Exploring the Law of Sines: A Step-by-Step Guide
The Law of Sines is an important equation used to solve triangles when some side lengths and angles are known. It is useful in many areas, including architecture, physics, and navigation. In this guide, we will explore the Law of Sines and refer to a few examples to illustrate how it works.
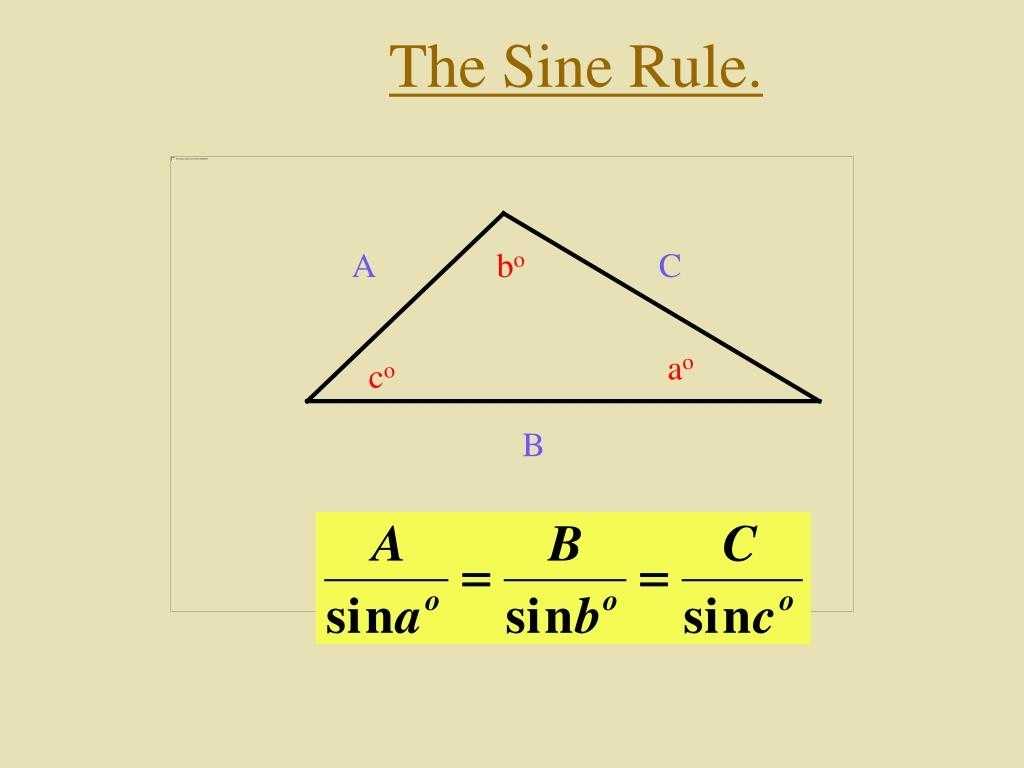
First, let’s review the equation itself. The Law of Sines states that the ratio of the length of any side of a triangle to the sine of its opposite angle is always the same. This can be written as:
a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC
[toc]
where a, b, and c are the sides of the triangle and A, B, and C are the angles opposite to them.
