Exploring the Foundations of Chemical Bonding: A Comprehensive Overview of the Chemical Bonds Worksheet Answers
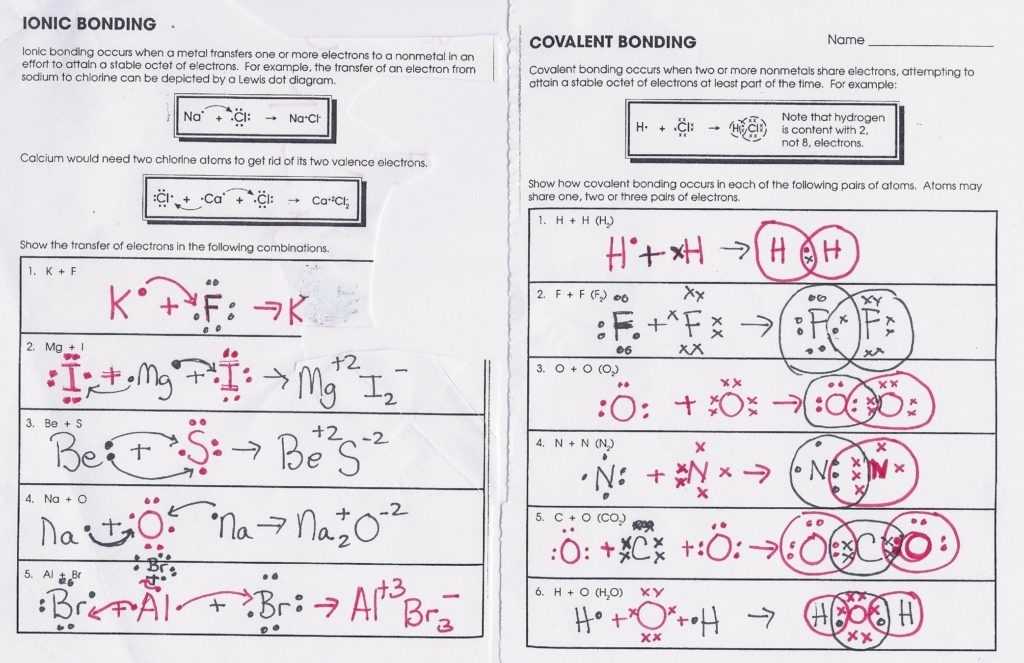
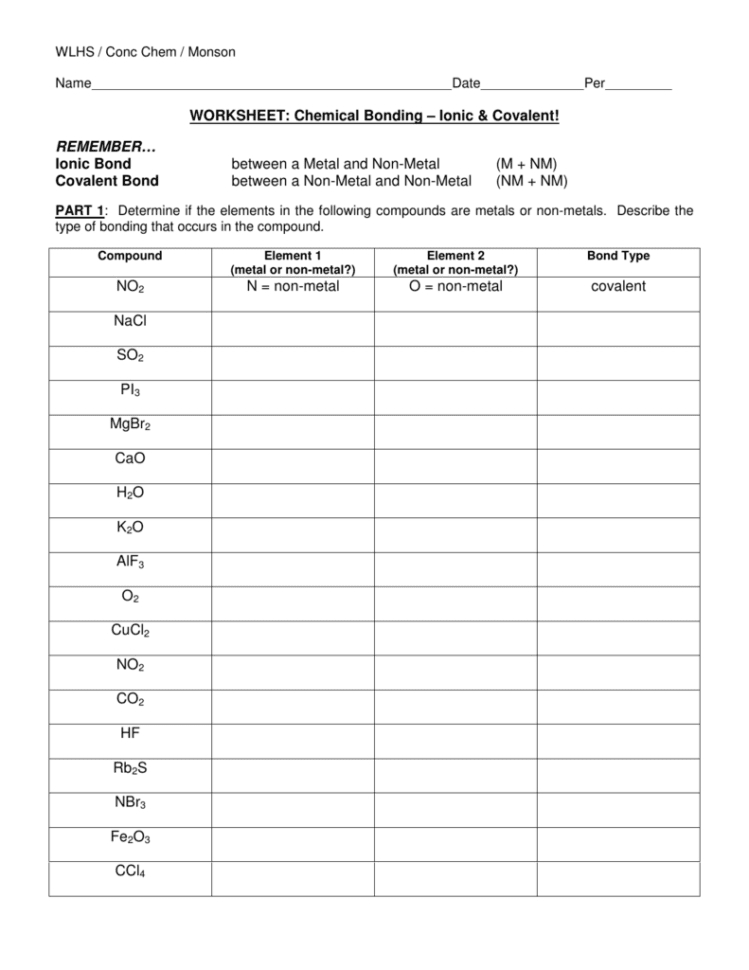
The chemical bonds worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the various types of chemical bonds and their associated properties. Chemical bonds are formed when two atoms exchange or share electrons, and the strength of the bond depends on the number of electrons shared. There are four different types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, metallic, and hydrogen. Each type of bond has its own characteristics and properties, which are essential for understanding the behavior of molecules.
Ionic bonds are formed when one atom gains an electron from another atom and is held together by an electrostatic force of attraction. These bonds are usually formed between an atom with a high electronegativity and a low electronegativity. Since the charges of the two atoms are opposite, the force of attraction is strong, making them very stable. The properties of ionic bonds include strong attractions between the atoms, high melting points, and the ability to conduct electricity.
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share electrons. These bonds are typically formed between atoms of the same or similar electronegativity, so the electrons are evenly shared between the two atoms. Covalent bonds are very strong, and they are often found in molecules such as water and DNA. The properties of covalent bonds include strong attractions between the atoms, higher melting points, and the ability to form crystals.
