How to Use a Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes Worksheet to Teach Biology
Teaching biology to students can be challenging due to the vast amount of information and complexity of the subject. Using a prokaryotes vs eukaryotes worksheet can be a valuable tool for helping students understand the basic concepts of biology.
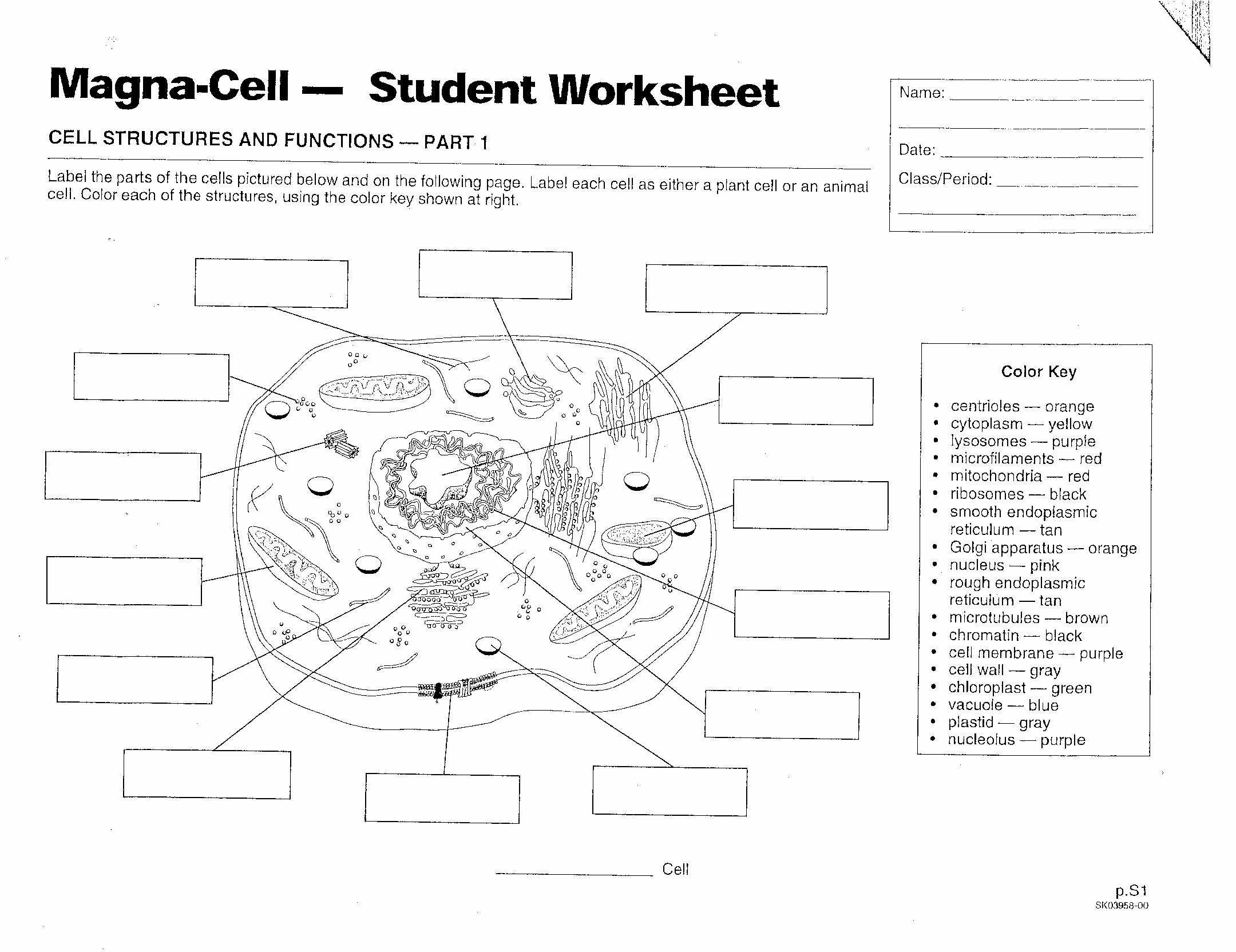
The prokaryotes vs eukaryotes worksheet is a simple and effective way to help students learn about the differences between the two types of cells. The worksheet begins by introducing students to the concept of prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and then provides a visual representation of the differences between the two. This helps students to easily grasp the concept and understand the differences between the two.
The worksheet then goes on to provide a detailed description of the characteristics of each type of cell and how they are different. This information can be used to introduce the students to the various structures and functions of each type of cell. The worksheet can also be used as a reference when teaching more complex concepts such as cell division, reproduction, and metabolism.
