Exploring the Anatomy and Function of the Circulatory System: A Comprehensive Worksheet Answer Guide
The circulatory system is an intricate and vital organ system in the human body. It is responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and organs of the body, and removing carbon dioxide and waste products. The circulatory system is composed of three main parts: the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart is the central organ of the circulatory system, and it is responsible for the pumping of the blood that transports oxygen and other nutrients throughout the body. The blood vessels are the vessels that transport the blood throughout the body. The blood is composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma.
The primary function of the circulatory system is to transport oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and organs of the body and to remove carbon dioxide and other waste products. The heart pumps the blood to the lungs, where it is oxygenated. The oxygenated blood is then pumped from the lungs to the rest of the body where it supplies oxygen and other nutrients to the tissues and organs. The blood also carries carbon dioxide and other waste products from the tissues and organs back to the lungs where it is exhaled.
The circulatory system is also responsible for regulating body temperature and maintaining homeostasis. It does this by controlling the flow of blood to the various organs and tissues in the body, to ensure that they receive the right amount of oxygen and nutrients. Additionally, the circulatory system plays an important role in the immune system by circulating white blood cells, which are responsible for defending the body against infection and disease.
[toc]
The circulatory system is an amazing and complex organ system that plays a vital role in the functioning of the human body. It is responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and organs, removing carbon dioxide and waste products, regulating body temperature and maintaining homeostasis, and playing a role in the immune system. Without the circulatory system, the human body would not be able to survive.
Examining the Interconnected Parts of the Circulatory System: A Step-by-Step Worksheet Answer Guide
Step 1: Overview
The circulatory system is one of the most important systems in the body. It is responsible for carrying oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to the organs and tissues, and for transporting waste products away from them. The system is made up of several interconnected parts that work together to keep the body functioning properly. These parts include the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
Step 2: The Heart
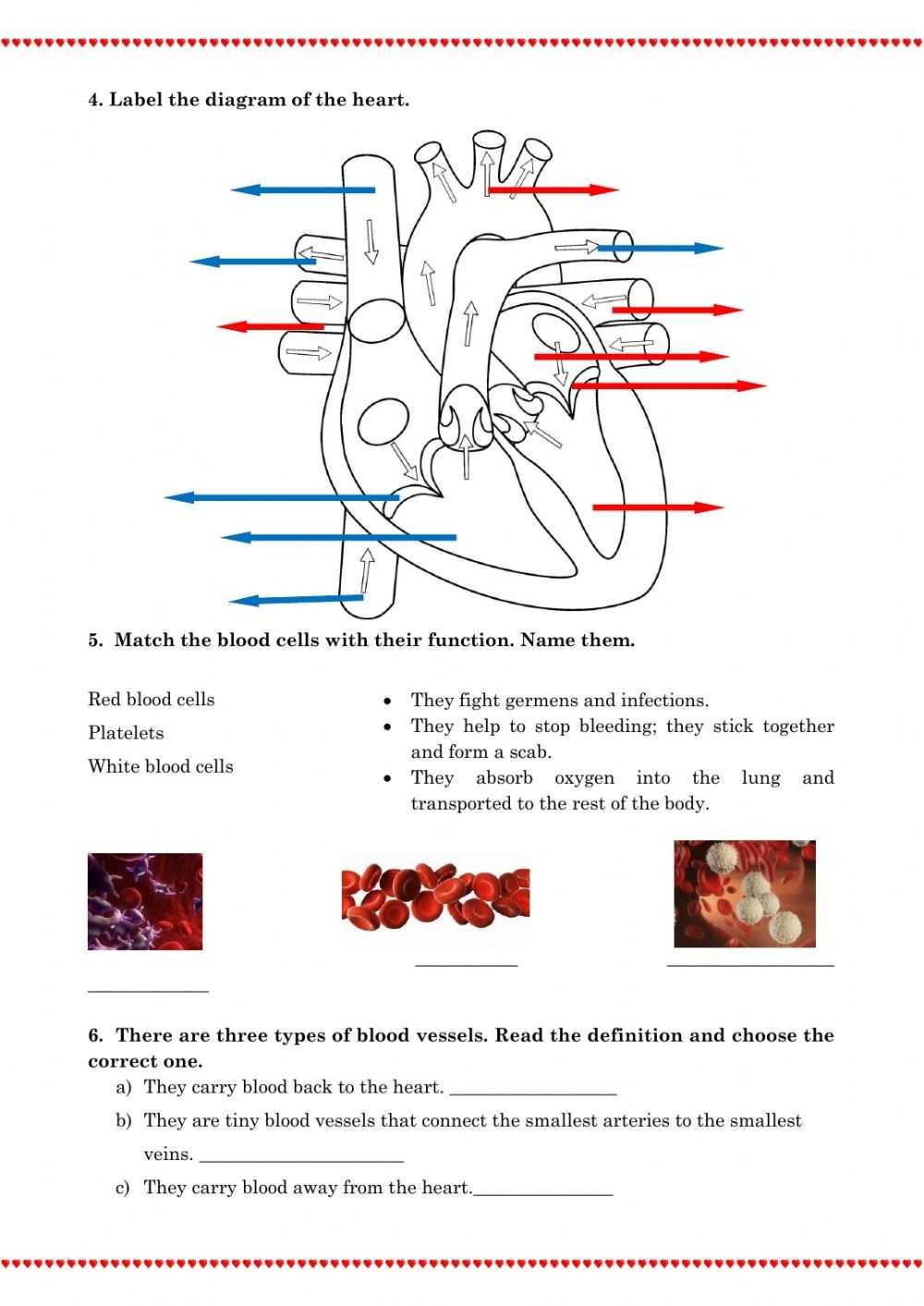
The heart is the main organ of the circulatory system. It is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It is divided into four chambers: the right atrium, the left atrium, the right ventricle, and the left ventricle. The heart also contains valves that control the flow of blood through the chambers.
