Exploring the Different Levels of Ecological Organization: A Worksheet Guide
Ecology is the study of the interactions between living organisms and their environment. An understanding of the different levels of ecological organization is essential in order to comprehend the complexities of these interactions. This worksheet is designed to help students explore the different levels of ecological organization and their associated concepts.
Level 1: Organism
An organism is an individual living thing. It can be a single cell or a complex multicellular organism such as a human. Examples of organisms include bacteria, plants, and animals.
[toc]
Questions to consider:
1. What are some notable features of the organism?
2. How does the organism interact with its environment?
3. What are the organism’s basic needs?
4. How does the organism reproduce?
Level 2: Population
A population is a group of organisms of the same species living in a particular area.
Questions to consider:
1. How does the population interact with its environment?
2. How does the population grow or decline?
3. What are some factors that can affect the size of the population?
4. What are some of the competition and predation relationships within the population?
Level 3: Community
A community is a group of populations of different species living together in an area.
Questions to consider:
1. What are some of the interactions between different species in the community?
2. How do the species within the community interact with the environment?
3. What are some factors that can affect the composition of the community?
4. How does the community respond to environmental changes?
Level 4: Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms and their physical environment.
Questions to consider:
1. How do the organisms within the ecosystem interact with their environment?
2. What are some of the physical and biological factors that affect the ecosystem?
3. How does energy flow within the ecosystem?
4. How does the ecosystem respond to environmental changes?
Level 5: Biome
A biome is a large area containing distinct communities of plants and animals.
Questions to consider:
1. What are the major components of the biome?
2. How do the physical characteristics of the biome affect the organisms living there?
3. What are some of the factors that can affect the biome’s climate and weather patterns?
4. How does the biome respond to environmental changes?
Investigating the Food Chain and Food Web: A Levels of Ecological Organization Worksheet
A food chain and food web are two distinct but related concepts in ecology. Both involve the transfer of energy and nutrients among species within an ecosystem, and both are fundamental components of any healthy ecosystem. Understanding the relationships among species in an ecosystem is essential to maintaining healthy populations and reducing the impacts of human activities on the environment. The following worksheet will explore the levels of ecological organization that make up a food chain and a food web.
Level 1: Producer
The first level of a food chain or food web is the producer. Producers are organisms that are capable of producing their own energy, usually through photosynthesis. Examples of producers include plants, algae, and some bacteria.
Level 2: Primary Consumer
The second level of a food chain or food web is the primary consumer. Primary consumers are animals that feed directly on producers, such as herbivores. Examples of primary consumers include rabbits, deer, and some insects.
Level 3: Secondary Consumer
The third level of a food chain or food web is the secondary consumer. Secondary consumers are animals that feed on primary consumers, such as carnivores. Examples of secondary consumers include wolves, bears, and some birds.
Level 4: Tertiary Consumer
The fourth level of a food chain or food web is the tertiary consumer. Tertiary consumers are animals that feed on secondary consumers, such as large predators. Examples of tertiary consumers include lions, tigers, and some sharks.
Level 5: Decomposer
The final level of a food chain or food web is the decomposer. Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organic matter into simpler compounds, such as bacteria and fungi. Decomposers play an important role in recycling nutrients and energy within an ecosystem.
A food chain and food web are complex systems that involve multiple levels of ecological organization. By understanding the relationships among species in an ecosystem, we can better manage our environment and reduce the impacts of human activities on the environment.
Understanding the Interrelationships of Organisms: A Levels of Ecological Organization Worksheet
Ecology is a broad and complex scientific field, and it can be difficult to comprehend all of the interrelationships between organisms. While the study of ecology involves many different levels, one of the most basic and fundamental ways to begin to understand the connections between organisms is by examining the various levels of ecological organization. By understanding the levels of organization, it is possible to gain a better understanding of the interactions between organisms and the environment they inhabit.
