Exploring the Inner Workings of Cell Transport with a Worksheet Biology Answer Key
Cell Transport Worksheet – Biology Answer Key
1. What is the role of the cell membrane in cell transport?
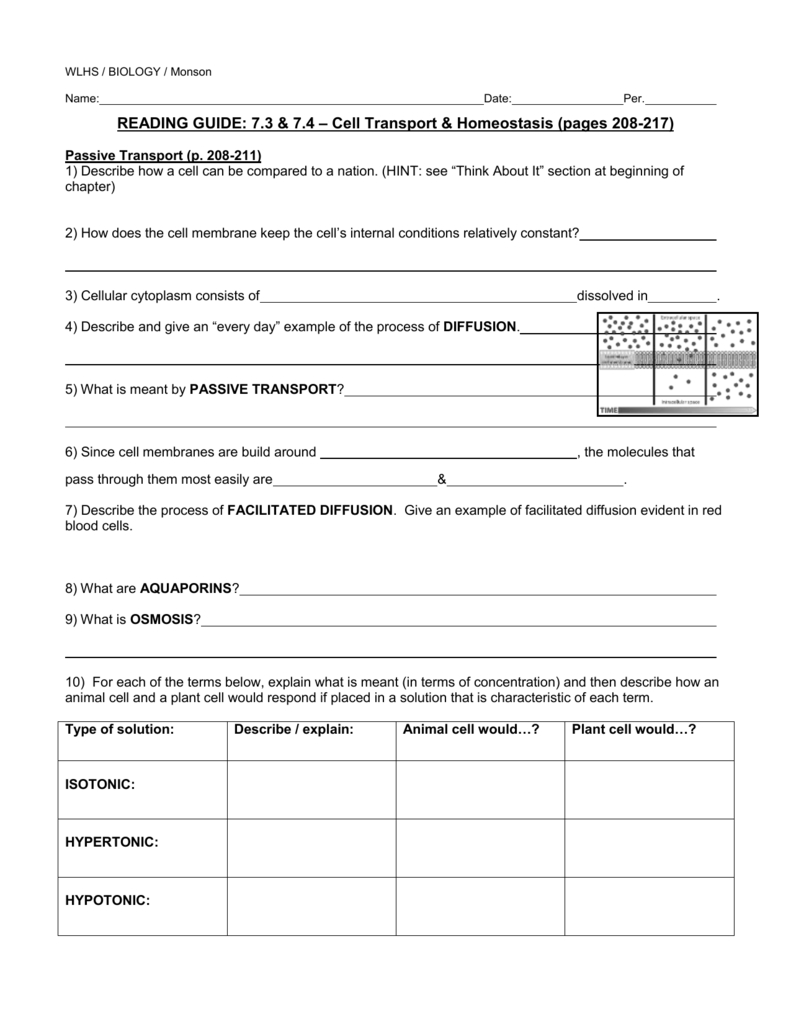
The cell membrane plays a crucial role in cell transport. It acts as a barrier that separates the inside of the cell from its environment, allowing molecules to enter and exit the cell. The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer, which is selectively permeable. This means that only certain molecules can move in and out of the cell, while others are unable to pass through. The cell membrane also contains proteins that act as channels, allowing specific molecules to move in and out of the cell.
[toc]
2. Describe active transport.
Active transport is a type of cell transport in which molecules move against their concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. This process requires energy, usually in the form of ATP, to overcome the concentration gradient and move the molecules across the cell membrane. Active transport is used to move important molecules, such as ions, glucose, and amino acids, into the cell.
3. Describe facilitated diffusion.
Facilitated diffusion is a type of cell transport in which molecules move down their concentration gradient, from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This process does not require energy, as the molecules are able to move freely through the cell membrane. However, facilitated diffusion does require the assistance of special proteins called channels and transporters. These proteins act as gateways, allowing molecules to enter and exit the cell.
4. How does osmosis work?
Osmosis is a type of cell transport in which water moves across the cell membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration. This process does not require energy, as the water molecules are able to move freely through the cell membrane. However, the movement of water molecules is affected by the presence of solutes, such as salts and sugars. If there is a higher concentration of solutes on one side of the cell membrane, then that side will become more concentrated and the water molecules will be drawn to the other side.
5. What is endocytosis?
Endocytosis is a type of cell transport in which large molecules, such as proteins and polysaccharides, are taken into the cell by the formation of small invaginations in the cell membrane. These invaginations then pinch off, forming small vesicles that contain the molecules taken in by the cell. Endocytosis can be divided into two categories: phagocytosis, in which cells engulf solid particles, and pinocytosis, in which cells take in fluid droplets.