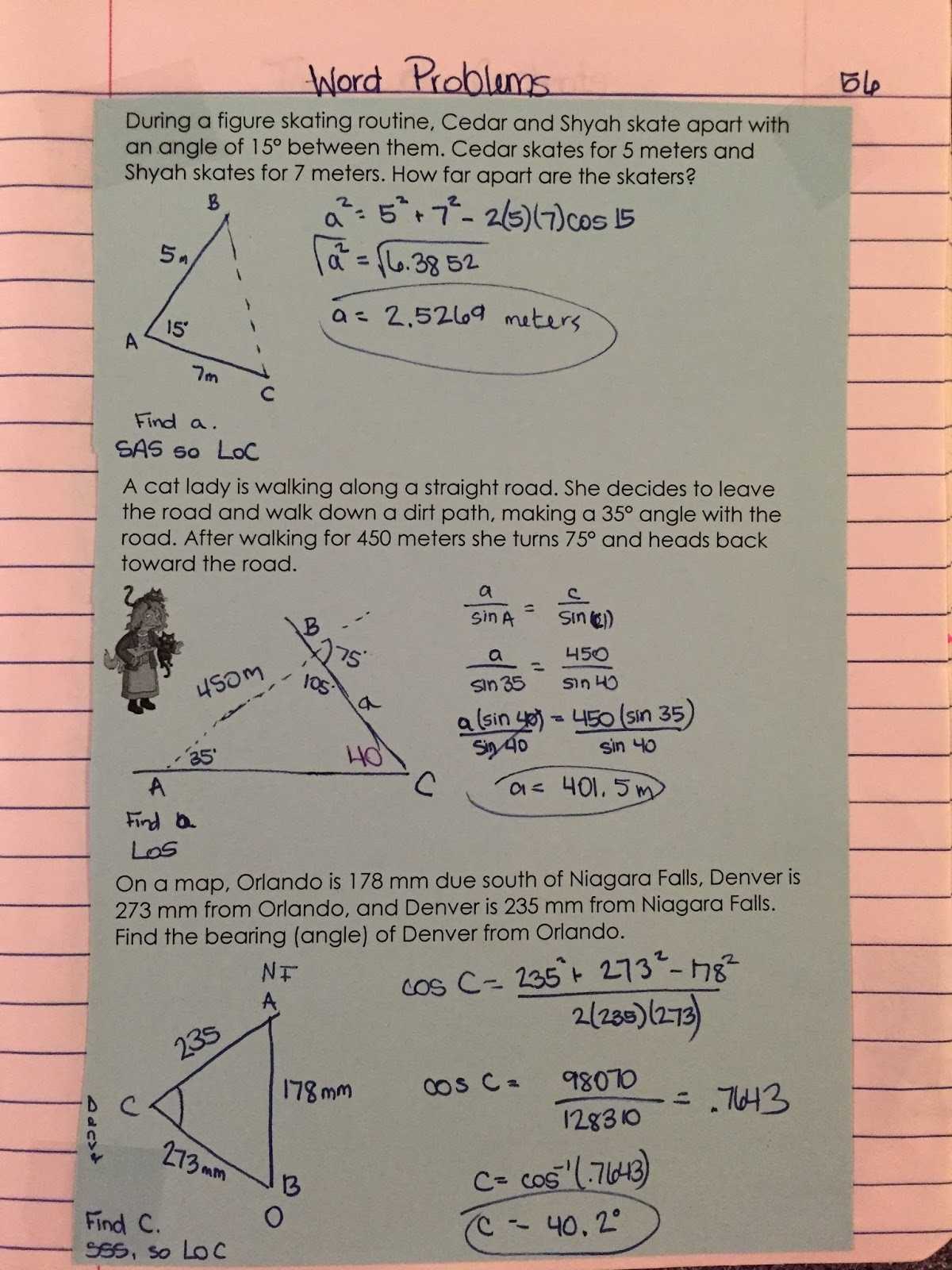
Now let’s look at a few examples. Suppose we want to find the length of side c in the triangle shown in the diagram below. We know the lengths of a and b and the angle C. To use the Law of Sines, we need to calculate the sines of angles A and B.
Using a calculator, we find that sinA = 0.8 and sinB = 0.6. Plugging these values into the Law of Sines equation, we get:
a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC
7/0.8 = 8/0.6 = c/0.45
c = 6.75
So the length of side c is 6.75.
The Law of Sines is a powerful tool for calculating the unknowns in a triangle when some of the sides and angles are known. With practice, you will become adept at using this equation to solve a variety of triangle-related problems.
How to Use the Law of Sines to Solve for Unknown Sides and Angles
The Law of Sines is a useful tool for calculating unknown sides and angles of a triangle when the measure of two sides and the included angle are known. It states that the ratio of the sine of any two angles to their opposite sides is equal. This law can be used to solve for any unknown sides or angles of a triangle, given that two angles and the length of one side are known.
To use the Law of Sines to solve for an unknown side or angle, first calculate the sine of each angle in the triangle. Then, divide the length of the known side by the sine of its opposite angle. This will give you the ratio of the sides to their opposite angles. This ratio can then be used to solve for any unknown sides or angles in the triangle. To solve for an unknown angle, take the inverse sine of the ratio and multiply it by the sine of the angle adjacent to the unknown angle. To solve for an unknown side, take the inverse sine of the ratio and multiply it by the sine of the angle opposite to the unknown side.
