What Are the Different Types of Membrane Structure and How Do They Affect Function?
Membrane structure is a crucial component of cellular function and there are several different types of membrane structure. Each type of membrane structure has a unique set of characteristics that affect its function.
One of the most common types of membrane structure is the lipid bilayer. This type of membrane structure consists of two layers of phospholipids that form a barrier to the movement of molecules. The lipid bilayer also has a number of proteins embedded within it, which serve to regulate the movement of molecules across the membrane. This type of membrane structure helps to maintain the cell’s internal structure and facilitate the transport of materials in and out of the cell.
Another type of membrane structure is the cell wall. The cell wall is composed of a tough outer layer of polysaccharides and proteins that provide structure and stability to the cell. The cell wall also serves to protect the cell from environmental damage and regulate the movement of molecules into and out of the cell.
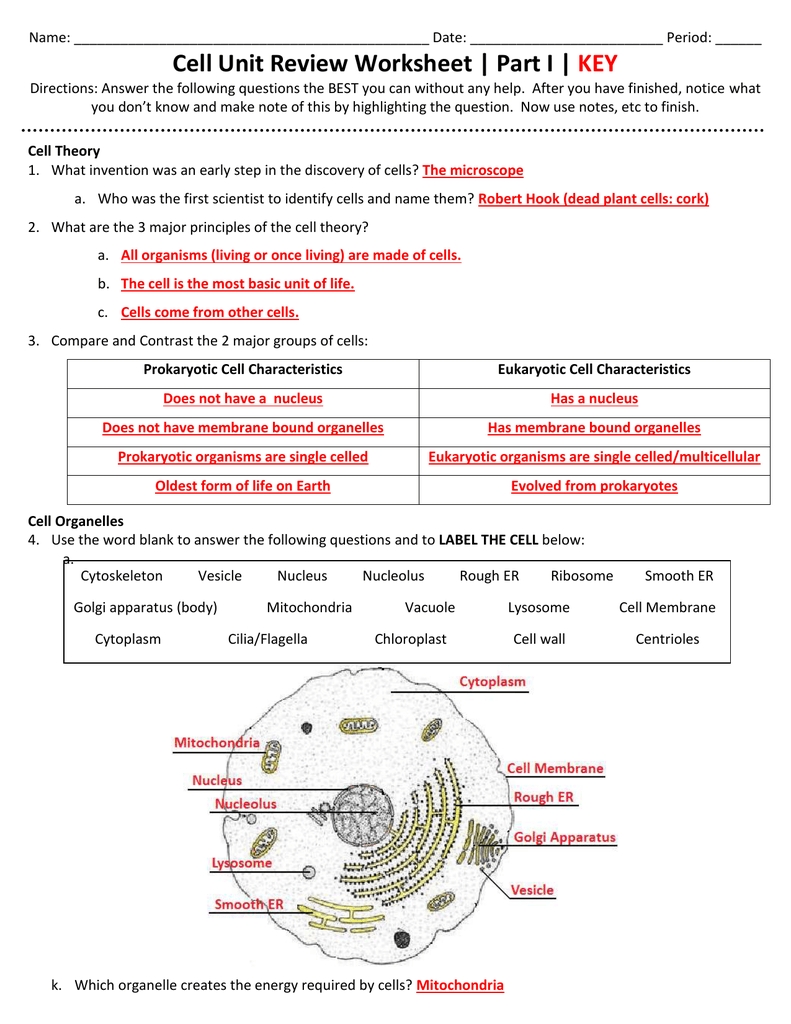
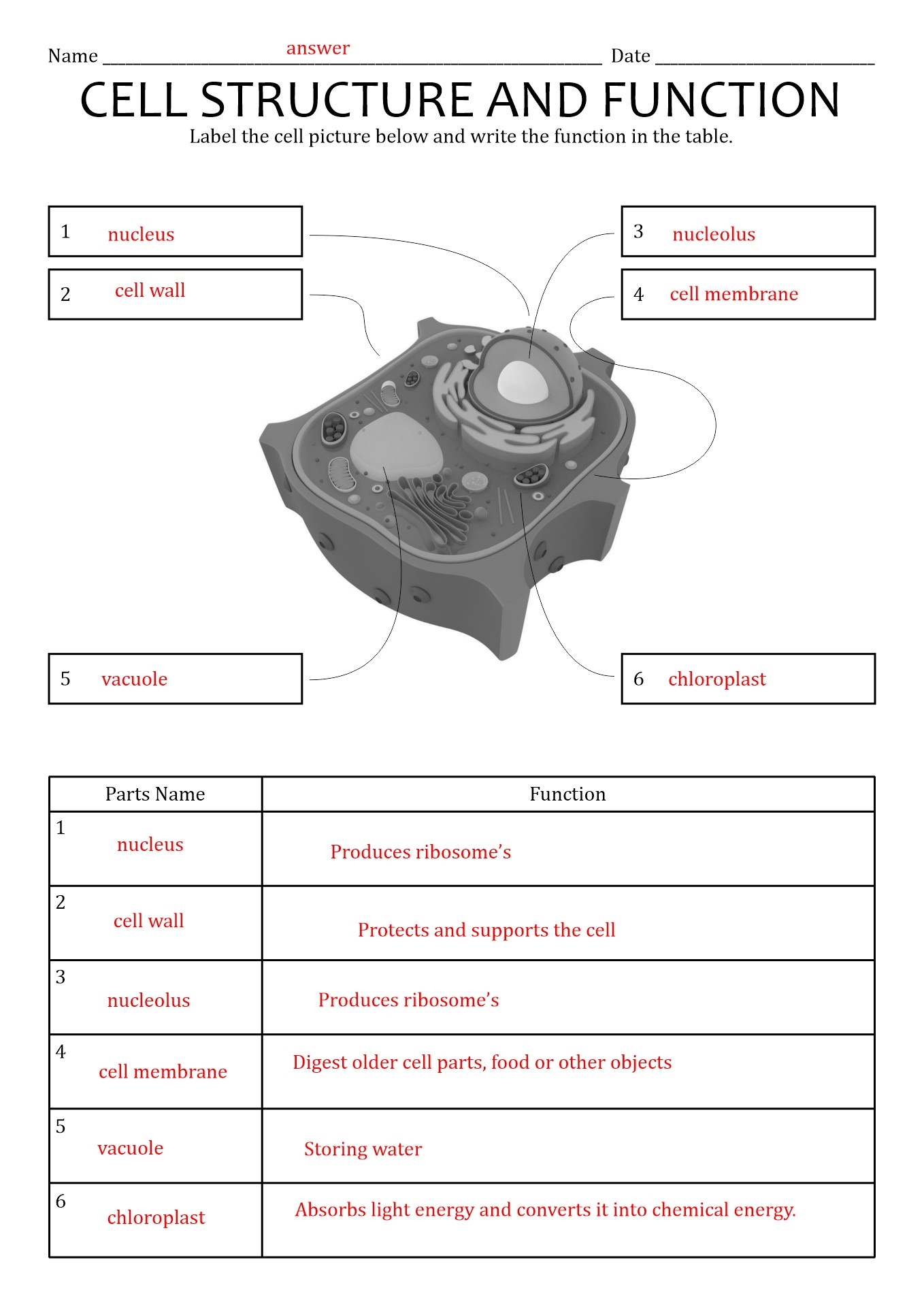
[toc]
The third type of membrane structure is the glycocalyx. This membrane structure is composed of a thin layer of carbohydrate molecules that surrounds the cell. It serves to protect the cell from damage and regulate the movement of molecules into and out of the cell.
The fourth type of membrane structure is the cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton consists of a network of proteins that provide support and structure to the cell. The cytoskeleton also helps to regulate the movement of molecules into and out of the cell.