[toc]
Metallic bonds are formed when atoms with similar electronegativities come together and form a lattice of metal ions. These bonds are very strong and are responsible for the properties of most metals. The properties of metallic bonds include high melting points, strength, and electrical conductivity.
Hydrogen bonds are the weakest type of bond, but they are still very important in biology. Hydrogen bonds are formed when hydrogen atoms are attracted to other atoms, such as oxygen, that have lone pairs of electrons. These bonds are essential for the formation of water molecules, proteins, and DNA. The properties of hydrogen bonds include low melting points and the ability to absorb and emit light.
The chemical bonds worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of each type of bond and its associated properties. Understanding the different types of bonds and their properties is essential for understanding the behavior of molecules and their role in biology.
Different Types of Chemical Bonds and What They Mean: Examining the Chemical Bonds Worksheet Answers
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together in molecules and chemical compounds. There are four major types of chemical bonds that are commonly encountered in chemistry: covalent, ionic, hydrogen, and metallic bonds. Each type of bond is characterized by distinct features, and understanding the differences between them is important for accurately predicting the behavior of a given substance.
Covalent bonds are the strongest type of chemical bond and involve the sharing of electrons between atoms. This results in a strong intermolecular force between the two atoms, making it difficult to break the bond. Covalent bonds are typically formed between nonmetals and are often seen in organic compounds.
Ionic bonds are the second strongest type of chemical bond and involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. The atom that donates the electron becomes positively charged, while the atom that accepts the electron becomes negatively charged. This creates an electrostatic attraction between the two atoms, which is what holds the bond together. Ionic bonds are commonly seen in salts and other compounds containing metals.
Hydrogen bonds are the weakest type of chemical bond but still play an important role in many processes. They result from the attraction between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen. This type of bond is relatively weak but is still strong enough to hold molecules together. Hydrogen bonds are commonly found in water molecules and other molecules containing hydrogen atoms.
Metallic bonds are the fourth type of chemical bond and involve the sharing of electrons between metal atoms. These bonds are relatively strong and create a lattice-like structure that allows the metal atoms to form a solid material. Metals are the most abundant elements on Earth and are essential for many everyday objects.
Understanding the different types of chemical bonds and what they mean is essential for accurately predicting the behavior of a given substance. Each type of bond is characterized by distinct features, and knowing the differences between them can provide valuable insight into why materials behave the way they do.
Understanding the Role of Ions and Electrons in Chemical Bonding: A Guide to Chemical Bonds Worksheet Answers
Ions and electrons play a critical role in chemical bonding, which is the process of two atoms or molecules combining to form a single, more complex molecule. In order to understand the role of ions and electrons in chemical bonding, it is important to understand the basic principles of how they interact.
Ions are atoms or molecules that have an electrical charge due to the imbalance of protons and electrons. Positively charged ions are called cations and are created when an atom or molecule loses electrons. Negatively charged ions, called anions, are created when an atom or molecule gains electrons. During a chemical bond, cations and anions will attract each other and form a stable bond.
Electrons are responsible for the attraction between cations and anions. Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus of an atom. When two atoms or molecules come into contact with each other, electrons from one atom will interact with the electrons from the other atom. If the interaction between the electrons is strong enough, the atoms will form a chemical bond.
The strength of a chemical bond is determined by the number of electrons that are shared between the atoms or molecules. If two atoms or molecules share a large number of electrons, the bond is said to be strong. If the atoms or molecules share a small number of electrons, the bond is said to be weak.
Ions and electrons play an integral role in chemical bonding. Ions are responsible for the attraction between atoms or molecules, while electrons are responsible for the strength of the bond. By understanding the role of ions and electrons in chemical bonding, we can better understand how molecules interact and form more complex structures.
An Overview of Covalent Bonding and Its Role in Chemical Bond Formation: Analyzing the Chemical Bonds Worksheet Answers
Covalent bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the sharing of electrons between atoms to form molecules. It is one of the most important types of chemical bonds and is essential to the formation of many compounds and materials.
Covalent bonds form when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing of electrons creates a strong bond between the atoms that is highly stable. The strength of the bond depends on the number of electrons that are shared and its stability is determined by the arrangement of the electrons around the nuclei of the atoms.
In order to understand the role of covalent bonding in chemical bond formation, it is important to consider the types of bonds that form. Covalent bonds can be single, double, or triple bonds, depending on the number of electrons shared between two atoms. Single bonds are relatively weak and are commonly found in molecules like water, whereas double and triple bonds are much stronger and are found in molecules like nitrogen and carbon dioxide.
The type of covalent bond that is formed can be used to determine the chemical properties of a molecule. For example, single bonds tend to be more polar, meaning that they attract more electrons from one atom than from the other. This allows them to form hydrogen bonds and allows them to form hydrogen bridges, which are important for the formation of many organic molecules. Double and triple bonds, however, are much less polar and have very different properties.
In addition to the type of bond, the strength of the covalent bond is also important to consider. The strength of the bond is determined by the types of atoms that are involved in the bond. Atoms with similar electronegativities will form relatively strong covalent bonds, while atoms with different electronegativities will form weaker bonds. This is because atoms with similar electronegativities will share electrons more efficiently, resulting in a stronger bond.
Covalent bonding is an essential part of many organic and inorganic compounds and materials. It is the primary type of bond in most molecules and plays a major role in chemical bonding and the formation of many materials. Understanding the role of covalent bonding in chemical bond formation is essential for understanding how materials form and interact with each other.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Overview Chemical Bonds Worksheet Answers provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of chemical bonds and their general characteristics. By studying these answers, students can gain a better understanding of the different types of chemical bonds and how they interact with each other. With this knowledge, students can then apply their understanding to the study of other areas of chemistry.
[addtoany]