Exploring the Relationship between Genotypes and Phenotypes: A Worksheet for Students
The relationship between genotypes and phenotypes is a fascinating and complex one that has captivated scientists for centuries. This worksheet is designed to help students explore the connection between the two. By working through the questions below, students will gain a better understanding of how genotypes and phenotypes interact to form the characteristics of an organism.
1. What is a genotype?
A genotype is a set of genes that an individual organism possesses. It is the genetic makeup of the organism that determines its traits and characteristics.
[toc]
2. What is a phenotype?
A phenotype is the physical expression of an organism’s genotype. It is the observable traits and characteristics of an organism, such as its physical appearance, behavior, and other observable characteristics.
3. How do genotypes and phenotypes interact?
Genotypes and phenotypes interact in a variety of ways. Genes act as instructions that tell the cells in an organism how to create proteins and other molecules, which in turn affect the physical characteristics of the organism. Additionally, environmental factors can influence the expression of the genotype, resulting in different phenotypes.
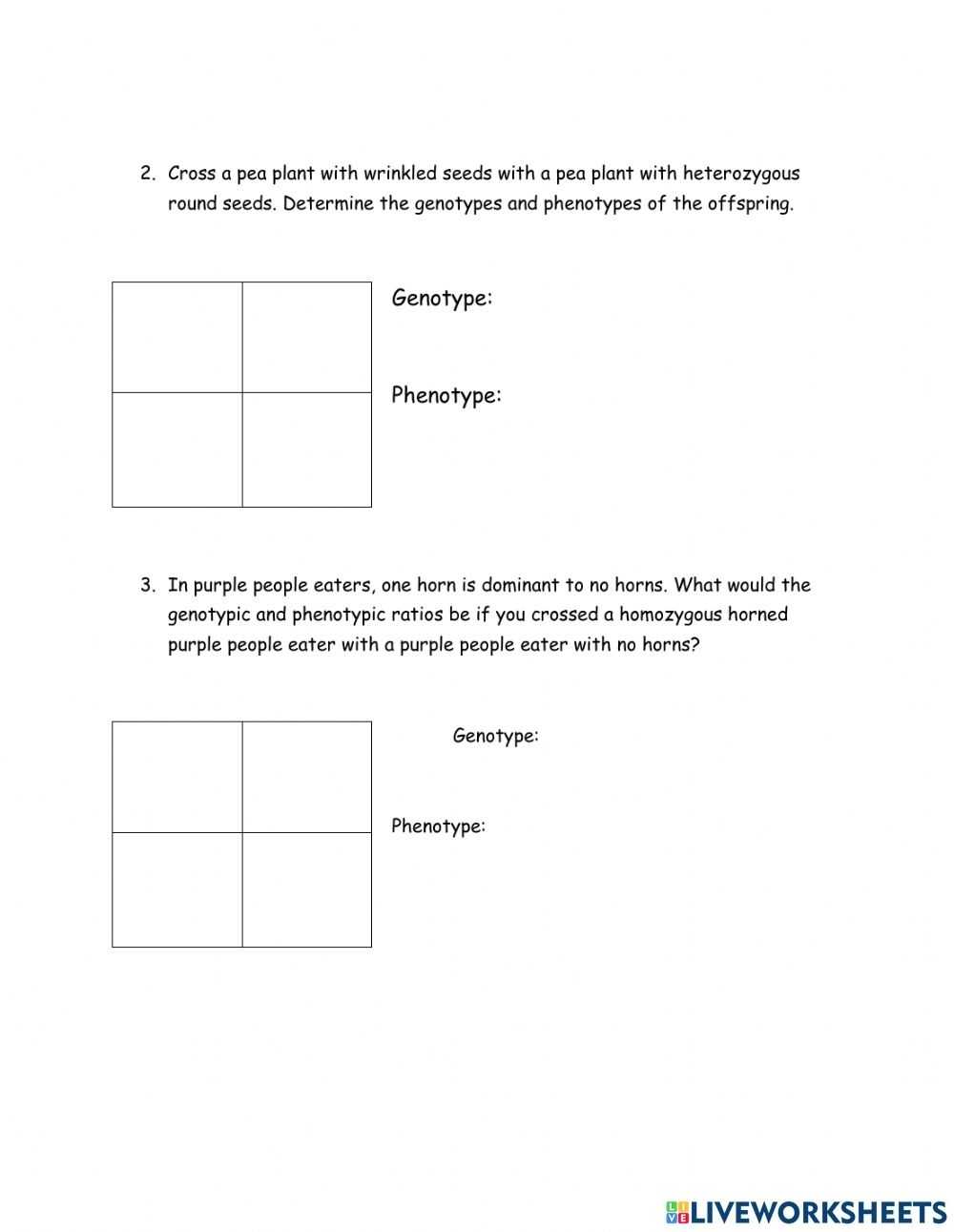
4. What are some examples of genotypes and phenotypes?
Examples of genotypes include genes that determine eye color, hair color, height, and other physical characteristics. Examples of phenotypes include the physical appearance of an individual, such as eye color, hair color, and height.