By using the Law of Sines, unknown sides and angles of a triangle can be calculated, given that two angles and the length of one side are known. This law is a powerful tool for solving a variety of triangle problems.
A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Law of Sines
The Law of Sines is a fundamental mathematical concept used to solve a variety of problems related to triangles. It states that in any triangle, the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is always the same. The Law of Sines is used extensively in trigonometry, navigation, surveying, and engineering.
At its most basic level, the Law of Sines states that for any triangle, the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is equal. This ratio is known as the sine ratio. If the lengths of two sides and the measure of the included angle are known, the sine ratio can be used to calculate the length of the third side. Conversely, if the lengths of two sides and the measure of the third angle are known, the sine ratio can be used to calculate the measure of the included angle.
The Law of Sines can be applied to oblique triangles, which are triangles that do not have a right angle. In an oblique triangle, the sine ratio can be used to find the measure of all three angles, as well as the length of all three sides.
The Law of Sines is also useful for solving triangles with one side and two angles. In this case, the sine ratio can be used to find the length of the unknown side, as well as the measures of the two angles.
In addition to its use in solving triangles, the Law of Sines is also useful for solving problems related to spherical triangles. Spherical triangles are triangles formed by three great circles on the surface of a sphere. The Law of Sines can be used to calculate the length of the sides and the measure of the angles of a spherical triangle.
The Law of Sines is an invaluable tool for solving a variety of problems related to trigonometry, navigation, surveying, and engineering. By understanding the concept and its applications, students and professionals alike can gain a better understanding of how to use the Law of Sines to their advantage.
Analyzing the Law of Sines: A Step-by-Step Worksheet
The law of sines is an important mathematical theorem used to solve triangles. This worksheet will outline a step-by-step process for using the law of sines to solve any triangle.
Step 1: Identify the given information.
The first step in solving a triangle using the law of sines is to identify the given information. Commonly, this information will include at least two angles and one side length. In some cases, the angles and side lengths may be labeled with either letters or numbers.
Step 2: Determine the missing angle.
Once the given information is identified, the missing angle can be determined by subtracting the known angles from 180 degrees.
Step 3: Calculate the sides.
Next, use the law of sines to calculate the unknown side lengths. The law of sines states that the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is constant for all sides in the triangle.
Step 4: Solve for the missing angle.
Once the side lengths are determined, the missing angle can be solved using the law of sines. To do this, take the ratio of the length of the side to the sine of the angle and solve for the angle.
Step 5: Check your work.
Finally, check your work to ensure that the triangle is valid. Use the law of sines to ensure that the ratios of all sides to their respective angles are equal. If they are not, there is an error in your calculations.
By following these steps, you can use the law of sines to solve any triangle.
Law of Sines: An In-Depth Look at the Formulas
The Law of Sines is a fundamental mathematical principle that is used to solve a variety of triangular problems. It states that, for any triangle, the ratio of the side lengths to the sines of their opposite angles is constant. This law can be used to calculate the lengths of the sides when two angles and one side are known, or to calculate the angles when two sides and one angle are known.
The Law of Sines is written mathematically as follows:
For any triangle, A, B and C represent the angles and a, b, and c represent the side lengths.
a/sin A = b/sin B = c/sin C
This formula can be rearranged to solve for any of the unknowns.
To calculate the length of a side when two angles and one side are known:
a = b*sin A/sin B
To calculate the angle when two sides and one angle are known:
A = arcsin (a*sin B/b)
The Law of Sines can be used to solve for any of the three angles and three sides of any triangle. It can be used to solve for the unknown side or angle in a right triangle as well as an oblique triangle.
The Law of Sines is a versatile tool that can be used in many different applications. It can be used to solve problems in trigonometry, navigation, surveying, engineering, and even astrophysics. With the Law of Sines, mathematicians and scientists can solve problems that have been impossible to solve without it.
Unlocking the Power of the Law of Sines: A Worksheet-Based Approach
The Law of Sines is a powerful tool for solving various types of problems in mathematics. It is a fundamental tool that can be used to solve triangles, find distances between points, and much more. This worksheet-based approach seeks to provide students with an interactive and enjoyable way to learn the basics of the Law of Sines.
