Uncovering the Radioactive Decay Worksheet Answers: A Comprehensive Guide
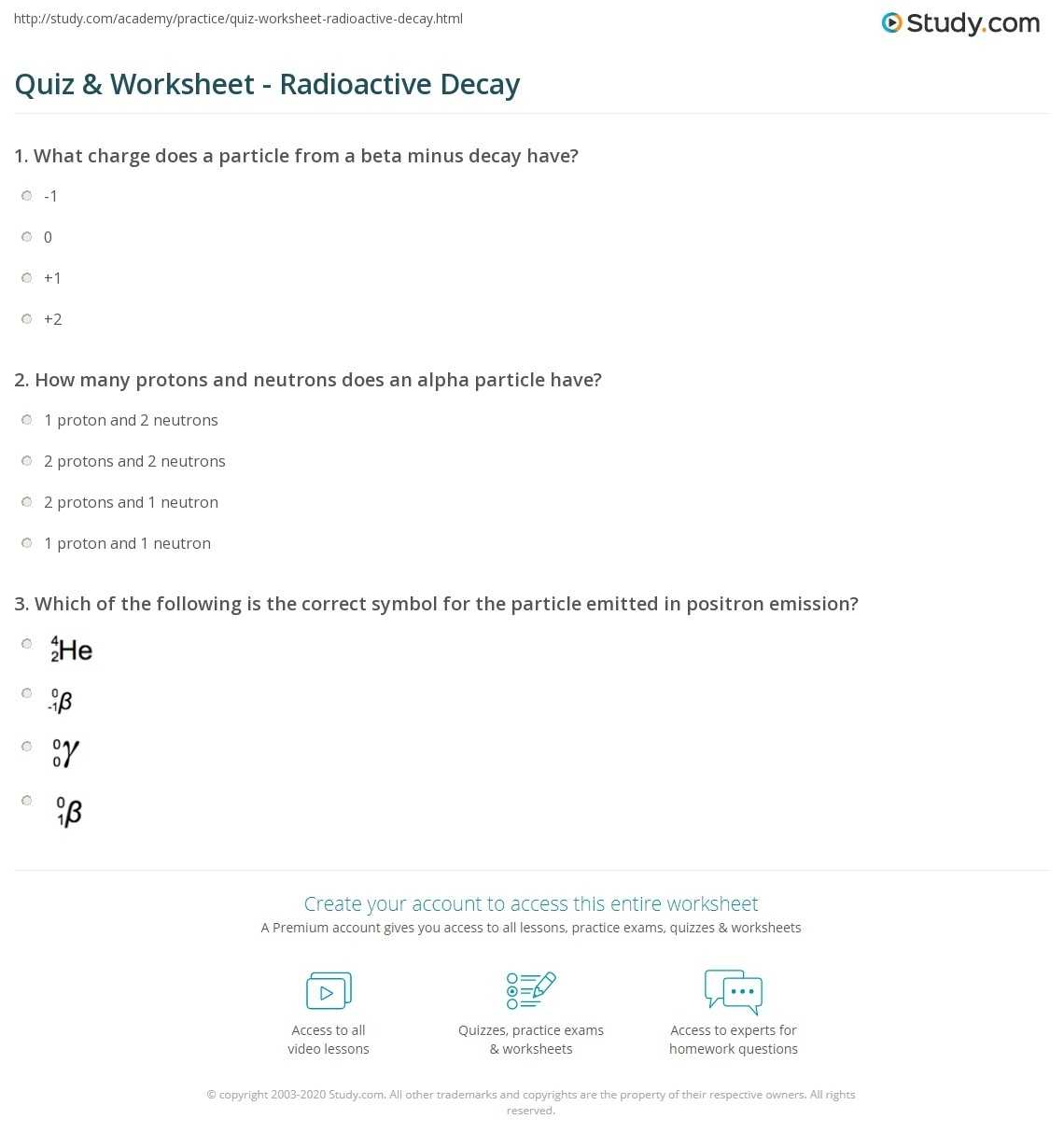
1. What Is Radioactive Decay?
Radioactive decay is the process in which a nucleus of an unstable atom spontaneously emits particles, usually alpha or beta particles. This process is also known as radioactivity. Radioactive decay is a random process, meaning that the rate at which the nucleus decays is unpredictable and is not affected by external factors such as temperature or pressure. Radioactive decay is the primary source of ionizing radiation, which can be hazardous to living organisms if not properly managed.