Step 3: Blood Vessels
The blood vessels are the channels through which blood flows in the body. They include arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the organs and tissues. Veins carry oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. Capillaries are the smallest of the blood vessels and are responsible for exchanging oxygen, nutrients, and hormones with the cells.
Step 4: Blood
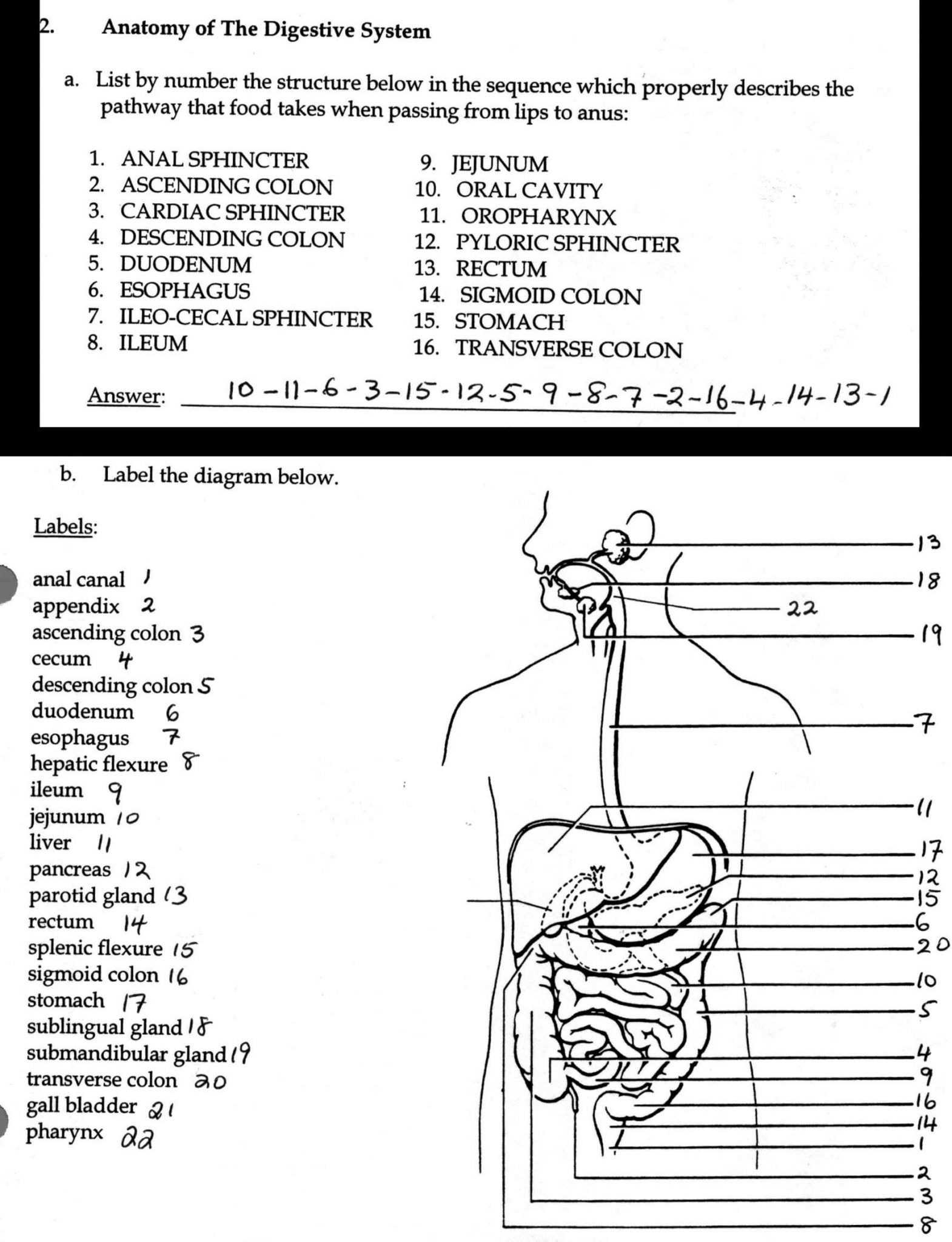
Blood is the fluid that is pumped through the body by the heart. It is composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Red blood cells carry oxygen to the body’s cells. White blood cells are part of the body’s immune system and help fight infection. Platelets help the blood to clot and prevent excessive bleeding. Plasma is the liquid portion of the blood and carries nutrients, hormones, and waste products.
