Exploring the Basics of Ions and Isotopes: A Worksheet for High School Chemistry Students
Introduction
Ions and isotopes are two important concepts in chemistry. They have a variety of applications from understanding atomic structure, to the behavior of elements in chemical reactions, to the study of the structure of molecules. In this worksheet, we will explore the basics of ions and isotopes and discuss their properties and applications.
What Are Ions?
[toc]
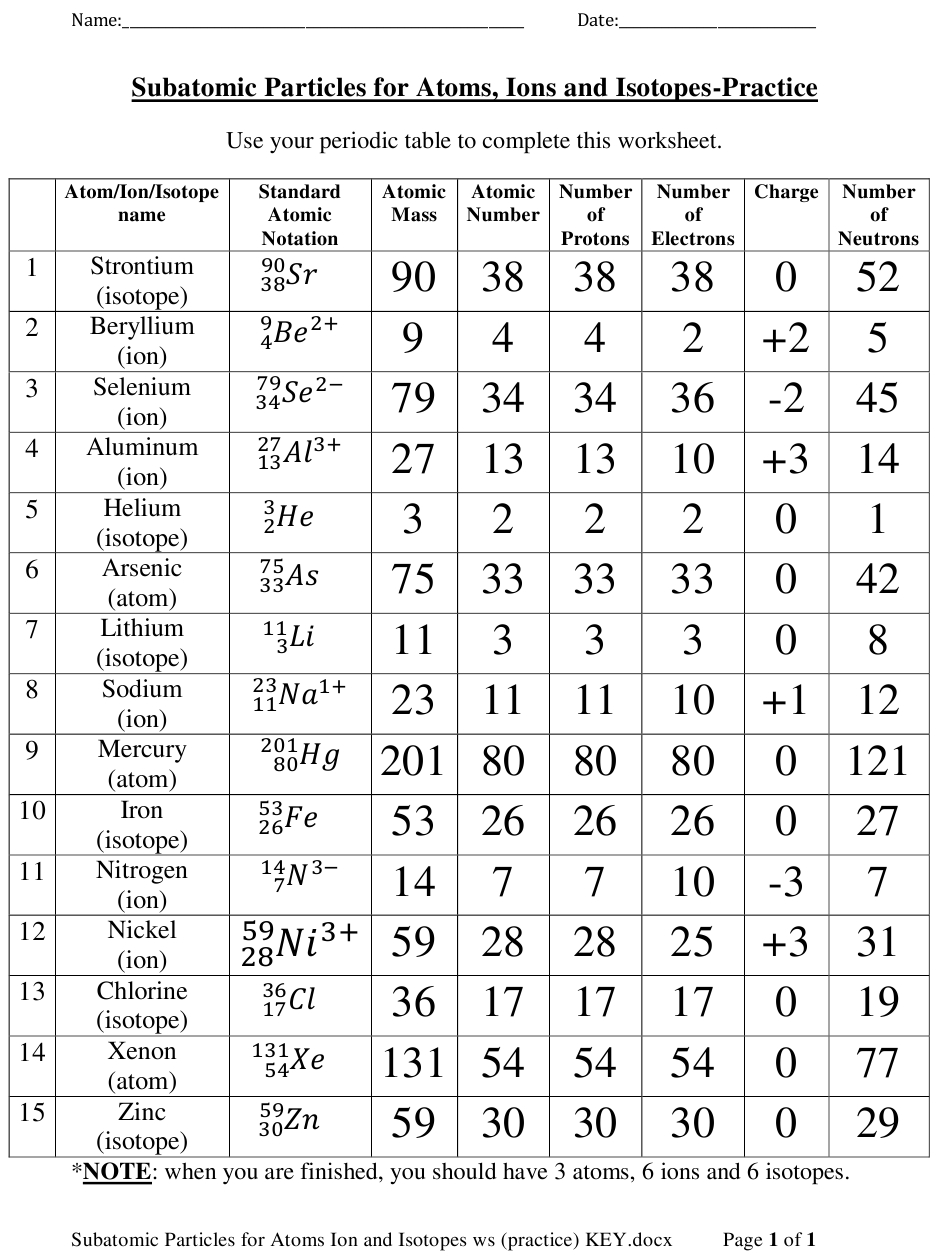
An ion is an atom or molecule that has acquired an electric charge due to the loss or gain of electrons. This charge can be either positive or negative. Positively charged ions are called cations, while negatively charged ions are called anions. Cations are formed when an atom loses electrons, while anions are formed when an atom gains electrons.
What Are Isotopes?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. This means that they have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes can be either stable or radioactive. Radioactive isotopes are unstable and decay over time, while stable isotopes are stable and do not decay.
Differences Between Ions and Isotopes
Ions and isotopes are both forms of atoms, but there are some important differences between them. Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, while isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ions have an electric charge, while isotopes do not. Ions can be formed through chemical reactions, while isotopes are formed naturally.
Applications of Ions and Isotopes
Ions and isotopes have a variety of applications in chemistry.