[toc]
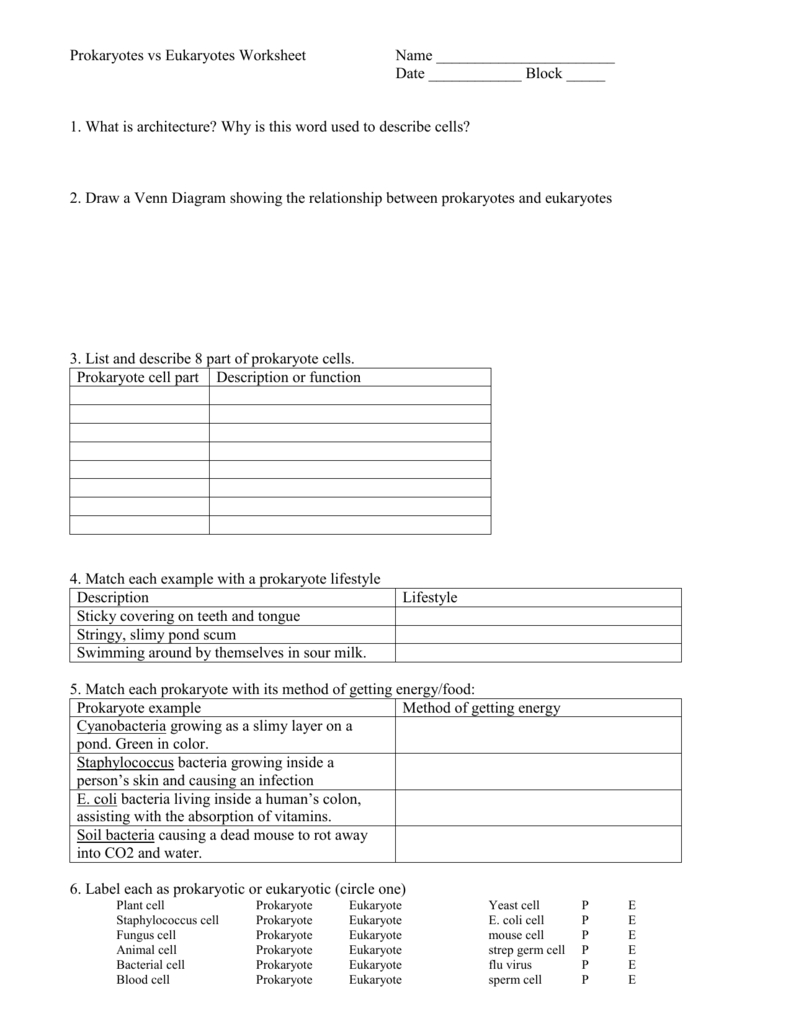
Once the student has a basic understanding of the two types of cells, the worksheet can be used as an assessment tool. Questions can be asked about the differences between the two types of cells and the functions of each. This allows the student to demonstrate their understanding of the material and allows the teacher to diagnose any areas of difficulty.
The prokaryotes vs eukaryotes worksheet is an effective way to help students understand the basic concepts of biology. By providing students with a visual representation of the differences between the two types of cells, and a detailed description of the characteristics of each type, students can better comprehend the material and apply it to other topics in biology. Additionally, the worksheet can be used as an assessment tool, allowing the teacher to identify any areas of difficulty and promote further learning.
Exploring the Differences Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes with a Worksheet
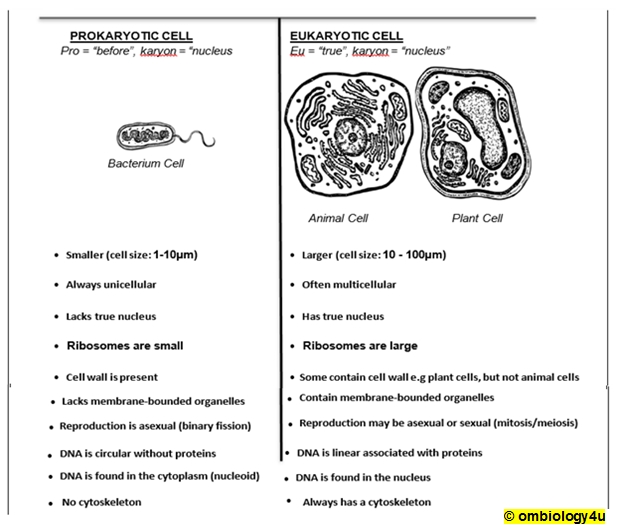
The differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes are vast, yet subtle. Both are types of organisms, but the structures of their cells and the complexity of their genetics set them apart. To better understand the differences between the two, let us explore the various characteristics associated with each.