This worksheet-based approach begins by introducing the basics of the Law of Sines, such as the formula, the types of triangles it applies to, and how to use it to solve for a missing side or angle. It then provides students with a series of practice problems to complete, allowing them to test their understanding of the material. As students work through the worksheet, they are given step-by-step instructions on how to use the Law of Sines to solve for the missing side or angle.
This worksheet-based approach also emphasizes the importance of understanding the underlying principles of the Law of Sines. By providing diagrams and explanations of the concepts, students are able to gain a deeper understanding of the material and develop a more rigorous problem-solving approach.
The worksheet is designed to be both engaging and challenging. It encourages students to explore the material in a systematic way, while providing ample opportunity for self-assessment and reflection. After completing the worksheet, students will have a strong foundation in the Law of Sines and be better equipped to tackle more complex problems.
Overall, this worksheet-based approach seeks to provide students with an interactive and enjoyable way to unlock the power of the Law of Sines. By providing a series of practice problems and step-by-step instructions, students will gain a deeper understanding of the material and be better prepared to tackle more complex problems. With this approach, students can unlock the power of the Law of Sines and use it to solve various types of problems in mathematics.
The Law of Sines: Exploring the Relationship Between Sides and Angles
The Law of Sines is an important mathematical relationship between the sides and angles of a triangle. This law states that the ratio of the length of a side of a triangle to the sine of its opposite angle is equal for all three sides and angles. As such, given the lengths of two sides and the measure of the angle between them, the length of the third side as well as the measure of the other two angles can be calculated.
The Law of Sines is a useful tool for solving a variety of problems, such as finding the area of a triangle or determining the size of a triangle given the size of two of its angles and one of its sides. Additionally, the law can be used to calculate the bearing of a point relative to a given point in a navigational problem.
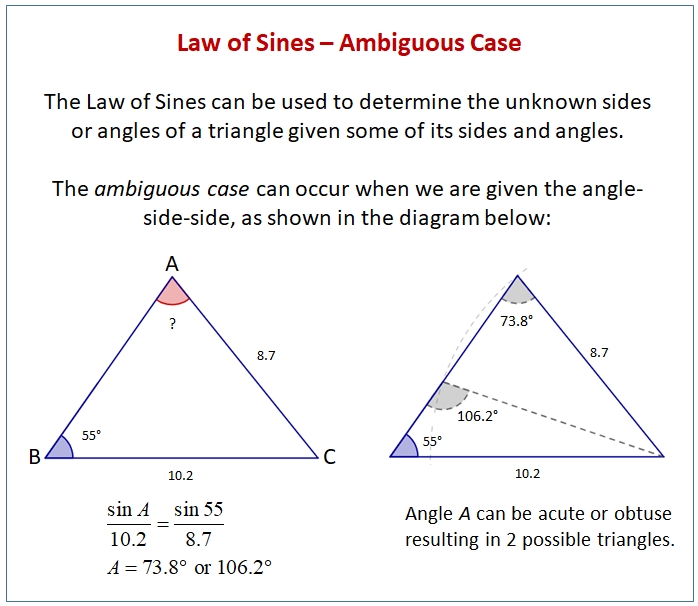
When working with the Law of Sines, it is important to remember that in order to use the law, all three angles of the triangle must be known, or two angles and one side. For example, if the length of two sides and the angle between them are given, the length of the third side and the measure of the other two angles can be calculated. However, if only two sides and one angle are known, the law cannot be used and another method must be employed.
Overall, the Law of Sines is a powerful mathematical relationship between the sides and angles of a triangle that can be used to solve for the unknowns in a variety of problems. Being familiar with the law and its limitations is essential for successfully working with triangles.
A Comprehensive Overview of the Law of Sines and How to Use It
The Law of Sines is an important mathematical concept commonly found in trigonometry and geometry. It states that for any triangle, the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is constant. This law can be used to calculate the lengths of the sides and angles of a triangle when given certain information, such as the lengths of two sides and the measure of the included angle.
To use the Law of Sines, one first needs to find the measure of the included angle between the two known sides. This measure can be found using the Law of Cosines, which states that for any triangle, the measure of the angle between two sides can be found using the following equation: c^2 = a^2 + b^2 – 2abcos(C). Once the measure of the included angle is known, the ratio of the length of one side to the sine of the opposite angle can be used to calculate the lengths of the other two sides.