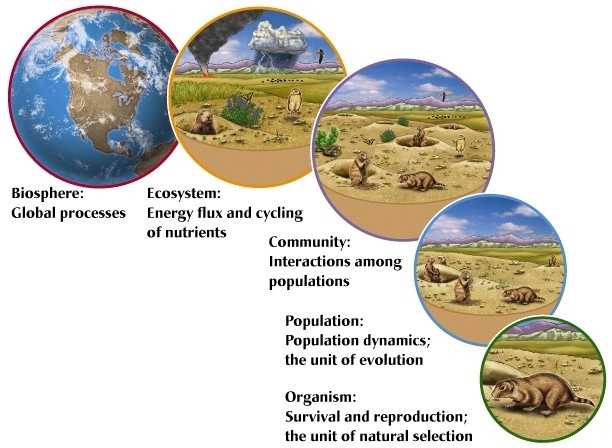
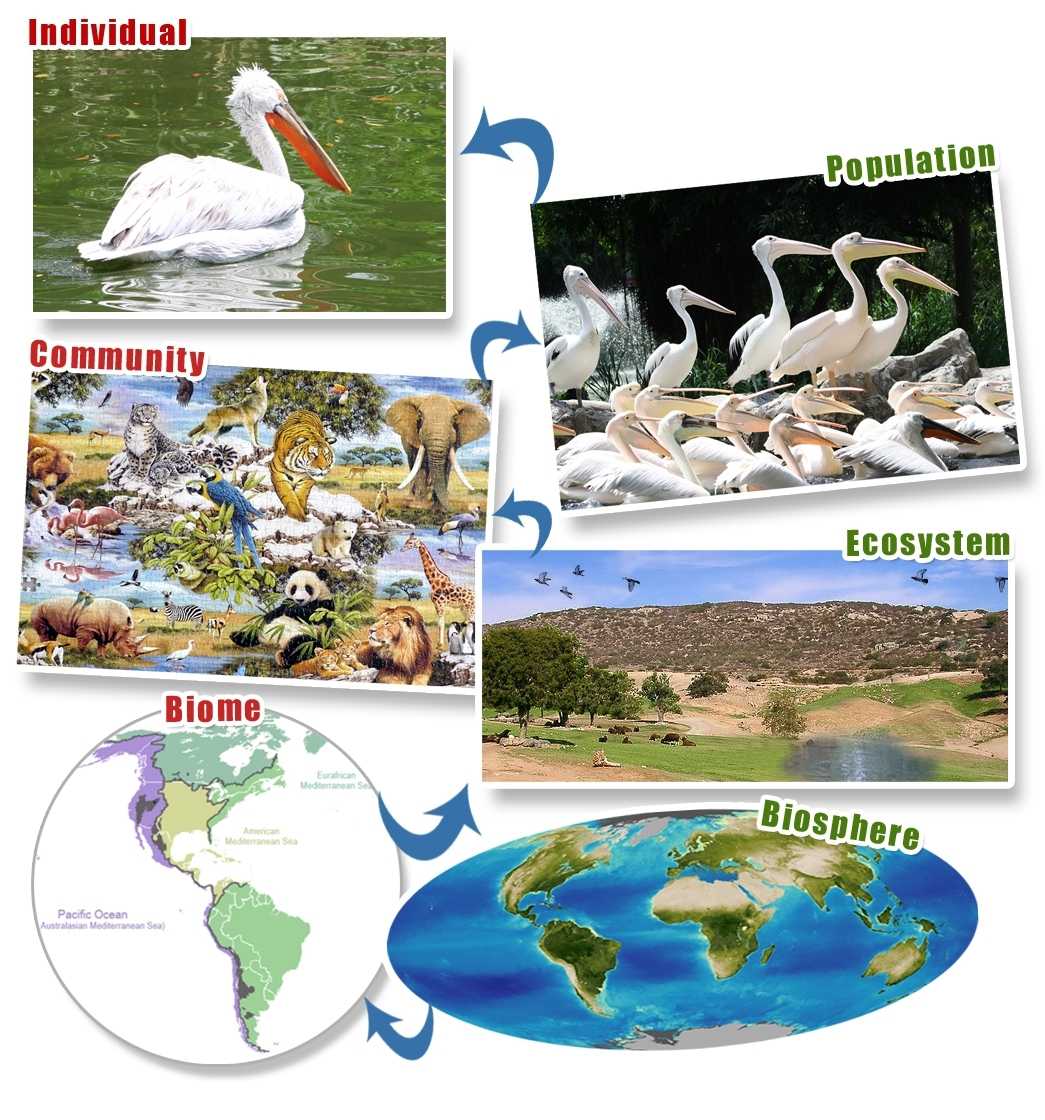
The first level of ecological organization is the individual organism. This is the basic unit of life, and each organism functions independently. Each organism must meet its own needs in order to survive, and its interactions with other organisms are usually limited to providing resources or competing for resources.
