Exploring Enzyme Reactions: An Overview of the Basics Using a Worksheet Answer Key
Enzyme reactions are a fundamental part of biological processes and are responsible for a wide range of biochemical activities. They are proteins that catalyze the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones or the formation of new molecules from smaller ones. Understanding the basics of enzyme reactions is essential for those studying biochemistry, as well as for those in the medical and pharmaceutical fields.
This worksheet provides an overview of the basic principles of enzyme reactions, along with an answer key.
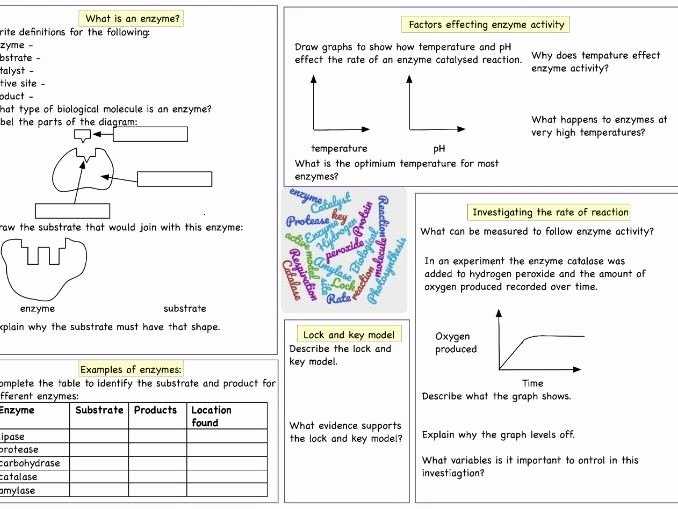
1. What is an enzyme?
An enzyme is a protein that catalyzes the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones or the formation of new molecules from smaller ones.
[toc]
2. What is the purpose of an enzyme?
The purpose of an enzyme is to speed up the rate at which chemical reactions occur. It does this by lowering the activation energy needed for a reaction to take place.
3. What is the active site of an enzyme?
The active site of an enzyme is the specific area of its structure that binds to the substrate and facilitates its conversion into a product.
4. What is the difference between a substrate and a product?
A substrate is a molecule that an enzyme acts upon and is converted into a product. A product is the molecule that is formed as a result of the enzyme’s activity.
5. What is an enzyme inhibitor?
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and prevents it from catalyzing a reaction. This can be done through competitive inhibition, in which a molecule competes with the substrate for binding to the active site, or through non-competitive inhibition, in which a molecule binds to a different site on the enzyme and changes its shape so that it cannot bind to the substrate.
Exploring the Kinetics of Enzyme Reactions: A Step-by-Step Guide with Worksheet Answer Keys
Introduction
Enzyme reactions are a critical component of biological processes and are essential for life to exist. They are responsible for an extensive range of reactions, from the digestion of food to the metabolism of energy. Understanding the kinetics of enzyme reactions is an important part of understanding how these reactions work and how they are regulated. With this in mind, this guide aims to provide a step-by-step understanding of the fundamentals of enzyme reaction kinetics, with worksheet answer keys to help guide your understanding.
Step 1: Understand the Basics of Enzyme Reactions
First, it is important to understand the basics of enzyme reactions. An enzyme is a protein that serves as a catalyst for a chemical reaction. Enzymes are specific to certain substrates, meaning that each enzyme will only work on particular substrates. The reaction rate of the enzyme depends on the concentration of substrate, the temperature, and the pH of the environment in which it is working.