2. What Are Alpha and Beta Particles?
[toc]
Alpha particles are positively charged particles that are composed of two protons and two neutrons, and are emitted from the nucleus of a radioactive atom. Alpha particles are relatively large and slow and can be stopped by a sheet of paper. Beta particles, on the other hand, are negatively charged and are composed of electrons, which are much smaller and faster than alpha particles. Beta particles can travel further than alpha particles, but can be stopped by a thin sheet of aluminum.
3. What Is Half-Life?
Half-life is the amount of time it takes for half of the nuclei in a sample of a radioactive material to decay. Half-life is an important property of radioactive materials, as it can be used to estimate the age of a sample or the rate at which it will decay. The half-life of an unstable atom is usually constant, though it can vary depending on the type of atom and the environmental conditions.
4. What Are Some Applications of Radioactive Decay?
Radioactive decay has a wide range of applications, including medical imaging, power generation, and research in the field of nuclear physics. In medical imaging, radioactive materials are used in order to create images that can be used to diagnose and treat diseases. Nuclear power plants use the energy released from nuclear fission to generate electricity. Finally, radioactive materials can be used in research to study the structure and dynamics of atoms and molecules.
Using Radioactive Decay Worksheet Answers to Teach Students About Nuclear Chemistry
Nuclear chemistry is an important and complex topic for students to understand, and the use of a Radioactive Decay Worksheet can be an effective tool to help illustrate the concepts involved. This worksheet can be used to show the different types of radioactive decay, the energy released during each type of decay, and the half-lives of different elements.
As students work through the worksheet, they can learn the difference between alpha, beta, and gamma decay, as well as the various isotopes of each element and the differences in their half-lives. The worksheet can also provide a visual representation of the decay process, helping students to understand the concept more clearly.
In addition, the worksheet can be used to introduce students to the concept of nuclear fission and explain the difference between fission and fusion. This can be a great starting point for discussions about nuclear power and its potential risks and benefits.
Finally, the worksheet can be used to demonstrate how radioactive decay can be used for practical purposes such as medical imaging, carbon dating, and the production of electricity. By doing this, students can gain a better understanding of the importance of nuclear chemistry and its applications.
By using a Radioactive Decay Worksheet, students can gain a better understanding of nuclear chemistry, as well as its practical applications. This worksheet can provide a valuable educational resource for teaching students about this complex and important field of study.
Exploring the Theory of Radioactive Decay Through Worksheet Answers
Radioactive decay is a fundamental process in nuclear physics and chemistry, and it is essential to understand the concept in order to comprehend the properties of nuclei and the behavior of radioactive substances. This worksheet is designed to help students explore the basic principles of radioactive decay and develop an intuitive understanding of the associated concepts.
The worksheet begins by introducing the concept of radioactive decay and discussing the three basic types: alpha decay, beta decay, and gamma decay. Afterward, the worksheet provides a brief overview of the nuclear equation associated with each type of decay. Then, the worksheet directs students to answer a series of questions that help them visualize and comprehend the process of radioactive decay.
These questions include: how does the atomic number of the parent nucleus change during radioactive decay? How does the mass number of the parent nucleus change during radioactive decay? What is the difference between alpha and beta decay? How does gamma decay differ from the other two types of radioactive decay?
By providing students with questions that require them to think critically about the concept of radioactive decay and visualize the process, this worksheet encourages students to develop a deeper understanding of the concept. Through worksheet answers, students can gain a greater appreciation for the complexity of radioactive decay and appreciate its importance in nuclear physics and chemistry.
Problems and Solutions in Radioactive Decay Worksheet Answers: Exploring the Core Concepts
Problem 1: What is radioactive decay?
Solution: Radioactive decay is a process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation. This process is also known as nuclear decay. The radiation emitted can consist of alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays, and other particles. Radioactive decay is a natural process that occurs spontaneously in all radioactive isotopes, and it is the primary mechanism of radioactive decay.
Conclusion
The Radioactive Decay Worksheet Answers provide an in-depth understanding of the principles of radioactivity and its decay. It is important for students to understand the concepts of radioactivity, its decay, and their application to the world around us. With the help of this worksheet, students can gain a better understanding of the science behind the process and its implications.
[addtoany]