Exploring Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) in the Classroom: A Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a MAD Worksheet
Mean absolute deviation (MAD) is an important concept for students to understand as they continue to develop their mathematical skills. This step-by-step guide will provide teachers with the resources and tools to create a MAD worksheet in the classroom.
The first step is defining the MAD concept to the students. Explain that MAD is the measure of the average distance of each data point from the mean. It is an important concept to understand because it allows students to measure how far a set of data points are from each other.
The second step is to provide the students with an example of MAD. Give an example of a data set, such as a list of test scores, and explain how to calculate the mean and MAD of the set. Have the students work through the example to ensure they understand the concept and the calculation process.
[toc]
The third step is to provide students with practice problems. Create a MAD worksheet with a variety of data sets. These could include test scores, exam grades, or any other type of data that is relevant to the class. Have students calculate the mean and MAD for each set of data.
The fourth step is to review the MAD worksheet with the students. Go over any questions students may have about the process and provide additional examples if needed.
The fifth step is to allow students to apply the MAD concept to real-world situations. Have students think of situations in which understanding MAD could be useful. This could include understanding how evenly-distributed a set of test scores are or how much variation there is in a certain population.
By following these steps, teachers can easily create a MAD worksheet for the classroom. This will help students to understand the MAD concept and apply it to real-world situations.
How to Use a Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) Worksheet to Analyze Data
Mean absolute deviation (MAD) worksheets are an effective tool for analyzing data. The MAD worksheet provides a numerical estimate of the size of the differences between the values of a dataset. It is used to assess variability and measure the dispersion of the data.
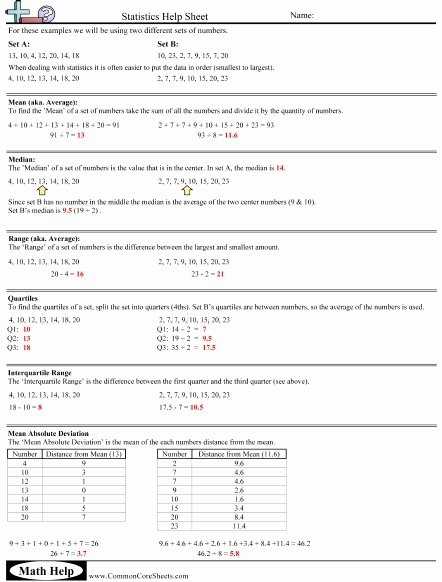
To use a MAD worksheet to analyze data, first, the data should be arranged in a table with the different values listed in the rows and columns. The MAD formula should be written at the top of the sheet. The formula is: MAD = (Σ|x – x̄|) / n.
The next step is to calculate the mean of the dataset by adding up all of the values and dividing by the total number of values. This value is denoted as x̄.
Once the mean has been calculated, the absolute values of the differences between each value and the mean should be calculated and written into the table. To do this, subtract the mean from each value and take the absolute value of the result.
The sum of the absolute differences should then be calculated and written into the table. This is done by adding up all of the absolute values of the differences.
Finally, the MAD should be calculated by dividing the sum of the absolute differences by the total number of values. This result is the mean absolute deviation of the dataset.
A MAD worksheet is a simple but effective way to analyze data. By using the MAD formula and following the steps outlined above, it is possible to quickly and accurately measure the variability of a dataset.
A Comprehensive Guide to Interpreting the Output of a Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) Worksheet
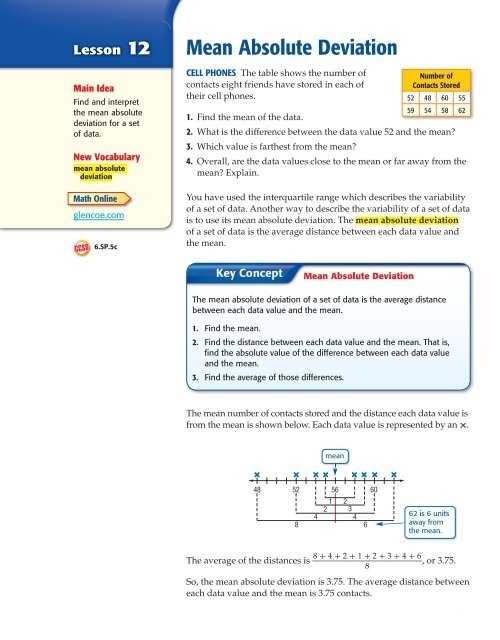
Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) is a measure of dispersion that can be used to determine the variability within a set of values. It is a useful tool for analyzing the distribution of data and making decisions about how to interpret it. MAD worksheets can be used to calculate the MAD for a given set of data. The output of an MAD worksheet is an array of values that show the MAD for each data point in the dataset.
The output of an MAD worksheet consists of three components: the mean, the absolute deviation, and the MAD. The mean is the average of all the values in the dataset. The absolute deviation is the difference between each data point and the mean. The MAD is calculated by taking the average of the absolute deviations of all the values in the dataset.
The output of an MAD worksheet can be used in several ways to interpret the data. First, it can be used to determine the overall distribution of the data. If the MAD is high, it indicates that the data is widely dispersed, while if the MAD is low, it indicates that the data is more closely concentrated around the mean.
Second, the output of an MAD worksheet can be used to identify outliers. Outliers are data points that are very far from the mean. These outliers may indicate incorrect data, or they may indicate that the data is especially variable.
Third, the output of an MAD worksheet can be used to identify trends in the data. If the MAD is increasing, it indicates that the data is becoming more dispersed. If the MAD is decreasing, it indicates that the data is becoming more concentrated around the mean.
Finally, the output of an MAD worksheet can be used to compare different datasets. Since MAD is a measure of dispersion, it can be used to compare the variability in two datasets. For example, if one dataset has a higher MAD than another, it indicates that the data in the first dataset is more widely dispersed than in the second.
In conclusion, the output of an MAD worksheet can be used to gain insight into the distribution of data and make decisions about how to interpret it. It can be used to determine the overall distribution of the data, identify outliers, identify trends in the data, and compare different datasets.
Conclusion
The Mean Absolute Deviation worksheet is a great tool for calculating and understanding the average of a set of data. It allows us to quickly identify outliers and measure the variability of a dataset. It is a useful tool for summarizing data, and can be used to compare different sets of data or to identify trends in data. With its easy-to-use interface, it is a great tool for any data analyst.
[addtoany]