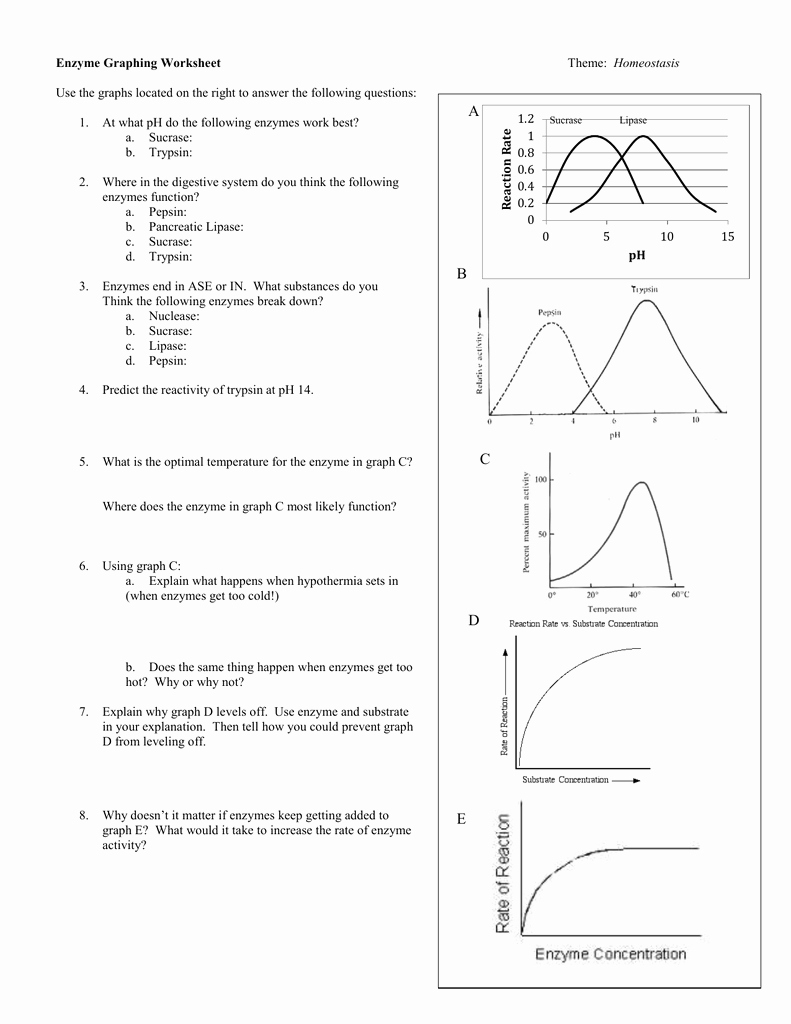
Step 2: Understand the Factors that Affect Enzyme Reaction Rates
The concentration of substrate is a major factor that affects the rate of an enzyme reaction. As the concentration of substrate increases, the rate of reaction increases as well. This is because the enzyme is able to bind more substrate molecules and increase the rate of the reaction. Temperature and pH also play a role in the rate of enzyme reaction. As the temperature increases, the rate of reaction increases as well. However, if the temperature gets too high, it can cause the enzyme to denature and the reaction rate will decrease. The same is true for pH; as the pH changes, the rate of reaction will also change.
Step 3: Understand the Different Types of Enzyme Reactions
Enzyme reactions can be divided into two main categories: reversible and irreversible. Reversible reactions are those in which the enzyme can bind and unbind the substrate multiple times, allowing for the reaction to be reversed. Irreversible reactions, on the other hand, are those in which the enzyme binds to the substrate once and the reaction can no longer be reversed.
Step 4: Calculate Enzyme Reaction Rates
Once you understand the basics of enzyme reactions, you can begin to calculate the reaction rate of an enzyme. This can be done by measuring the rate of substrate consumption and/or product formation over time. The reaction rate can be determined by dividing the change in substrate concentration over time by the total substrate concentration.
Conclusion
Enzyme reactions are a critical component of biological processes and understanding the kinetics of enzyme reactions is an important part of understanding how they work and how they are regulated. This guide provides a step-by-step understanding of the fundamentals of enzyme reaction kinetics, with worksheet answer keys to help guide your understanding. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you will be able to calculate the reaction rate of an enzyme and gain a better understanding of how these reactions work.