Using a Worksheet Biology Answer Key to Uncover the Mysteries of Cell Transport
Cell transport is a complex process that is essential to the functioning of all living organisms. It involves the movement of molecules, ions, and other particles across the cell membrane in order to maintain homeostasis and enable the cell to carry out its necessary functions. To gain a better understanding of cell transport and its mechanisms, it is helpful to use a worksheet biology answer key.
A worksheet biology answer key can provide the necessary information to answer questions about cell transport. It typically contains diagrams, descriptions, and explanations of the various types of cell transport and how they work. The diagrams can help to visualize the movement of particles and the various types of transport that occur. Descriptions can provide an overview of the process, and explanations can provide a deeper understanding of the mechanisms at work.
The worksheet biology answer key can also be used to answer questions about the different factors that influence cell transport. These can include the types of molecules, ions, and other particles that can move across the cell membrane, the direction of transport, the rate of transport, and the energy required for transport. Knowing the answers to these questions can help to understand the importance of cell transport and how it affects the cell’s ability to function.
By using a worksheet biology answer key, the mysteries of cell transport can be uncovered. It can provide an overview of the process, help to visualize the movement of particles, and answer questions about the factors that influence cell transport. With this knowledge, it is possible to gain a better understanding of how cell transport works and its importance in the functioning of all living organisms.
Examining the Different Types of Cell Transport and Their Impact on Biology
Cell transport is the movement of molecules across a biological membrane. It is a fundamental process that is essential for the functioning of all living cells. Cell transport plays an important role in biology, as it allows for the exchange of necessary materials between a cell and its environment. There are many different types of cell transport, each of which has a distinct impact on biological processes.
One of the most common types of cell transport is passive transport. This type of transport does not require energy and does not involve the use of proteins. Instead, molecules and ions simply move across the membrane due to their concentration gradient, which is created by different concentrations of molecules on either side of the membrane. Passive transport is important for allowing cells to take up nutrients and other materials that they need to survive.
Another type of cell transport is active transport. This type of transport involves the use of proteins to move molecules against their concentration gradient. Active transport requires energy, typically in the form of ATP, and thus is more costly to the cell. However, it is also necessary for the uptake of certain molecules, such as glucose, that would otherwise not be able to move across the membrane.
A third type of cell transport is endocytosis. This is a process in which a cell engulfs a particle or molecule and transports it across the membrane. There are two types of endocytosis: phagocytosis and pinocytosis. In phagocytosis, a cell engulfs a large particle, such as a bacterium, and transports it across the membrane. In pinocytosis, small particles, such as ions and molecules, are transported across the membrane by the formation of small vesicles.
Finally, there is exocytosis, which is the reverse of endocytosis. In exocytosis, a particle or molecule is transported from inside a cell to outside through a vesicle. This is an important process for the removal of unwanted materials from the cell, such as waste products.
Cell transport plays an essential role in biology and is necessary for the survival of all living cells. Different types of cell transport have distinct impacts on biological processes, and it is important to understand how these processes work in order to better understand the functioning of cells.
Understanding the Role of Membranes in Cell Transport Through Worksheet Biology Answers
Membranes play a crucial role in cell transport. In order to understand this role more clearly, it is important to explore the various components of a membrane and the ways in which they facilitate movement of substances across the cell.
The membrane itself is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which is a double layer of lipid molecules that have a hydrophobic core and hydrophilic head and tail groups. This structure allows for the formation of a selectively permeable barrier that allows some substances to pass through while blocking others. These lipids are also arranged in proteins that help to regulate the movement of molecules across the membrane.
The first type of transport across a membrane is passive transport. This is a form of transport that does not involve energy consumption and relies on the concentration gradient of particles. For example, in a process called simple diffusion, particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. As the concentration gradient decreases, the rate of diffusion slows down.
The second type of transport is active transport. This type of transport requires energy to move particles against the concentration gradient. This can be done in several ways, such as through the use of transmembrane proteins called carriers, or through the movement of ions across the membrane.
The last type of transport across a membrane is called endocytosis. This is a process where a cell will take in substances from outside of itself. In endocytosis, the cell engulfs the substance in a vesicle and then brings it inside. This occurs in two forms: phagocytosis and pinocytosis. Phagocytosis is when a cell engulfs a large particle, such as a virus or bacteria, while pinocytosis is when a cell takes in liquid droplets.
Membranes play an essential role in cell transport by providing a selectively permeable barrier and helping to regulate the movement of molecules across the membrane. Through passive transport, active transport, and endocytosis, cells are able to move substances in and out of the cell and maintain homeostasis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cell Transport Worksheet Biology Answers provides a comprehensive overview of the cell transport process. It explains the different types of transport, the different types of molecules that can be transported, and the various forces that act on the molecules. It also outlines the steps in the transport process and how each step helps to move molecules from one part of the cell to another. By understanding how transport occurs and how it affects the entire cell, students can better understand the cell’s functioning and ensure that it functions efficiently.
[addtoany]