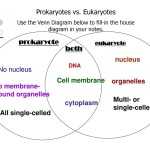
Exploring the Differences Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: A Comprehensive Worksheet
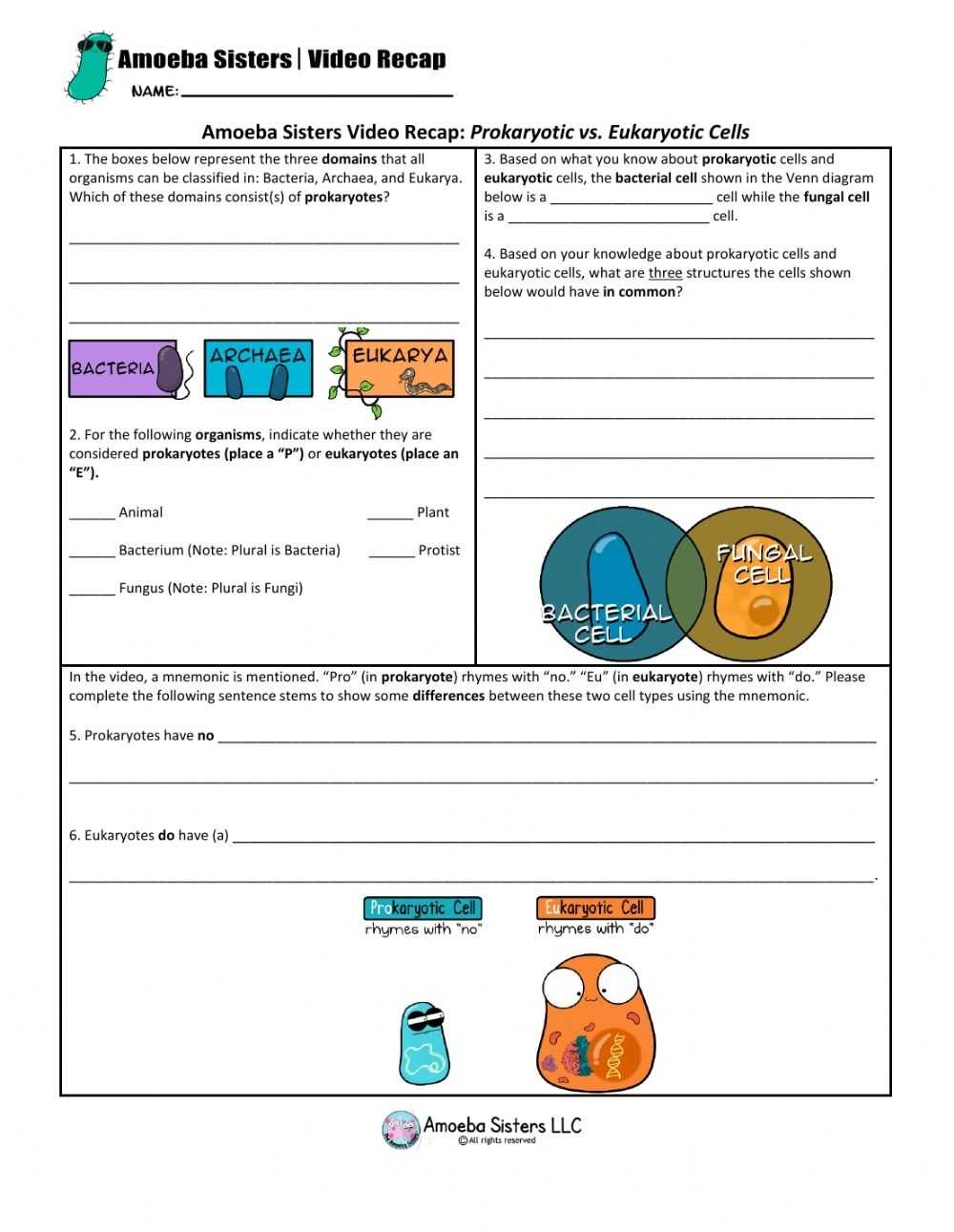
The fundamental differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes are essential to understand when exploring the diversity of life on earth. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms and are considered the simplest form of life. They are found in a wide variety of habitats and generally lack a nucleus and other organelles. Eukaryotes, on the other hand, are more complex cells that have a nucleus and other organelles. They can range from single-celled protists to multicellular plants and animals. When comparing these two types of cells, there are several distinct characteristics that set them apart.
One of the major differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is the size and complexity of their cells. Prokaryotes are much smaller in size than eukaryotes and have a simpler internal structure. They lack a nucleus and other organelles, and their genetic material is found in the form of a single, circular chromosome. On the other hand, eukaryotic cells are much larger and more complex. They contain a nucleus, which houses the genetic material, as well as several other organelles.