For example, if the lengths of two sides of a triangle are known, along with the measure of the included angle, the Law of Sines can be used to calculate the length of the third side. The equation for the Law of Sines is a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC, where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides and A, B, and C are the measures of the angles opposite them. By plugging in the known values and solving for the unknown side, the length of the third side can be found.
The Law of Sines can also be used to calculate the measures of the angles of a triangle when given the lengths of its sides. The equation for this is sinA/a = sinB/b = sinC/c, where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides and A, B, and C are the measures of the angles opposite them. By plugging in the known values and solving for the unknown angles, the measures of the angles can be found.
The Law of Sines is an essential tool for solving triangles and can be used to calculate the lengths of sides and measures of angles when given certain information. It is important to remember that the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is constant for any triangle, regardless of its size.
Making Sense of the Law of Sines: A Step-by-Step Worksheet
The Law of Sines is a mathematical tool used to find the unknown sides or angles of a triangle when given two angles and one side. It is a useful tool for solving a variety of problems in trigonometry, geometry, and other mathematical applications. But understanding the Law of Sines can be challenging. This worksheet is designed to help you better understand this important law and how to use it to solve problems.
Step 1: Understand the Law of Sines
The Law of Sines states that in any triangle, the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is equal to the ratio of the length of any other side to the sine of its opposite angle. This can be written mathematically as: a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC.
Step 2: Identify What Is Given
When using the Law of Sines, it is important to identify what is given in the problem. Typically, you will be given two sides and the measure of their included angle. However, you may sometimes be given two angles and one side or three sides. Make sure to identify the given information in the problem before attempting to solve it.
Step 3: Set Up the Equation
Once you have identified the given information, you can set up the equation. For example, if you are given two sides and their included angle, you can set up the equation as follows: a/sinA = b/sinB, where a and b are the lengths of the given sides and A and B are the measures of the included angles.
Step 4: Solve for the Unknown
Once you have set up the equation, you can solve for the unknown side or angle. You can do this by isolating the unknown variable on one side of the equation. For example, if you are trying to find the length of the unknown side c, you can rearrange the equation to solve for c. The resulting equation would be c = a/sinA x sinB.
Step 5: Check Your Answer
Once you have solved for the unknown variable, it is important to check your answer. To do this, plug your answer into the original equation and make sure it is equal to the other side of the equation. For example, if you have solved for c, you should check that c = a/sinA x sinB is equal to b/sinB. If it is not equal, then you have made a mistake somewhere and will need to go back and check your work.
By following these steps, you should be able to understand and use the Law of Sines to solve a variety of problems. With practice and patience, you will be able to easily master this important law.
How to Use the Law of Sines to Determine Unknown Sides and Angles
The Law of Sines is an important equation in trigonometry that can be used to determine unknown sides and angles of a triangle. It states that for any triangle, the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is constant. In other words, the sine of any angle in the triangle is equal to the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse.
To use this equation, the sides and angles of the triangle must be known. The unknown sides and angles can be determined by using the ratios of the known sides and angles. The Law of Sines can be written as a three-part equation: A/sin A = B/sin B = C/sin C, where A, B, and C represent the sides and angles of the triangle.
To solve for an unknown side or angle, the equation can be rearranged and the sine of the known angle can be replaced with the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse. The equation can then be solved to determine the unknown side or angle.
For example, if two sides and one angle of a triangle are known, the Law of Sines can be used to determine the length of the third side. By rearranging the equation, the length of the third side can be determined by multiplying the sine of the known angle by the ratio of the other two sides.
The Law of Sines can also be used to determine the missing angle in a triangle. By rearranging the equation, the angle can be determined by finding the inverse sine of the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse.
In summary, the Law of Sines is a useful equation for determining unknown sides and angles of a triangle. By rearranging the equation and replacing the sine of the known angle with the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, the length of an unknown side or the measure of an unknown angle can be determined.
Conclusion
The Law of Sines worksheet is a great tool to help students understand and apply the Law of Sines to various problems. By completing this worksheet, students will gain a solid understanding of the Law of Sines, as well as how to use it to find the missing side lengths and angles of a triangle. This is a valuable skill that students can use to solve more complicated problems in mathematics.
[addtoany]