. With its comprehensive and clear explanations, this worksheet is an invaluable resource for anyone wanting to learn more about the female reproductive system.
[addtoany]