Prokaryotic Cells:
• Smaller in size than eukaryotes
• No nuclei or membrane bound organelles
• DNA is not organized into chromosomes
• Single circular chromosome in the cytoplasm
• Have a cell wall and cell membrane
• Reproduce through binary fission
Eukaryotic Cells:
• Larger and more complex than prokaryotes
• Have a nucleus, membrane bound organelles, and chromosomes
• DNA is organized into multiple linear chromosomes
• Have a cell membrane, but no cell wall
• Reproduce through mitosis
Overall, the most significant difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes lies in the complexity of their cells. Prokaryotes are much simpler in structure, while eukaryotes are complex, housing a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. The presence of a nucleus and chromosomes in eukaryotes also allows for more sophisticated genetic processes. Finally, the method of reproduction is different for each, with prokaryotes reproducing through binary fission and eukaryotes reproducing through mitosis.
Understanding the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is essential in the field of biology. Each type of organism has its own characteristics and purpose, and it is important to recognize these differences in order to better understand the natural world.
Comparing the Structures of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes with a Worksheet
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are the two main types of cells that form the basis of all living organisms. While both groups of cells share some similarities, there are also many differences between them. To help compare and contrast these two types of cells, a worksheet can be used to examine their respective structures, functions, and components.
The worksheet should first list the structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are much simpler than eukaryotic cells and lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Instead, they contain a single, circular DNA molecule that is located within the cytoplasm. Other structures found in prokaryotic cells include ribosomes, a cell wall, and a cell membrane.
Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are more complex and contain a nucleus and numerous membrane-bound organelles. These organelles include the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and lysosomes. The nucleus of a eukaryotic cell is surrounded by a double membrane and contains DNA that is organized into chromosomes.
The worksheet should then compare and contrast the functions of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are able to carry out basic metabolic activities such as respiration, energy production, and cell division. They are also able to synthesize molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids.
Eukaryotic cells, in contrast, are able to carry out much more complex activities. They are able to produce hormones, transport materials within the cell, and generate energy through photosynthesis. Additionally, they are able to replicate their DNA and divide into two daughter cells.
Finally, the worksheet should examine the components of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells contain cytoplasm, ribosomes, a cell wall, and a cell membrane. Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and lysosomes.
Using a worksheet to compare and contrast the structures, functions, and components of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells can help to better understand the differences between them. By examining each of these characteristics, it is possible to gain a better appreciation for the complexity of eukaryotic cells and the importance of prokaryotes in the natural world.
Understanding the Role of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes in Biology with a Worksheet
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are two distinct forms of life, and they play an important role in biology. Prokaryotes are the simplest forms of life, while eukaryotes are more complex. In this worksheet, we will explore the differences between the two and how they contribute to biology.
1. What are prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are the most abundant form of life on Earth and can be found in almost any environment. Prokaryotes are divided into two main groups: bacteria and archaea. Bacteria are the most well-known type of prokaryote and are found in a variety of habitats, including soil, water, and the human body. Archaea are usually found in extreme environments, such as hot springs and deep-sea vents.
2. What are eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes are organisms that have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They include plants, animals, fungi, and protists. Eukaryotes are much more complex than prokaryotes and are generally larger in size. They have evolved more advanced systems for reproduction, metabolism, and other functions.
3. How do prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ?
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ in their structure, metabolism, and reproduction. Prokaryotes lack a nucleus and other organelles, while eukaryotes have a nucleus and other organelles. Prokaryotes reproduce asexually, while eukaryotes can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Prokaryotes are capable of creating their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, while eukaryotes must obtain food from other sources.
4. How do prokaryotes and eukaryotes contribute to biology?
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are essential to biology. Prokaryotes are important for soil fertility, as they are the primary decomposers of organic matter. They are also important for the production of antibiotics, food products, and other industrial products. Eukaryotes are important for their role in the food chain, as well as for their ability to produce oxygen through photosynthesis. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes play a vital role in the health of the planet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, prokaryotes and eukaryotes are two very different types of cells. Prokaryotes are much simpler and can be found in a wide range of environments, while eukaryotes are much more complex and are usually found in multicellular organisms. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes have many differences, including the structure of their cells, the DNA within the cells, and the way they reproduce. The differences between these two organisms are essential when considering the diversity of life on Earth.
[addtoany]