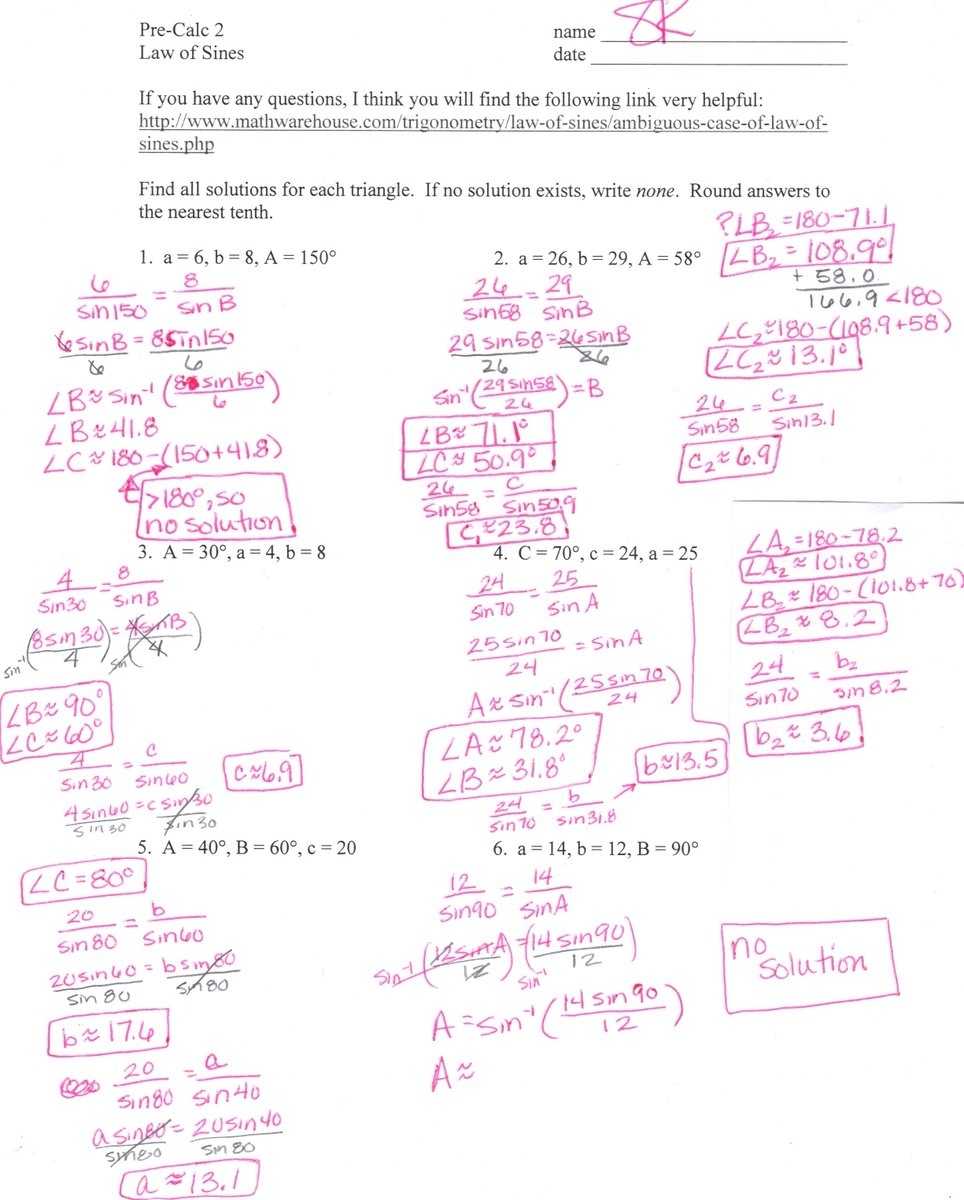
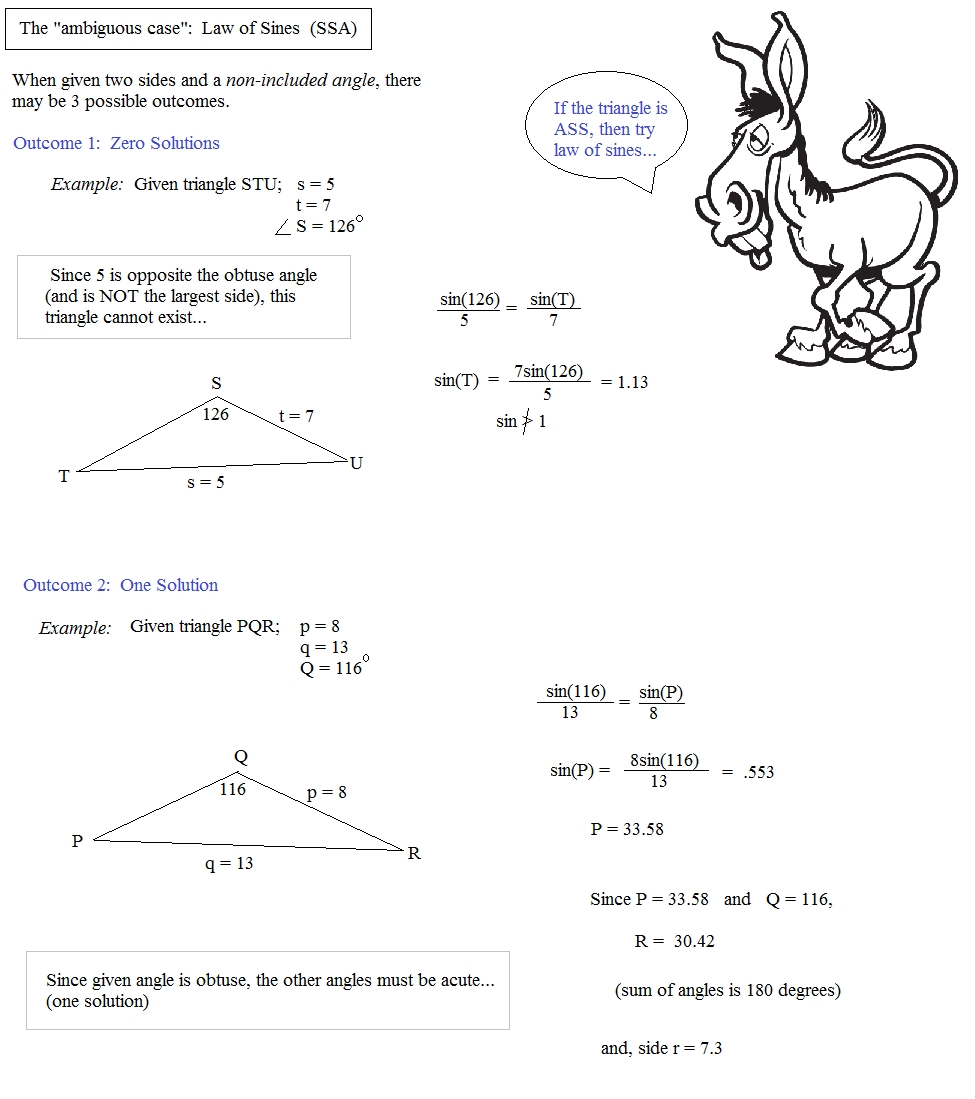
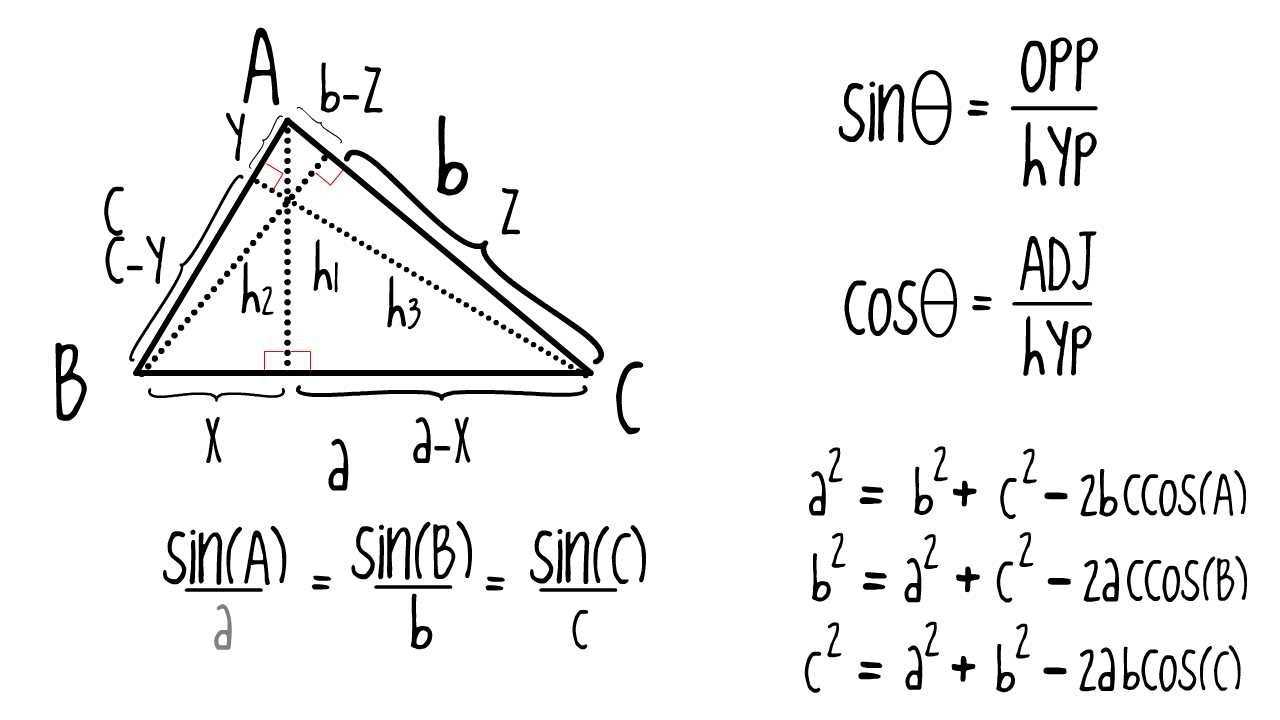
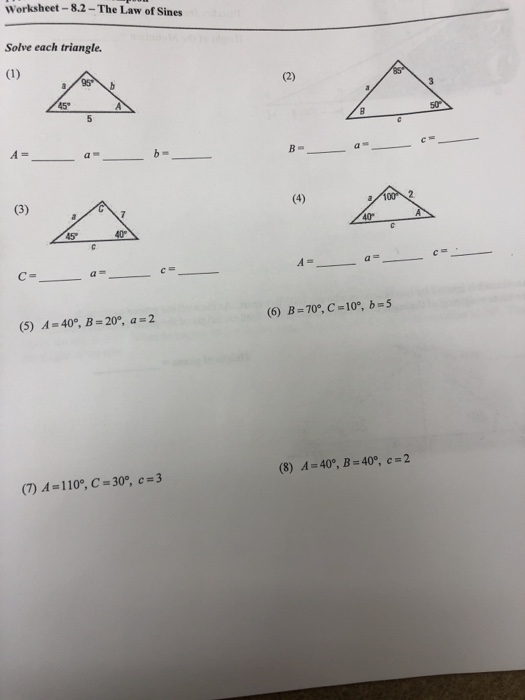
Exploring the Basics of the Law of Sines: A Step-by-Step Worksheet with Answers
The Law of Sines is an important tool for solving triangles. It is a fundamental theorem of trigonometry that helps us to calculate the unknown sides and angles of a triangle when the other measurements are known. This worksheet will provide an introduction to the Law of Sines and will guide you step-by-step through the calculation process.