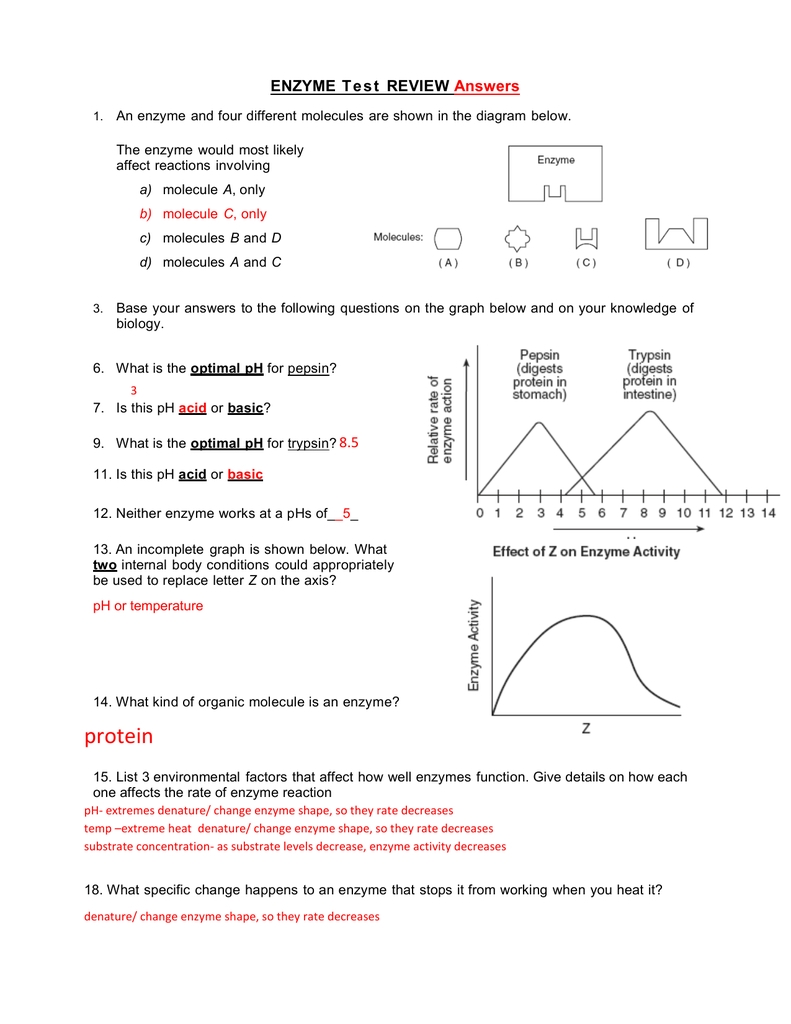
Analyzing the Effects of pH on Enzyme Reactions: A Worksheet Answer Key Guide
The effects of pH on enzyme reactions can be analyzed through a worksheet. To help guide you in exploring the effects of pH on enzyme reactions, this answer key provides an in-depth overview of the worksheet.
The first section of the worksheet requires you to define the pH scale. This scale is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It is measured on a scale from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, 0 being extremely acidic, and 14 being extremely alkaline.
The second section of the worksheet requires you to explain the effects of pH on enzyme reactions. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts for chemical reactions. The activity of enzymes is dependent on the pH of their environment. Generally speaking, enzymes work best at a pH that is close to their optimal pH. As such, when the pH is too low or too high, the enzyme activity decreases. This is because the enzyme’s structure is affected by the pH of its environment, and when the pH is too low or too high, the enzyme’s structure is disrupted, making it less effective at catalyzing the reaction.
The third section of the worksheet requires you to explain how enzymes can be used to measure pH. Enzymes can be used to measure pH by measuring the rate of reaction that they catalyze. The rate of reaction is directly related to the pH of the environment, and so by measuring the rate of reaction, the pH of the environment can be determined.
The fourth section of the worksheet requires you to explain how pH can be changed to optimize enzyme activity. One way to optimize enzyme activity is to adjust the pH of the environment in order to get the enzyme to its optimal pH. This can be done by adding an acid or base to the environment.
The fifth section of the worksheet requires you to explain the effects of temperature on enzyme reactions. Generally speaking, increasing the temperature of the environment will increase the rate of reaction of the enzyme. However, if the temperature is too high, the enzyme’s structure may be disrupted, making it less effective at catalyzing the reaction.
This answer key has provided an in-depth overview of the worksheet exploring the effects of pH on enzyme reactions. It has defined the pH scale, explained the effects of pH on enzyme reactions, discussed how enzymes can be used to measure pH, and explained how pH can be changed to optimize enzyme activity. Additionally, it has also discussed the effects of temperature on enzyme reactions. With this information, you should now have a better understanding of how pH affects enzyme reactions.
Conclusion
The Enzyme Reactions Worksheet Answers provides students with a comprehensive overview of enzyme reactions and the role they play in biochemical processes. Through this worksheet, students can gain a better understanding of how enzymes work and how to identify the different types of enzymes and their functions. This worksheet can also help students gain insight into how enzymes participate in various biochemical pathways, and how to recognize and utilize enzymes in laboratory experiments. With a better understanding of enzyme reactions, students can be better equipped to apply their knowledge to real-life scenarios.
[addtoany]