Each type of membrane structure has a unique set of characteristics that affect its function. The lipid bilayer helps to maintain the cell’s internal structure and facilitate the transport of materials in and out of the cell. The cell wall provides structure and stability to the cell, protects the cell from environmental damage and regulates the movement of molecules into and out of the cell. The glycocalyx serves to protect the cell from damage and regulate the movement of molecules into and out of the cell. Finally, the cytoskeleton helps to provide support and structure to the cell and regulate the movement of molecules into and out of the cell.
Investigating the Relationship Between Membrane Structure and Cell Signaling.
The relationship between membrane structure and cell signaling is a complex one that has been widely studied in the scientific community. It has been identified that the structure of the cell membrane is integral to the successful transmission of signals throughout the cell.
The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that consists of a hydrophobic core and hydrophilic heads at the surface. This structure is responsible for the selective permeability of the membrane, allowing certain molecules to pass through and others to be excluded. The bilayer structure also provides the foundation for many important cell processes including the transport of molecules, the activity of enzymes, and cell signaling.
Cell signaling is initiated by a stimulus, which can be either an external or an internal factor. This stimulus triggers a series of reactions that involve the cell membrane. One such reaction is the conformational change of membrane proteins, which can be triggered by the binding of a ligand. This will result in the exposure of different domains and the activation of the receptor proteins. This can then initiate a cascade of further reactions leading to a response from the cell.
Cell signaling is also heavily dependent on membrane lipids, which are important for the correct assembly and functioning of proteins. These lipids can be classified into two groups; structural lipids and signaling lipids. Structural lipids are responsible for maintaining the integrity of the membrane, while signaling lipids are involved in the regulation of cell signaling.
The structure of the cell membrane is therefore essential for the successful transmission of signals throughout the cell. The combination of its phospholipid bilayer, membrane proteins, and lipids make it an ideal platform for the initiation and propagation of signals. Without these components, the cell would not be able to recognize and respond to external or internal stimuli. It is clear that the structure of the cell membrane plays a critical role in cell signaling and is essential for the normal functioning of the cell.
Exploring the Role of Membrane Proteins in Cell Membrane Structure and Function.
Membrane proteins are integral components of the cell membrane, playing a key role in the structure and function of the membrane. These proteins are embedded in the lipid bilayer of the membrane, and are involved in a variety of processes, including cellular communication, transport of molecules, and enzymatic activity.
The structure of membrane proteins is highly conserved, consisting of a hydrophobic transmembrane domain, a hydrophilic extracellular domain, and a hydrophobic cytoplasmic domain. This arrangement helps to stabilize the lipid bilayer, as the hydrophobic transmembrane domain interacts with the surrounding lipids, and the hydrophilic domains interact with the aqueous environment outside and inside the cell. This arrangement also helps to determine the membrane’s permeability, as the hydrophobic transmembrane domain can act as a barrier to the passage of certain molecules.
Membrane proteins are also involved in a variety of processes important to cell function. For example, membrane proteins can act as receptors, binding to specific molecules and initiating a signal transduction cascade. They can also act as transporters, allowing for the movement of molecules across the membrane in response to a concentration gradient. Additionally, some membrane proteins are enzymatically active, catalyzing reactions that are important for cellular metabolism.
In summary, membrane proteins play a critical role in the structure and function of the cell membrane. They stabilize the lipid bilayer, determine membrane permeability, and are involved in a variety of processes, including signal transduction, transport, and enzymatic activity. As such, membrane proteins are essential for the survival and proper functioning of cells.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Membrane Structure and Function Worksheet is a great tool for learning about the components of a cell membrane and their functions. It provides an interactive way to understand the structure and function of the membrane, and how they are related. This worksheet helps to develop a student’s understanding of the cell membrane and its components, as well as its role in maintaining a cell’s homeostasis.
[addtoany]