Another key difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is the way in which they reproduce. Prokaryotes reproduce asexually, meaning they can divide and produce exact copies of themselves. This process is known as binary fission. Eukaryotes, on the other hand, reproduce sexually, meaning they must find a mate in order to produce offspring.
[toc]
Other differences between these two types of cells include the presence of a cell wall and the way in which they obtain their energy. Prokaryotes have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan, which gives them their shape and protects them from the environment. They can also obtain energy through photosynthesis and respiration. Eukaryotes, on the other hand, lack a cell wall and obtain their energy through cellular respiration.
Finally, one of the most important differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is the presence of a mitochondria. Prokaryotes lack a mitochondria and therefore do not have an energy efficient way of producing ATP. Eukaryotes, however, have a mitochondria and can use it to produce ATP in a much more efficient manner.
In summary, prokaryotes and eukaryotes have a number of distinguishing characteristics that set them apart. Prokaryotes are smaller and simpler cells, lacking a nucleus and other organelles. They reproduce asexually and obtain their energy through photosynthesis and respiration. Eukaryotes, on the other hand, are larger, more complex cells that contain a nucleus and other organelles. They reproduce sexually and obtain their energy through cellular respiration. The presence of a mitochondria is also an important distinction between these two types of cells. Understanding the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is an essential part of understanding the diversity of life on earth.
How Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Differ: A Printable Worksheet for Biology Students
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are two distinct types of cells found in the living world. Although each cell type shares some common features, they also exhibit distinct differences that are important for students of biology to understand. This worksheet will help students explore the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Prokaryotes:
1. Describe the structure of prokaryotic cells:
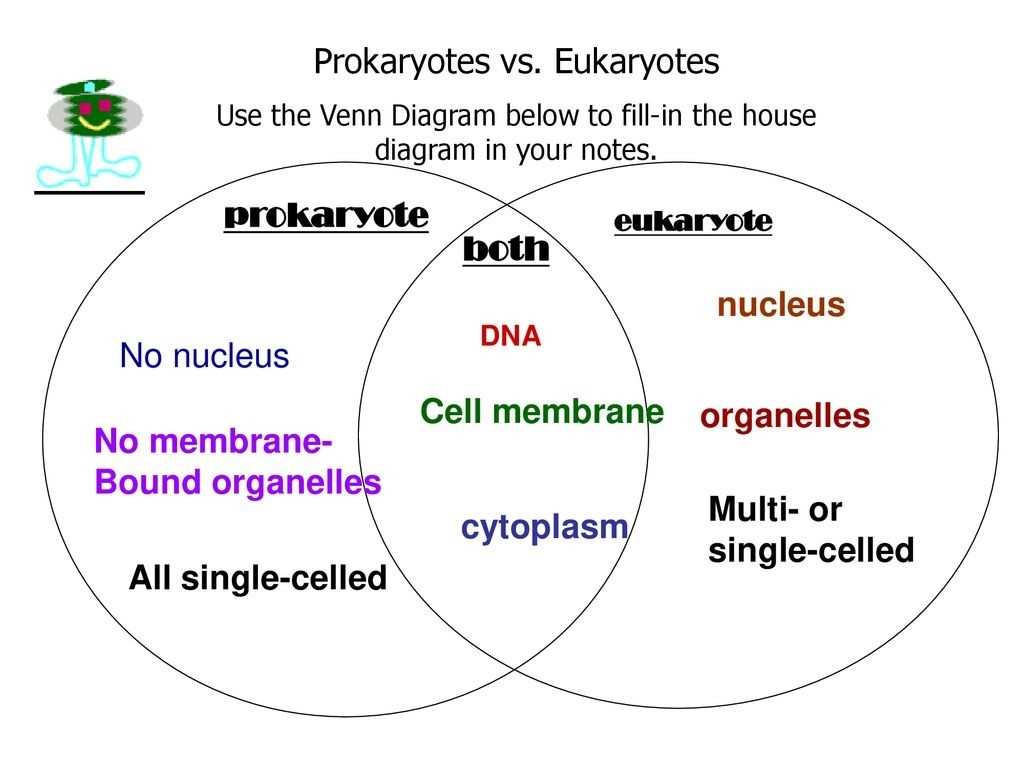
Prokaryotic cells are relatively small and simple in structure, consisting of a single, circular piece of genetic material (DNA) surrounded by a membrane. The cell does not contain any membrane-bound organelles, such as nuclei or mitochondria.
