Exploring the Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answers
1. What are nucleic acids?
Nucleic acids are large biologically important molecules that are found in all living organisms. They are composed of nucleotides, which are made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Nucleic acids are essential for the storage and expression of genetic information, as well as for cell functioning.
2. What are the two types of nucleic acids?
The two types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA is responsible for the storage and expression of genetic information, while RNA is involved in protein synthesis.
3. What are the components of a nucleotide?
A nucleotide is composed of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The sugar, or pentose, can be either ribose or deoxyribose. The phosphate group is composed of a negatively charged phosphate ion and two hydrogens. The nitrogenous base can be either a purine or a pyrimidine.
[toc]
4. What is the structure of DNA?
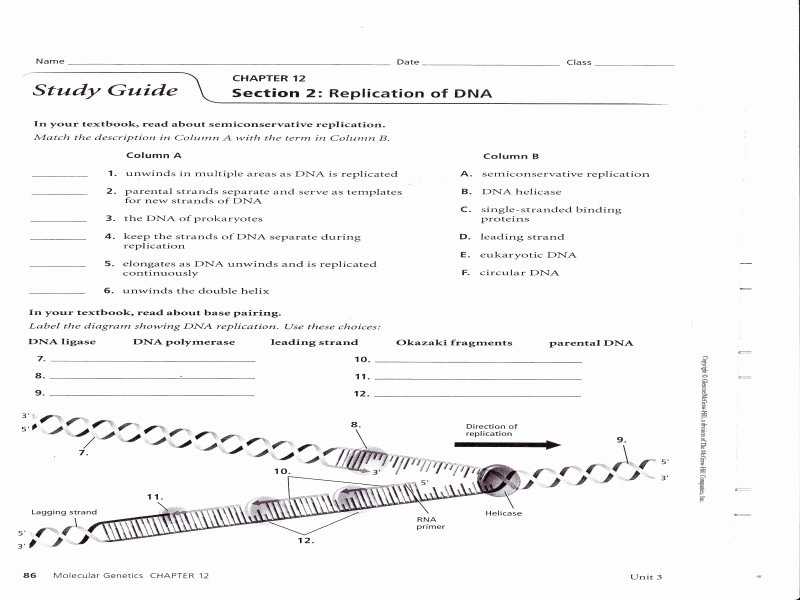
DNA is a double-stranded structure composed of two strands of nucleotides that are intertwined in a helical shape. Each strand is composed of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The two strands of nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds between the complementary nitrogenous bases A-T and G-C.
5. What is the role of DNA in genetic information storage and expression?
DNA serves as the permanent storage of genetic information in a cell. It contains the instructions for making proteins and is responsible for transmitting genetic information from one generation to the next. It is also responsible for the regulation of cellular processes, such as cell differentiation and growth.
An Overview of the Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding its Purpose
Nucleic acids are a large class of biological molecules that play a vital role in the functioning of all living cells. They are composed of two types of molecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), that together store and transmit genetic information. As such, they are essential for all metabolic processes and for the replication, expression, and transmission of genetic information.
The nucleic acids worksheet is a comprehensive guide to understanding the purpose and function of these molecules. It covers the structure and components of nucleic acids, their role in the cell cycle, and their importance in the transmission of genetic information. It also explores the different types of nucleic acids, as well as their interaction with other biomolecules and enzymes.
The worksheet begins with an introduction to the structure and components of DNA and RNA. It explains the differences between the two, including the structure of the sugar-phosphate backbone, the four nitrogenous bases, and the paired hydrogen bonds that link the strands of DNA. It also covers the differences between the three types of RNA and the properties of each.
Next, the worksheet explores the role of nucleic acids in the cell cycle, which is the process by which cells divide and replicate. It explains the role of DNA in providing the genetic information needed for replication and transcription, and the role of RNA in carrying out these processes. It also outlines how DNA and RNA interact with other biomolecules and enzymes to carry out the cell cycle.
Finally, the worksheet covers the importance of nucleic acids in the transmission of genetic information. It explains the role of DNA in providing the genetic code for the production of proteins, and how DNA and RNA interact to carry out transcription and translation. It also describes the role of RNA in controlling gene expression and how mutations in DNA can lead to changes in gene expression.