Ions can be used to help understand the behavior of atoms in chemical reactions. By studying the charges of the atoms involved, chemists can predict the products of the reactions and the stability of the compounds formed.
Isotopes can be used to study the structure of molecules. By comparing the masses of different isotopes of the same element, chemists can determine which atoms make up a molecule and how they are bonded together.
Isotopes can also be used to date objects. By measuring the amount of a particular radioactive isotope in an object, scientists can determine how old the object is.
Conclusion
Ions and isotopes are two important concepts in chemistry. Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, while isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ions and isotopes have a variety of applications in chemistry, from understanding atomic structure to dating objects. Through this worksheet, we have explored the basics of ions and isotopes and discussed their properties and applications.
Designing Experiments with Ions and Isotopes: A Worksheet for College Chemistry Students
This worksheet is designed to help college chemistry students become familiar with the design and implementation of experiments involving ions and isotopes. The worksheet will provide an overview of the different types of ions and isotopes, the processes used to measure their concentration, and the methods used to determine their behavior in different environments.
Types of Ions and Isotopes
Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net change in charge. Common ions include cations, which are positively-charged ions, and anions, which are negatively-charged ions. Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons. This results in a different mass, but the same chemical properties.
Measuring the Concentration of Ions and Isotopes
The concentration of ions and isotopes can be measured through a variety of techniques, such as flame photometry or inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Flame photometry can be used to measure the concentration of monoatomic ions, such as sodium, potassium, and lithium. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry is used to measure the concentrations of all types of ions and isotopes.
Determining the Behavior of Ions and Isotopes
The behavior of ions and isotopes can be studied through a variety of methods, such as adsorption, desorption, and diffusion. Adsorption is the process by which ions and isotopes are attracted to a solid surface and held in place. Desorption is the opposite process, in which ions and isotopes are released from the surface. Diffusion is the process by which ions and isotopes move through a material due to differences in concentration.
Conclusion
This worksheet has provided an overview of the different types of ions and isotopes, the processes used to measure their concentration, and the methods used to determine their behavior in different environments. By becoming familiar with the design and implementation of experiments involving ions and isotopes, college chemistry students will be better equipped to understand and analyze chemical reactions.
Understanding the Nuclear Structure of Isotopes: A Worksheet for Advanced Chemistry Students
This worksheet is designed to help advanced chemistry students gain a better understanding of the nuclear structure of isotopes. Through the completion of this worksheet, students will be able to explore the differences between isotopes and compare the properties of various elements.
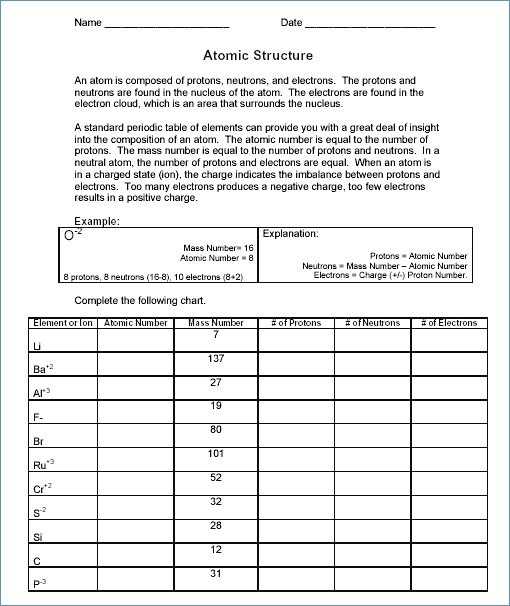
Atoms are composed of three main components: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are positively charged particles, while neutrons are neutrally charged particles. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, while the number of neutrons determines the mass of the atom. Isotopes are atoms that contain the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This means that isotopes of the same element have the same atomic number but different atomic masses.
The mass of an atom is measured in atomic mass units (amu). The amu is based on the mass of a single proton. Since isotopes have different numbers of neutrons, they have different atomic masses. This can be seen in the following chart:
Isotope | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass (amu)
Hydrogen-1 | 1 | 1.0078
Hydrogen-2 | 1 | 2.0141
Carbon-12 | 6 | 12.0000
Carbon-13 | 6 | 13.0034
Carbon-14 | 6 | 14.0031
As you can see, isotopes of the same element can have different atomic masses. This difference in mass causes isotopes to behave differently and can be used to study the properties of an element.
To complete this worksheet, students should be able to do the following:
1. Identify the components that make up an atom: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
2. Explain what an isotope is and how it is different from other atoms of the same element.
3. Calculate the atomic mass of various isotopes.
4. Describe how isotopes can be used to study the properties of an element.
By completing this worksheet, students will gain a better understanding of the nuclear structure of isotopes, allowing them to explore the differences between isotopes and compare the properties of various elements.
Conclusion
This worksheet has provided a useful overview of ions and isotopes and their various properties. It has highlighted the differences between the two types of particles, and has also explained how they can interact with each other. This knowledge can be applied to many scientific disciplines, such as chemistry and physics, making it a valuable resource for students and researchers.
[addtoany]