The next level of organization is the population. A population is a group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area and interact regularly. Populations can be influenced by the availability of resources, the presence of predators, and competition between members of the population.
The next level of organization is the community. A community is composed of several populations of different species that interact with each other and their environment. Communities interact with each other to form an ecosystem, which is a complex network of interactions between organisms and their environment.
The fourth level of organization is the biome. A biome is a large area of land or water with a similar climate and type of vegetation. Biomes contain many different types of organisms, and they can be affected by global changes in climate, such as global warming or drought.
Finally, the fifth level of organization is the biosphere. The biosphere is the entire global ecosystem, which includes all of the biomes, communities, and populations on the planet. The biosphere is affected by global changes that occur on a larger scale, such as climate change or ocean acidification.
By understanding the various levels of organization in ecology, it is possible to gain a better understanding of the relationships between organisms and their environment. By looking at the interactions between organisms at each level of organization, it is possible to gain insight into how ecosystems and biomes are formed and how they are affected by changes in their environment.
Analyzing Human Impact on the Environment: A Levels of Ecological Organization Worksheet
The ecological organization of the environment is a complex, interconnected system that is essential to the well-being of all living beings. Human activities can have a significant impact on the environment and its components, ranging from local to global scales. This worksheet aims to provide an overview of the levels of ecological organization and how human actions can affect them.
At the most basic level, organisms are the fundamental building blocks of the environment. Humans have the capacity to affect the populations of species through activities such as habitat destruction, over-harvesting, and pollution. These activities can have both short-term and long-term impacts on the health and abundance of species.
The next level of ecological organization is the community. Communities are composed of the populations of species present in a given area. Human activities such as land clearing and urbanization can alter the composition of species communities and reduce the diversity of species present. Changes to the community can also affect the ecosystem services provided, such as food production, pollination, and nutrient cycling.
Ecosystems are composed of communities and the physical environment. Human activities such as the introduction of invasive species, the use of fertilizers and pesticides, and climate change can alter the structure and function of ecosystems. These activities can have far-reaching impacts, including changes to species interactions, nutrient cycling, and energy flow.
At the global scale, the biosphere is composed of all the living and non-living components of the environment. Human activities such as deforestation, over-fishing, and the emission of greenhouse gases can have an impact on global processes such as the carbon cycle, climate patterns, and ocean currents. These activities can have both short-term and long-term effects on global ecosystems, including the potential for species extinction and changes to global climate.
In conclusion, human activities can have a significant impact on the environment at all levels of ecological organization. It is important to consider how our actions might influence the environment in order to promote sustainable practices and preserve the health of the environment for future generations.
Conclusion
The Levels of Ecological Organization Worksheet is a great tool to help students understand the complexities of an ecosystem. By breaking down an ecosystem into its basic components, students can gain a better understanding of the interactions between organisms, physical environment, and abiotic components of the environment. Through their exploration of the levels of ecological organization, students can gain a better understanding of the interdependence of living systems, the importance of biodiversity, and the processes necessary for ecosystems to sustain themselves.
[addtoany]