The Basics of Current, Voltage and Resistance: An Overview
Current, voltage, and resistance are three fundamental concepts in the field of electrical engineering. They are related to each other in that they are all measures of energy flow in an electrical system and, when combined, form Ohm’s Law.
Current is the measure of the amount of electric charge passing through a conductor or wire per unit of time. It is typically measured in amperes (A). Current is proportional to the voltage, or potential difference, between two points.
Voltage is a measure of the electrical potential energy between two points. It is typically measured in volts (V). Voltage is the force that causes electrons to move through a conductor.
[toc]
Resistance is the measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit. It is typically measured in ohms (Ω). Resistance is proportional to the length and cross-sectional area of a conductor as well as its material composition.
These three concepts are essential for understanding the behavior of electrical systems. Together, they form a basic law of electricity known as Ohm’s Law. This states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance.
When dealing with electrical circuits, it is important to consider the interactions between current, voltage, and resistance. Combining these three concepts results in a much better understanding of how electrical systems work.
How to Calculate the Current, Voltage and Resistance Using Worksheets
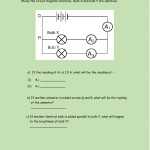
Calculating the current, voltage and resistance using worksheets is a simple process that requires only basic mathematics. To calculate the current, voltage and resistance of a given circuit, one must first identify the components of the circuit and their corresponding resistances. Once these components have been identified, the worksheet should be filled out with the values of the resistances and the equations for each component.
The current of the circuit can be calculated by dividing the voltage of the circuit by the total resistance. This can be calculated with the equation I=V/R. The voltage of the circuit can also be determined by multiplying the current of the circuit by the total resistance. This equation is V=I*R. The total resistance of the circuit can be determined by adding up all the individual resistances in the circuit.
Once all the components of the circuit have been identified and their corresponding resistances have been filled out, the worksheet can be used to calculate the current, voltage and total resistance of the circuit. To do this, the equations mentioned above should be used. The resulting values can then be written onto the worksheet and used to understand the circuit better.
Exploring Ohm’s Law and Its Applications to Current, Voltage and Resistance
Ohm’s law is one of the most fundamental laws of electrical engineering and is named after the German physicist Georg Ohm. It states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points. In other words, the voltage and the current are directly related. This law is expressed mathematically as V = IR, where V is the voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance.
This law can be used to calculate the amount of current in a circuit when the voltage and resistance are known. The formula can also be used to calculate the resistance of a circuit when the voltage and current are known. It is also useful in determining the voltage of a circuit when the current and resistance are known.
Ohm’s law is especially useful in calculating the power of a circuit. Power is the rate at which energy is transferred, and it is calculated by multiplying the voltage by the current. This means that if the voltage and current are known, the power of the circuit can be calculated.
Ohm’s law is also useful in understanding the behavior of various electrical components. For example, it can be used to calculate the voltage drop across a resistor in a circuit. It can also be used to determine the amount of current that will flow through a conductor of a given resistance.
Finally, Ohm’s law can be used to study the relationships between current, voltage, and resistance in electrical circuits. By using this law, the behavior of a circuit can be studied and analyzed, allowing engineers to design circuits that operate efficiently and safely.
Troubleshooting Common Issues Related to Current, Voltage and Resistance Worksheets
Current, voltage, and resistance are all related electrical concepts that are essential to understand in order to properly troubleshoot any issue related to electrical equipment. In order to properly diagnose any electrical issue, one must understand how these three concepts interact with one another.
When troubleshooting current, voltage, and resistance issues, it is important to begin by understanding the basics of each concept. Current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor, such as a wire. Voltage is the potential difference between two points, such as a battery terminal and the other end of a wire. Resistance is the opposition to current flow and can be caused by a number of factors, including the material of the conductor, the length of the conductor, and the temperature of the conductor.
Once the basics of current, voltage, and resistance have been understood, it is important to determine the cause of the issue. This can be done by using a current, voltage, and resistance worksheet. These worksheets provide diagrams and equations that allow the user to calculate the amount of current, voltage, and resistance that is present in a given circuit. By analyzing the diagram, the user can easily identify any abnormalities or issues that may be present.
Once the issue has been identified, it is important to use the worksheet to determine the corrective action that should be taken. Depending on the type of issue, this may include replacing faulty components, repairing any damaged wiring, or increasing the amount of current or voltage in the circuit.
Troubleshooting current, voltage, and resistance issues can be a complicated process. However, having a proper understanding of the basics of each concept and having an accurate current, voltage, and resistance worksheet can make the process much simpler. By understanding the basics and having an accurate worksheet, the user can quickly identify any issues and take the necessary steps to correct them.
Conclusion
The Current Voltage and Resistance Worksheet provides students with the opportunity to practice the principles of electricity in a hands-on way. By completing the worksheet, students gain a better understanding of the properties of electricity, including current, voltage, and resistance. With this knowledge, students can apply what they have learned to real-world situations, such as building circuits and troubleshooting electrical problems.
[addtoany]