Step 1: Understand the Basics
The Law of Sines states that:
[toc]
The ratio of the length of a side of a triangle to its opposite angle is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the other two sides to their respective opposite angles.
In other words, the ratio of any side of a triangle to the sine of its opposite angle is equal to the ratios of the other two sides to their respective opposite angles.
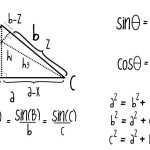
Step 2: Draw a Triangle
To better understand this theorem, let’s draw a triangle and label the angles and sides.
Step 3: Label the Angles and Sides
Now let’s label the angles and sides of the triangle. We will label the angles A, B, and C, and the sides a, b, and c.
Step 4: Calculate the Sines of the Angles
The next step is to calculate the sine of each angle. To do this, use a calculator or look up the values in a trigonometric table.
The sines of the angles are:
Sine A = 0.5
Sine B = 0.866
Sine C = 0.707
Step 5: Substitute Values into the Law of Sines
Now let’s substitute the values for the angles and sides into the Law of Sines.
a/sin A = b/sin B = c/sin C
0.5/sin A = b/0.866 = c/0.707
Step 6: Solve for the Unknown Side
We can now solve for the unknown side. To do this, we will multiply both sides of the equation by the sine of the corresponding angle.
0.5*sin A = b*0.866 = c*0.707
This gives us the equation:
b = 0.5*sin A/0.866 = c*0.707/0.866
We can now use this equation to calculate the length of the unknown side.
b = 0.5*0.5/0.866 = 0.287
c = 0.5*0.707/0.866 = 0.414
Step 7: Check Your Answer
Finally, let’s check our answer. To do this, we can use the Law of Sines again.
a/sin A = b/sin B = c/sin C
0.5/sin A = 0.287/0.866 = 0.414/0.707
This confirms that our answer is correct.
Conclusion
The Law of Sines is an important theorem that can be used to calculate the unknown sides and angles of a triangle when the other measurements are known. This worksheet has provided a step-by-step guide to help you understand and apply the Law of Sines.
Unraveling the Mysteries of the Law of Sines: Working Through the Challenging Problems with Answers
The Law of Sines is an invaluable tool for solving triangles, and it can be used to solve a variety of challenging problems. But, understanding the Law of Sines can be a daunting task, as the problems can be complex and the solutions are often counter-intuitive. To help unravel the mysteries of the Law of Sines, it is important to understand the basics and to work through some challenging problems, with answers.
The Law of Sines states that in any triangle, the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is constant. This means that for any triangle, if two sides and the angle between them are known, then the remaining sides and angles can be calculated using the Law of Sines. To demonstrate, let’s consider a triangle with sides of length a, b, and c, and angles A, B, and C opposite the respective sides. The Law of Sines can then be expressed as:
a/sin A = b/sin B = c/sin C
Using this equation, we can solve for the remaining sides and angles of the triangle. For example, if we know the angles A and B, and the side a, then we can solve for the remaining sides and angles as follows:
b = a*(sin B/sin A)
c = a*(sin C/sin A)
C = arcsin(a*sin C/c)
B = arcsin(a*sin B/b)
Now that we understand the basics, let’s look at a challenging problem. Consider the following triangle:
a = 8, B = 45°, C = 105°
Using the Law of Sines, we can solve for the remaining sides and angles.
b = 8*(sin 45°/sin 105°)
c = 8*(sin 105°/sin 45°)
A = arcsin(8*sin 45°/b)
C = 105°
Therefore, the remaining sides and angles of the triangle can be calculated to be:
b = 6.92
c = 13.86
A = 29.5°
By carefully working through the Law of Sines, we can solve a variety of challenging problems. Although the problems can be complex and the solutions counter-intuitive, understanding the basics and working through examples can help to unravel the mysteries of the Law of Sines.