The nucleic acids worksheet is an invaluable resource for anyone interested in learning more about these important molecules. It provides a comprehensive overview of their structure, function, and role in the cell cycle, as well as their importance in the transmission of genetic information.
Analyzing the Different Types of Nucleic Acids: Breaking Down the Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answers
Nucleic acid is a macromolecule that plays a major role in the functioning of all living organisms. In this worksheet, we will analyze the different types of nucleic acids and their roles in the body.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): DNA is a double-stranded nucleic acid molecule that stores and transmits genetic information from one generation to the next. It is composed of four different nucleotides – adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) – that are connected to one another in a specific sequence. This sequence determines the genetic code, which serves as the blueprint for the production of proteins. DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell and is responsible for the development and function of the organism.
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid): RNA is a single-stranded nucleic acid molecule that plays an important role in the expression of genetic information. It is composed of four different nucleotides – adenine (A), uracil (U), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) – that are connected to one another in a specific sequence. This sequence determines the genetic code, which serves as the instruction manual for the production of proteins. RNA is found in many different parts of the cell, including the nucleus, cytoplasm, and ribosomes, and is involved in the formation of proteins, regulation of gene expression, and other important processes.
mRNA (Messenger RNA): mRNA is a single-stranded nucleic acid molecule that is involved in the transfer of genetic information from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. It is composed of four different nucleotides – adenine (A), uracil (U), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) – that are connected to one another in a specific sequence. This sequence determines the genetic code, which serves as the instruction manual for the production of proteins. mRNA is synthesized from DNA in the nucleus and is then transported to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm where it is translated into proteins.
tRNA (Transfer RNA): tRNA is a single-stranded nucleic acid molecule that is involved in the synthesis of proteins. It is composed of four different nucleotides – adenine (A), uracil (U), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) – that are connected to one another in a specific sequence. This sequence determines the genetic code, which serves as the instruction manual for the production of proteins. tRNA is responsible for the transport of amino acids to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm where they are incorporated into proteins.
rRNA (Ribosomal RNA): rRNA is a single-stranded nucleic acid molecule that is involved in the formation of ribosomes. It is composed of four different nucleotides – adenine (A), uracil (U), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) – that are connected to one another in a specific sequence. This sequence determines the genetic code, which serves as the instruction manual for the assembly of ribosomes. rRNA forms the core of the ribosome and is responsible for the recognition and binding of mRNA and
