Understanding the Anatomy of the Cardiovascular System: A Comprehensive Worksheet Guide
The cardiovascular system is a complex and intricate network of organs and tissues that play a key role in ensuring the body’s health and wellbeing. This system is comprised of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, which together carry out a range of vital functions. In order to understand how the cardiovascular system works, it is important to understand the anatomy of the system and the roles each of its components play in the functioning of the body. This worksheet provides a comprehensive guide to the anatomy of the cardiovascular system and how it functions.
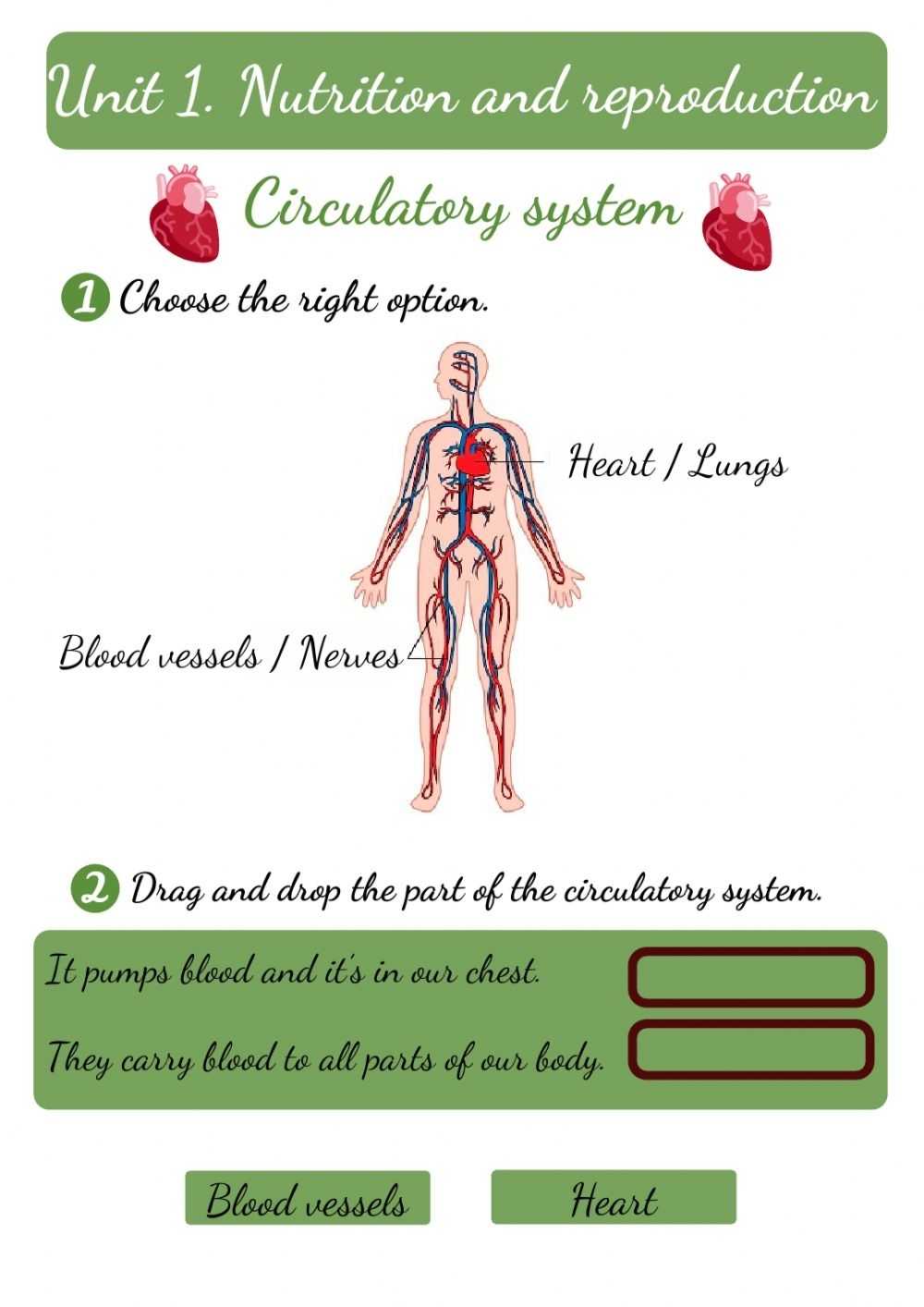
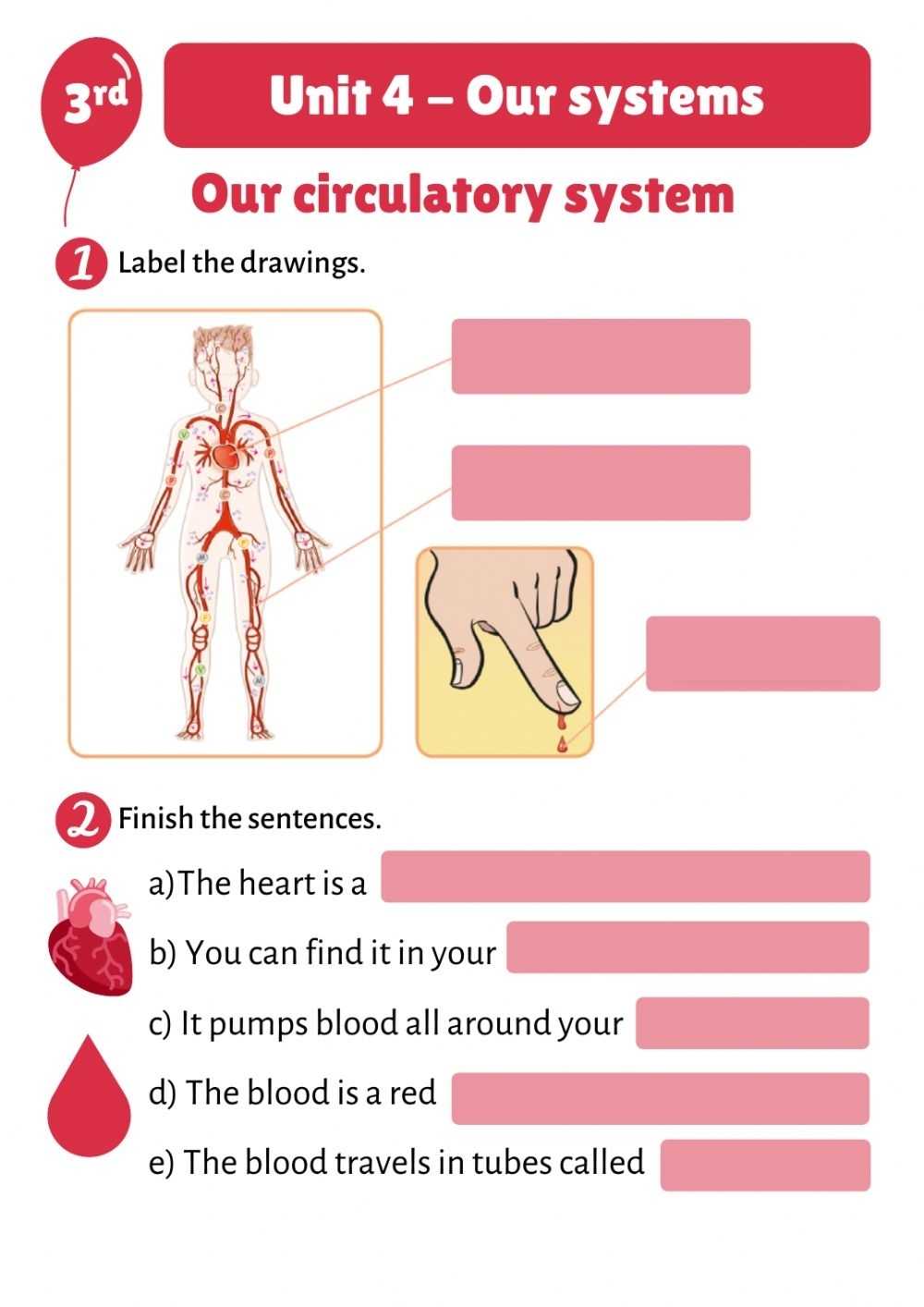
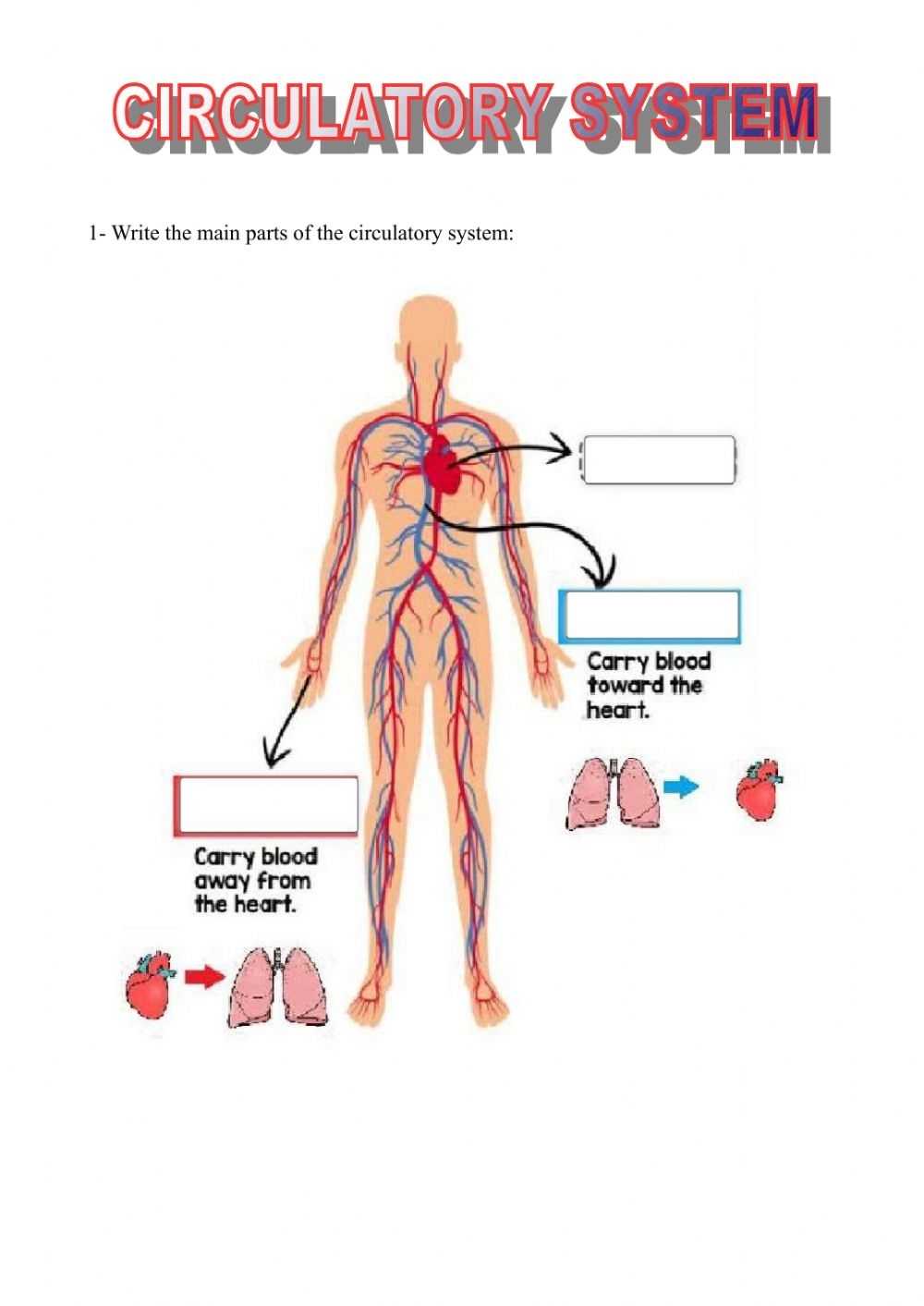
The heart is the central organ of the cardiovascular system and is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to various parts of the body. It is a hollow, cone-shaped organ located in the thoracic cavity and composed of four chambers – two atria and two ventricles. The right atrium and right ventricle are responsible for circulating deoxygenated blood to the lungs, while the left atrium and left ventricle are responsible for circulating oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. The heart is also composed of a number of valves which regulate the flow of blood and prevent backflow.