2. What is the cell wall of prokaryotic cells composed of?
The cell wall of prokaryotic cells is composed of peptidoglycan, a type of carbohydrate molecule. This cell wall gives the cell its shape and helps to protect it from environmental stressors.
3. What type of energy does a prokaryote use for cellular functions?
Prokaryotes use chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to power their various cellular functions.
Eukaryotes:
1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic cells:
Eukaryotic cells are much larger and more complex in structure than prokaryotic cells. They contain a nucleus, which houses their genetic material (DNA), as well as a variety of other organelles, such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
2. What is the cell wall of eukaryotic cells composed of?
The cell wall of eukaryotic cells is composed of cellulose, a type of carbohydrate molecule. This cell wall gives the cell its shape and helps to protect it from environmental stressors.
3. What type of energy does a eukaryote use for cellular functions?
Eukaryotes use chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to power their various cellular functions, as well as light energy for photosynthesis.
Comparing and Contrasting Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: A Worksheet for High School Biology Classrooms
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are two distinct groups of organisms that differ in several ways. While both groups contain cells, the structure of the cells and the various features they possess differ significantly. This worksheet will help high school biology students compare and contrast prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
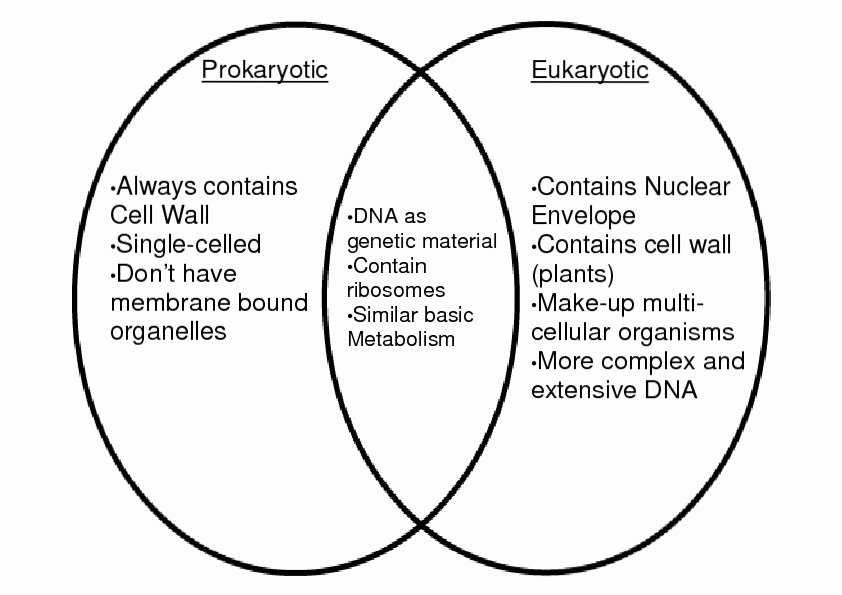
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms, while eukaryotes are multi-celled. The cells of prokaryotes are much simpler than those of eukaryotes. The cells of prokaryotes lack a nucleus and other organelles, while the cells of eukaryotes have a nucleus and many other membrane-bound organelles.
The genetic material of prokaryotes is located in a single circular DNA strand, while eukaryotes have multiple linear chromosomes. Prokaryotes have much smaller genomes than eukaryotes. Prokaryotes use binary fission for reproduction, while eukaryotes use mitosis and meiosis.
Prokaryotes are able to survive in a wide range of environments, while eukaryotes are more specialized and are found in more specific habitats. Prokaryotes are generally much smaller than eukaryotes and lack the structural complexity of eukaryotes.
In summary, prokaryotes and eukaryotes are distinct groups of organisms that differ in several ways. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms with simple cells that lack a nucleus and other organelles, while eukaryotes are multi-celled organisms with complex cells that have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotes have much smaller genomes than eukaryotes and use binary fission for reproduction. Prokaryotes are able to survive in a wide range of environments, while eukaryotes are more specialized and are found in more specific habitats.
Conclusion
The Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Worksheet provides an excellent overview of the differences between the two types of cells. It gives students a chance to practice comparing and contrasting these two types of cells, and to learn more about the structure and function of each. This worksheet can help students better understand the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes and how they relate to each other. With this knowledge, students can gain a deeper understanding of the cellular world and how it works.
[addtoany]





![48 Pythagorean Theorem Worksheet With Answers [Word + Pdf] for Pythagorean Theorem Practice Worksheet](https://worksheet1.wp-json.my.id/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/48-pythagorean-theorem-worksheet-with-answers-word-pdf-for-pythagorean-theorem-practice-worksheet-150x150.jpg)