Demystifying the Basics of Nucleic Acids: An Overview of the Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answers
Nucleic acids are macromolecules that are essential for the functioning of all living organisms. They are the molecules responsible for carrying genetic information and replicating it. This worksheet will help demystify the basics of nucleic acids, including their structure, components, and functions.
1. What are nucleic acids?
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are composed of two types of molecules: DNA and RNA. DNA is responsible for carrying genetic information, while RNA is responsible for transferring genetic information to protein-building machinery. Nucleic acids are found in the nucleus of a cell and are the main component of chromosomes.
2. What are the components of nucleic acid molecules?
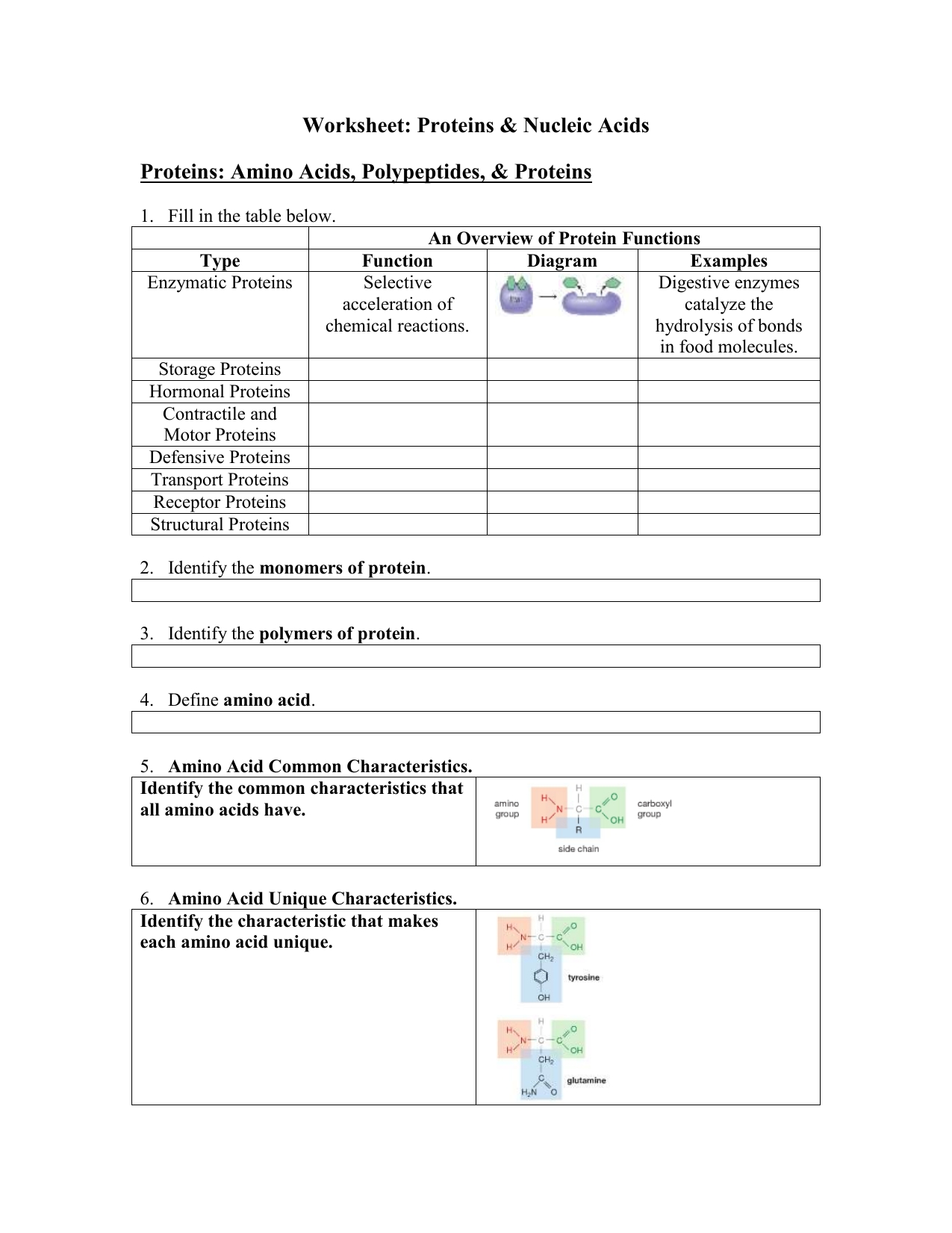
Nucleic acid molecules are composed of two parts, a sugar molecule and a phosphate group. The sugar molecule can be either deoxyribose (in DNA) or ribose (in RNA), while the phosphate group is always composed of three phosphate molecules. The combination of these components forms a backbone of the nucleic acid molecule and is referred to as the ‘sugar-phosphate backbone’. Attached to the backbone are components known as nucleotides, which are made of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and one or two phosphate groups.
3. What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA and RNA are both nucleic acid molecules, however, they differ in a few key ways. DNA is composed of deoxyribose sugar and double-stranded, whereas RNA is composed of ribose sugar and is single-stranded. DNA is responsible for carrying genetic information, while RNA is responsible for transferring genetic information to protein-building machinery. Another key difference is that DNA contains the nitrogenous bases adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine, while RNA contains the nitrogenous bases adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine.
4. What is the function of nucleic acids?
The main function of nucleic acids is to store and transmit genetic information. DNA holds the genetic code which is essential for the functioning of all living organisms. RNA is responsible for decoding the genetic code and transferring it to protein-building machinery. Nucleic acids also play a role in the regulation of gene expression, which is the process by which genetic information is translated into proteins.
5. What is the structure of nucleic acid molecules?
Nucleic acid molecules have a double helix structure, meaning that they are composed of two strands that are wound around each other in a spiral formation. The strands are composed of nucleotides, which contain a nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and a phosphate group. The sugar-phosphate backbone of the nucleic acid molecule is responsible for holding the strands together. The nitrogenous bases are responsible for providing the ‘rungs’ of the ladder and form base pairs with their complementary bases.
Conclusion
The Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answers provide a comprehensive look at the structure and function of nucleic acids. By understanding their structure and function, students can gain a better understanding of the role of these molecules in living organisms. With a better understanding of these molecules, students can develop an appreciation of the importance of these molecules in everyday life.
[addtoany]