The blood vessels are the tubes through which the blood travels in the body and are divided into two categories – arteries and veins. Arteries are vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while veins are vessels that carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. The walls of the vessels contain smooth muscle which can expand and contract, allowing the vessels to regulate the flow of blood.
[toc]
The blood is composed of plasma, red and white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma is a yellowish liquid that carries dissolved substances such as hormones, nutrients, and waste products. Red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide, while white blood cells are responsible for fighting infection. Platelets are involved in the clotting of blood.
The cardiovascular system is an integral part of the body and is responsible for the transport of oxygen and nutrients to various parts of the body, as well as the removal of waste products. By understanding the anatomy of the system, one can gain a better understanding of its function and its importance to overall health and wellbeing.
Exploring the Physiology of the Cardiovascular System: A Step-by-Step Worksheet
Step 1: Overview
The cardiovascular system is an essential organ system that functions to transport oxygen, nutrients, and other substances throughout the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, as well as the lymphatic system and the immune system. The heart pumps blood through the body, and the blood vessels act as a conduit for the blood to travel. The lymphatic system is responsible for the return of fluids and waste to the bloodstream, and the immune system helps protect against infection and disease. This step-by-step worksheet will explore the physiology of the cardiovascular system and how it works.
Step 2: The Heart
The heart is the most important organ of the cardiovascular system. It is a four-chambered muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It consists of the right atrium and ventricle, and the left atrium and ventricle. Blood enters the right atrium from the body and is then pumped into the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs, where it receives oxygen. The oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium, which pumps it into the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps the blood out of the heart and into the rest of the body.