Step 5: Interactions
All of the parts of the circulatory system work together to keep the body functioning properly. The heart pumps blood throughout the body via the blood vessels. The blood carries oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to the cells and transports waste products away from them. The blood vessels also help to regulate blood pressure, which is important for healthy functioning of the body.
Understanding the Role of the Heart in the Circulatory System: A Worksheet Answer Guide
The heart is an integral part of the circulatory system, and understanding how it works is essential to understanding the overall functioning of the body. The heart is responsible for the movement of oxygen-rich blood throughout the body and removing carbon dioxide. Here is a closer look at the role of the heart in the circulatory system.
The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest cavity, and its primary role is to pump oxygenated blood throughout the body. It does this by contracting and relaxing in a rhythmic pattern. The heart has four chambers, two atria and two ventricles, which contract and relax in an alternating sequence. The left ventricle is the largest and pumps oxygenated blood to the body. The right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
The heart is responsible for carrying oxygenated blood to the body’s cells, organs, and tissues and removing carbon dioxide. The oxygen-rich blood enters the body through the left ventricle and is then carried to the organs, tissues, and cells through the arteries. The oxygen is used by the cells and the carbon dioxide is sent back to the lungs. The carbon dioxide is then expelled from the body when it is exhaled.
The heart is also responsible for maintaining the body’s blood pressure. When the heart contracts, it creates pressure that pushes blood through the arteries and veins. The amount of pressure generated by the heart determines the body’s blood pressure.
Finally, the heart is also responsible for controlling the body’s blood flow. When the heart contracts, it pumps more blood and when it relaxes, it pumps less. This ensures that the body’s organs and tissues receive the right amount of oxygenated blood.
The heart plays a vital role in the circulatory system and its function is essential for the proper functioning of the body. It is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to the body, removing carbon dioxide, maintaining blood pressure, and controlling the body’s blood flow. Understanding the role of the heart helps us to better understand the overall functioning of the body.
Exploring the Interaction between the Heart and Lungs in the Circulatory System: A Worksheet Answer Guide
The interaction between the heart and lungs in the circulatory system is a complex yet essential process. The heart acts as a pump to circulate the blood around the body while the lungs are responsible for oxygenating the blood cells. To understand this interaction, we must first examine the structure and components of the circulatory system, and how the heart and lungs work together to ensure the efficient transport of oxygen and nutrients throughout the body.
The Circulatory System:
The circulatory system consists of the heart and lungs, along with a network of blood vessels that carry red blood cells and oxygen to the various parts of the body. The heart is the primary organ responsible for pumping the blood throughout the body, while the lungs are responsible for oxygenating the blood cells. The blood vessels in the circulatory system are responsible for transporting the oxygenated blood and nutrient-rich plasma to the various organs, tissues, and cells, allowing them to function properly.
The Heart and Lungs:
The heart and lungs are responsible for the efficient transport of oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. The heart pumps the oxygenated blood from the lungs to the body’s organs, tissues, and cells. The lungs take in oxygen from the air and pass it on to the red blood cells, which then carry the oxygenated blood throughout the body. The human body needs oxygen to carry out its metabolic processes, and therefore, the proper functioning of the heart and lungs is essential for the optimal functioning of the body.
Interaction between the Heart and Lungs:
The interaction between the heart and lungs is part of a complex and dynamic process that ensures that oxygen and nutrients are transported throughout the body. This process begins with the heart pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs to the organs and tissues. The blood then passes through the capillaries, which are the smallest of blood vessels, allowing the oxygen and nutrients to be taken up by the cells. The cells then use the oxygen and nutrients to carry out their metabolic processes. The heart then pumps the deoxygenated blood back to the lungs, where it is re-oxygenated and returns to the heart, completing the cycle.
In conclusion, the interaction between the heart and lungs in the circulatory system is a complex yet essential process. The heart pumps the oxygenated blood from the lungs to the organs, tissues, and cells of the body, while the lungs are responsible for taking in oxygen from the atmosphere and passing it on to the red blood cells. This process ensures the optimal functioning of the body by providing it with oxygen and nutrients, allowing it to carry out its metabolic processes.
Conclusion
The Circulatory System Worksheet Answers provide a great overview of the human circulatory system and the different parts it contains. By understanding the components and functions of the circulatory system, one can have a better understanding of how the body works as a whole. The answers to this worksheet can also be used as a reference when studying the circulatory system or when researching other related topics.
[addtoany]