Exploring Newton’s Laws of Motion Worksheet: An Introduction to the Basics
Sir Isaac Newton was an English physicist and mathematician who lived during the late 17th and early 18th centuries. He is famous for his three laws of motion, which form the foundation of classical mechanics. The three laws of motion are fundamental to our understanding of the physical world and are used to describe the motion of objects in a variety of contexts.
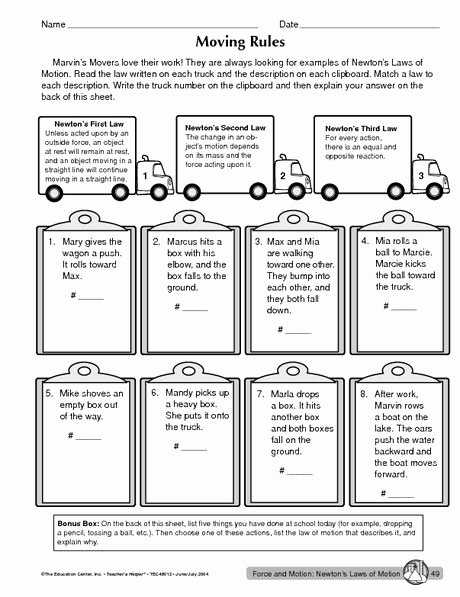
The first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia, states that an object in motion will remain in motion unless it is acted upon by an external force. This law states that a body at rest will remain at rest unless an external force is applied to it, and a body in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity unless an external force is applied to it. In other words, a body in motion will continue to move in a straight line at a constant speed unless it is acted upon by a force.
The second law of motion states that the rate of change of momentum of a body is proportional to the net force acting on it. This law states that when a force is applied to an object, it will cause an acceleration proportional to the magnitude of the force. This law can be expressed as F=ma, where F is the force, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration of the object.
[toc]
The third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This law states that when a force is applied to an object, the object will exert an equal and opposite force on the force that is being applied to it. This law can be expressed as F= -F, where F is the force exerted by the object and F is the force applied to the object.
These three laws of motion form the basis of classical mechanics, which is used to explain the motion of objects. They are fundamental to our understanding of the physical world and are used to describe the motion of objects in a variety of contexts.
Tips for Making the Most of Newton’s Laws of Motion Worksheet in the Classroom
1. Introduce Newton’s Laws of Motion: Before beginning the worksheet, explain the three laws of motion and their implications. This will help students understand and remember the content throughout the worksheet.
2. Encourage Collaboration: Allow students to work together to complete the worksheet. This encourages problem-solving skills and allows students to ask each other questions.
3. Provide Examples: Provide examples of each law in action. This will give students an easier way to understand the information.
4. Involve the Whole Class: Ask questions throughout the worksheet to engage the entire class. This will help keep students engaged and allow them to ask questions.
5. Check for Understanding: Give students time to review their answers and ask questions. This will help ensure that students have a clear understanding of the material.
6. Reinforce the Content: Use additional activities to reinforce the material covered in the worksheet. This could include additional reading, videos, or experiments to make the material more memorable.
Creative Ways to Engage Students with Newton’s Laws of Motion Worksheet Activities
1. Kinetic Chain: Students can create a kinetic chain to demonstrate the laws of motion. Group students into teams and provide each team with a set of basic materials such as rubber bands, paper clips, and other objects that can be connected in a chain. Ask them to create a chain that will move when one of the links is pulled. Explain how the chain works and how each link in the chain is affected by the movement of the links around it. Relate this to Newton’s laws of motion and ask the students to explain the connection.
2. Parachute Drop: Ask students to create a parachute using paper, tape, and string. After the parachutes are built, have them drop them from a height and observe what happens. Ask students to explain the behavior of the parachutes in terms of Newton’s laws of motion. Discuss how the force of gravity is acting on the parachutes and how the drag created by the parachute affects the rate of descent.
3. Car Collision: Set up a simple experiment in which two toy cars are placed on an inclined plane or ramp and then released at the same time. Ask the students to observe what happens and explain it in terms of Newton’s laws of motion. Discuss how the momentum of the cars affects their motion and how outside forces such as friction and gravity act on them.
4. Balloon Car Races: Give each team of students a balloon and some materials such as cardboard, straws, and tape. Ask them to use the materials to build a car that is powered by the force of the balloon. Have the teams race their cars and explain how the forces acting on them relate to Newton’s laws of motion.
5. Egg Drop Challenge: Challenge the students to design a container to protect an egg from breaking when dropped from a height. Ask them to explain why their design works and how Newton’s laws of motion are involved. Discuss how the forces acting on the egg and container can be minimized to ensure the egg doesn’t break.
Conclusion
Newton’s Laws of Motion Worksheet provides an excellent introduction to the basics of physics. It is a great way to gain an understanding of the fundamental principles of motion and how they relate to everyday life. By completing the worksheet, students have the opportunity to gain a better understanding of the principles of motion, and how they can be applied to real-world situations. With this knowledge, students will be better equipped to make informed decisions in their day-to-day lives.
[addtoany]