Step 3: Blood Vessels
The blood vessels of the cardiovascular system are responsible for carrying blood throughout the body. The three main types of blood vessels are arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries are thick-walled vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Capillaries are thin-walled vessels that connect the arteries and veins and provide the connection between the blood and other tissues of the body.
Step 4: Blood
Blood is a fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. It consists of cells and other substances suspended in plasma. The red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body’s cells, and the white blood cells help to fight infection and disease. Platelets help with clotting, and plasma is the liquid that carries all of the other components of blood.
Step 5: The Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system helps to maintain the balance of fluids in the body and is responsible for the return of fluids and waste to the bloodstream. It includes a network of vessels, lymph nodes, and organs that help to move fluid, collect waste, and filter out toxins. The lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that act as filters, trapping and destroying harmful substances.
Step 6: The Immune System
The immune system is a complex system of cells and proteins that help to protect the body against infection and disease. It helps to identify and destroy foreign substances such as bacteria and viruses, and it also helps to produce antibodies that target specific foreign substances. The immune system works together with the lymphatic system to protect the body from infection and disease.
Conclusion
The physiology of the cardiovascular system is complex and multifaceted. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, blood, lymphatic system, and immune system, each of which plays an important role in maintaining the health of the body. By understanding the components of the cardiovascular system and how they work together, we can gain a better understanding of how this essential organ system functions
Comparing and Contrasting Cardiovascular Disease and Treatment Options: A Worksheet
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a group of disorders that affect the heart and blood vessels. These diseases are among the leading causes of death throughout the world, and range from coronary artery disease, stroke, and heart failure, to other conditions such as arrhythmia and congenital heart defects.
The treatments for CVDs vary depending on the type, severity, and progression of the disease. Some of the most common treatments include lifestyle modifications, medications, and surgical interventions.
Lifestyle modifications for CVDs typically involve changes to diet and exercise. Eating a heart-healthy diet, limiting salt and fat intake, avoiding cigarette smoking, and engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce the risk of CVDs and manage existing conditions.
Medications to treat CVDs may include cholesterol-lowering drugs, blood pressure medications, anticoagulants, and antiplatelets. These drugs can help reduce the risk of complications such as stroke and heart attack, as well as manage symptoms.
Surgical interventions for CVDs may include coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), valve replacement, and angioplasty. CABG is a procedure to improve the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart, while valve replacement is a procedure to replace a heart valve that is not functioning properly. Angioplasty is a procedure to open a blocked or narrowed artery.
In conclusion, CVDs are a major health concern worldwide, and the treatments for them vary depending on the type, severity, and progression of the disease. Lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise can help reduce the risk of CVDs and manage existing conditions. Medications can also be used to help manage symptoms, while surgical interventions can be used to improve the flow of blood to the heart or replace a damaged valve.
Examining the Role of Genetics in Cardiovascular Health: A Worksheet Guide
Introduction
Cardiovascular health is an important factor in maintaining overall health and well-being. While proper nutrition and physical activity are known to be key components of a healthy lifestyle, genetics also plays a role in determining one’s cardiovascular health. This worksheet guide will explore the role of genetics in cardiovascular health, as well as provide an overview of risk factors and potential interventions.
What Is the Role of Genetics in Cardiovascular Health?
The genetic components of cardiovascular health include a variety of factors, such as the size and shape of the heart, the number of vessels that supply the heart, and the ability of the body to synthesize and utilize cholesterol. Genetics can also influence blood pressure, heart rate, and the body’s response to exercise. Additionally, genetics may play a role in the development of certain conditions, such as coronary artery disease, hypertension, and stroke.
What Are the Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease?
There are a number of risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease, many of which are related to lifestyle choices. These include smoking, obesity, physical inactivity, and an unhealthy diet. Other risk factors include age, gender, hypertension, diabetes, and family history.
What Are Potential Interventions to Improve Cardiovascular Health?
There are a number of potential interventions that can help improve cardiovascular health. These include lifestyle modifications such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight. Additionally, medications such as statins and blood pressure medications can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Finally, regular health screenings can help identify risk factors and detect early signs of cardiovascular disease.
Conclusion
Genetics plays an important role in determining one’s cardiovascular health. It is important to be aware of risk factors and to take steps to reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Lifestyle modifications, medications, and regular health screenings can all help to improve one’s cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Conclusion
The Cardiovascular System Worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the organs, tissues, and cells that comprise the human cardiovascular system. It is a great tool for students to deepen their understanding of this complex system and its vital role in maintaining health. With the knowledge gained from this worksheet, students can apply their understanding of the cardiovascular system to their daily lives, making healthier choices and understanding the signs and symptoms of cardiovascular disease.
[addtoany]