5. How can understanding the relationship between genotypes and phenotypes help us?
Understanding the relationship between genotypes and phenotypes can help us better understand the genetic basis of disease, as well as the effects of environmental factors on an individual’s physical and behavioral traits. Additionally, it can help us better understand how to breed and select for desirable traits in different species.
How Gene Expression Affects Phenotypes: A Worksheet for Exploring the Science of Genetics
Gene expression is a fundamental process in the field of genetics that determines the characteristics and traits of an organism. It is the process by which the genetic information contained in a gene is converted into a functional product, usually a protein, which then influences and dictates the phenotype of an organism. In this worksheet, we will explore how gene expression affects phenotypes and how it can be manipulated in order to understand the science of genetics.
The first step in understanding gene expression is to understand the genetic code, which is made up of four bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Each base is paired with its complementary base, creating a double-helix structure that stores genetic information. This information is then transcribed from DNA into mRNA and then translated into proteins, which are responsible for producing the phenotypic traits of an organism.
The second step in understanding gene expression is to understand the role of transcription factors. These molecules bind to specific regions of DNA and regulate the expression of certain genes, thus controlling the production of certain proteins. Thus, the expression of certain genes can be altered by manipulating the concentration of these transcription factors, which can have an effect on the phenotype of an organism.
The third step in understanding gene expression is to understand the role of epigenetics. Epigenetics refers to the process by which environmental factors can alter gene expression without changing the actual genetic code. Examples of epigenetics include DNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNAs. These epigenetic changes can influence the expression of certain genes and thus affect the phenotype of an organism.
Finally, gene expression can also be manipulated through genetic engineering, which involves introducing foreign genes into an organism’s genome. This can be done in order to produce certain desired traits, such as a resistance to disease or increased tolerance to certain environmental conditions.
In conclusion, gene expression is a complex process that plays a vital role in determining the phenotype of an organism. Through the manipulation of transcription factors, epigenetics, and genetic engineering, scientists are able to study the science of genetics in order to better understand the process of gene expression and its effects on phenotypes.
Exploring the Complexity of Genotypes and Phenotypes: A Worksheet for Advanced Students
Introduction
The relationship between genotypes and phenotypes is a complex one, and understanding it can be difficult. In this worksheet, we will explore the complexity of genotypes and phenotypes, and how they interact to produce different traits in organisms. This worksheet is intended for advanced students and will cover topics such as the role of gene expression, DNA structure, and the effect of environmental factors on phenotype. By the end of this worksheet, students should understand the complexity of the relationship between genotypes and phenotypes and how they interact to produce the characteristics of an organism.
Part 1: What is a Genotype?
A genotype is an organism’s genetic makeup, which is determined by the combination of alleles it carries. Alleles are different versions of a gene, and each gene can have multiple alleles. For example, the gene for eye color in humans can have two alleles, brown and blue. An organism’s genotype is the combination of alleles it carries for each gene, and this determines its phenotype.
Part 2: What is a Phenotype?
A phenotype is an organism’s physical characteristics, which are determined by its genotype. For example, if an organism has two brown eye alleles, its phenotype will be brown eyes. However, not all phenotypes are determined by genotype. In some cases, environmental factors can influence an organism’s phenotype. For example, if an organism lives in a cold climate, its fur may be thicker than it would be if it lived in a warm climate.
Part 3: What is Gene Expression?
Gene expression is the process by which genetic information is translated into proteins. It is the way in which a gene’s instructions are used to create a particular phenotype. For example, a gene’s instructions may be to produce a protein that gives an organism blue eyes. However, if the gene is not expressed, then the organism may not have blue eyes, even if it has the gene.
Part 4: What is the Structure of DNA?
DNA is made up of four nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). These nucleotides form a double-stranded molecule known as a helix. The sequence of these nucleotides forms the genetic code, which is responsible for creating proteins and other molecules that are responsible for an organism’s phenotype.
Conclusion
This worksheet has explored the complexity of the relationship between genotypes and phenotypes, and how they interact to produce the characteristics of an organism. We have discussed the role of gene expression, DNA structure, and the effect of environmental factors on phenotype. By the end of this worksheet, students should understand the complexity of the relationship between genotypes and phenotypes and how they interact to produce the characteristics of an organism.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Genotypes And Phenotypes Worksheet Answers provide a great way to understand how genotypes and phenotypes work together. By understanding the structure and function of genetic traits, students can better understand the relationship between genotypes and phenotypes. Understanding this relationship is important for students to be able to make decisions about their own genetic makeup and those of their offspring.
[addtoany]