How to Use the Law of Sines to Solve Trigonometric Problems: A Comprehensive Worksheet with Answers
The Law of Sines is a powerful tool used to solve trigonometric problems. It states that in any triangle, the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is constant. This ratio is referred to as the sine ratio. The Law of Sines is useful for finding missing side lengths and angle measures in triangles. This worksheet will provide a comprehensive guide to using the Law of Sines to solve trigonometric problems.
To begin, it is important to understand the three different types of triangles: acute, right, and obtuse. An acute triangle is a triangle in which all three angles are less than 90 degrees. A right triangle is a triangle with one 90 degree angle and two acute angles. An obtuse triangle is a triangle with one angle greater than 90 degrees.
The Law of Sines can be used to solve for the missing sides or angles of a triangle when two sides and their opposite angles are known. The Law of Sines states that the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is equal to the ratio of the length of any other side to the sine of its opposite angle. This can be expressed as:
a/sin A = b/sin B = c/sin C
Where a, b, and c represent the lengths of the sides of the triangle and A, B, and C represent the angles opposite those sides.
To solve for a missing side or angle, use the following steps:
Step 1: Determine the type of triangle.
Step 2: Label the known sides and angles.
Step 3: Write an equation using the Law of Sines.
Step 4: Substitute the known values for the sides and angles into the equation.
Step 5: Solve the equation for the missing side or angle.
For example, consider the triangle shown in the figure below.
In this triangle, we are given the lengths of two sides and the angle opposite one of those sides. We want to find the length of the third side and the angle opposite it.
Step 1: This is an acute triangle because all three angles are less than 90 degrees.
Step 2: We label the known sides and angles as follows: a = 6, b = 7, and A = 30 degrees.
Step 3: We write the Law of Sines equation as follows:
6/sin 30 = b/sin B = c/sin C
Step 4: We substitute the known values for a, A, and b into the equation. This gives us:
6/sin 30 = 7/sin B = c/sin C
Step 5: We solve for b and c. This can be done by cross-multiplying and then dividing. This gives us:
sin B = (7/6)sin 30
B = arcsin((7/6)sin 30)
c = (7/sin B)sin C
C = arccos(7/(6/sin 30))
Therefore, the length of the third side is c = 7.35 and the angle opposite it is C = 75.26 degrees.
This worksheet has provided
Unpacking the Law of Sines: Breakdown of the Formula and How to Use it with Answers
The Law of Sines, also known as the Sine Rule, is a powerful mathematical tool used to solve for unknown sides and angles in a triangle. This formula is particularly useful when dealing with triangles that are not right-angled, as the length of their sides and angles can be calculated even when only two sides and one angle are known.
The Law of Sines is expressed mathematically as follows:
a/sin (A) = b/sin (B) = c/sin (C)
Where a, b, and c represent the lengths of the triangle’s sides, and A, B, and C represent the angles opposite those sides.
In order to use the Law of Sines, one must first identify the two known values for the triangle. This can be either two sides and one angle, or two angles and one side. Once these values are identified, they can be plugged into the formula.
For example, if we have a triangle with side a = 6, side b = 8, and angle A = 30°, we can plug these values into the formula as follows:
6/sin (30°) = 8/sin (B)
We can then isolate the unknown angle B by multiplying both sides of the equation by sin (30°):
6 = 8/sin (B) * sin (30°)
We can then simplify the equation to:
6 = 8 * (1/2)
Which can be further simplified to:
B = arcsin (1/4)
Therefore, we can conclude that angle B in our example triangle is equal to 45°.
Using the Law of Sines, it is possible to solve for unknown sides and angles in any triangle, as long as two values are known. It is a valuable tool for mathematicians and problem solvers alike and can be used to calculate the dimensions of any triangle.
Conclusion
The Law of Sines Worksheet Answers is a great resource for students to use to help them understand the Law of Sines and its applications. It provides step-by-step explanations of how to solve the Law of Sines problems, as well as providing detailed explanations of the principles behind the law. With the help of this worksheet, students can gain a better understanding of the Law of Sines and its applications in geometry and trigonometry.
[addtoany]