Exploring the Basic Principles of the Cell Membrane: A Comprehensive Look at the Cell Membrane Worksheet Answers
The cell membrane worksheet answers provide an in-depth look at the basic principles of the cell membrane, a structure that is essential to the functioning of all living cells. This worksheet explores the structure, composition, and functions of the cell membrane, which is the gatekeeper of a cell.
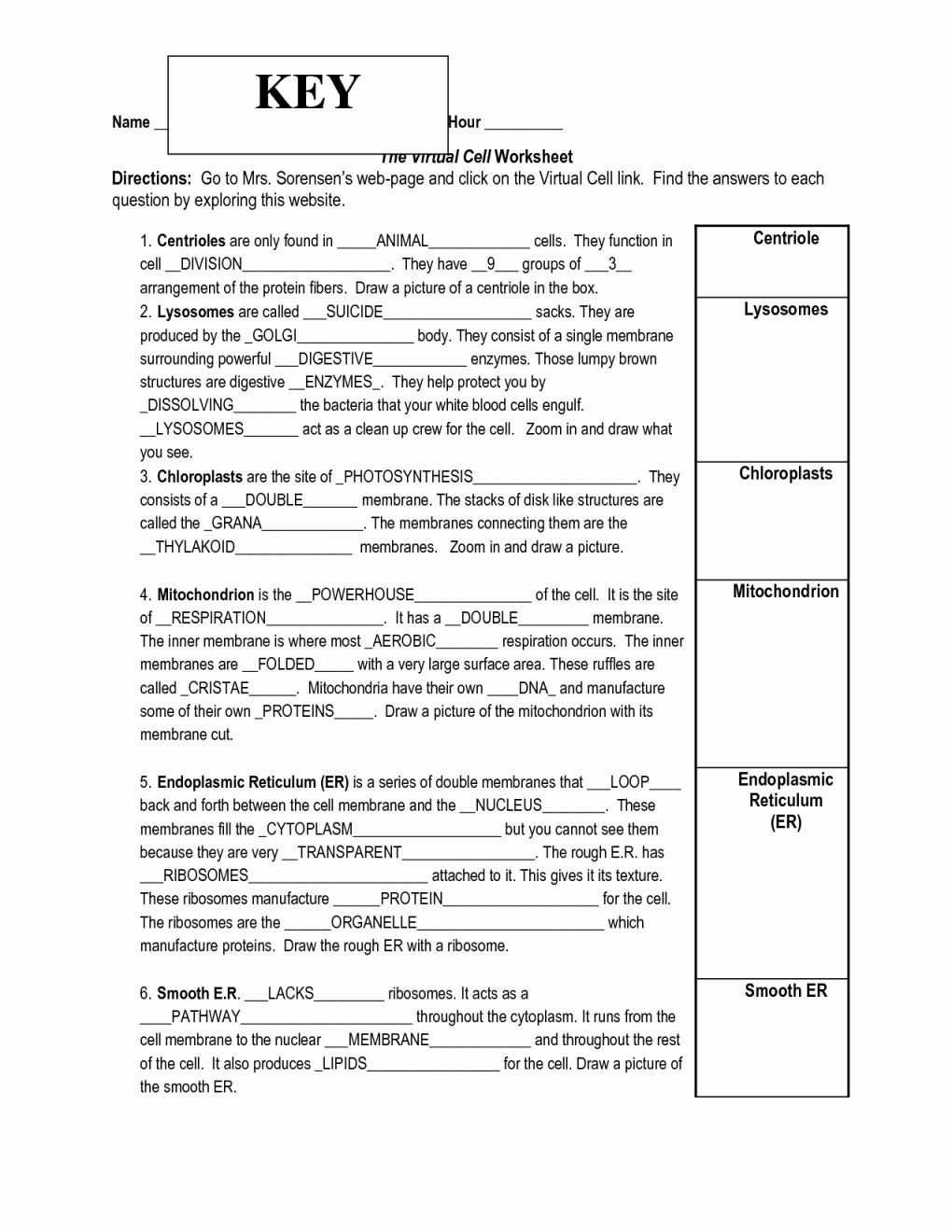
The cell membrane is composed of two layers of phospholipids, which are amphipathic molecules that have a hydrophobic “tail” and a hydrophilic “head”. This arrangement of molecules gives the cell membrane its selective permeability, which allows certain molecules to enter and exit the cell while blocking others. The cell membrane also contains proteins, which act as channels and pores, allowing for the selective transport of substances across the membrane.
The cell membrane is also responsible for maintaining the cell’s homeostasis, or balance of chemicals and ions inside and outside the cell. This is accomplished through active and passive transport, which are processes that use energy to move substances across the membrane. Additionally, the cell membrane is involved in cell-cell recognition, which allows cells to recognize and respond to signals from other cells.
[toc]
The cell membrane is also involved in cell signaling, by which cells communicate with each other. This communication is accomplished through the release of signaling molecules, which are molecules that interact with receptors on the surface of the cell membrane. This interaction triggers a series of biochemical reactions, which can result in changes in the cell’s activity or its response to a stimulus.
Finally, the cell membrane is also involved in cell metabolism, which is the metabolic processes that occur within a cell. These processes include the production of energy, the synthesis and degradation of macromolecules, and the transport of molecules and ions.
The cell membrane worksheet answers provide an in-depth look at the basic principles of the cell membrane and its many functions. By understanding these principles, one can gain a better appreciation of the importance of the cell membrane and its role in the functioning of all living cells.
What Can We Learn from Cell Membrane Worksheet Answers? Examining the Function and Structure of the Cell Membrane
Cell membranes are essential components of all cells, yet their structure and function can remain mysterious to many. To gain a better understanding of how a cell membrane works, it is important to explore both its structure and its function.
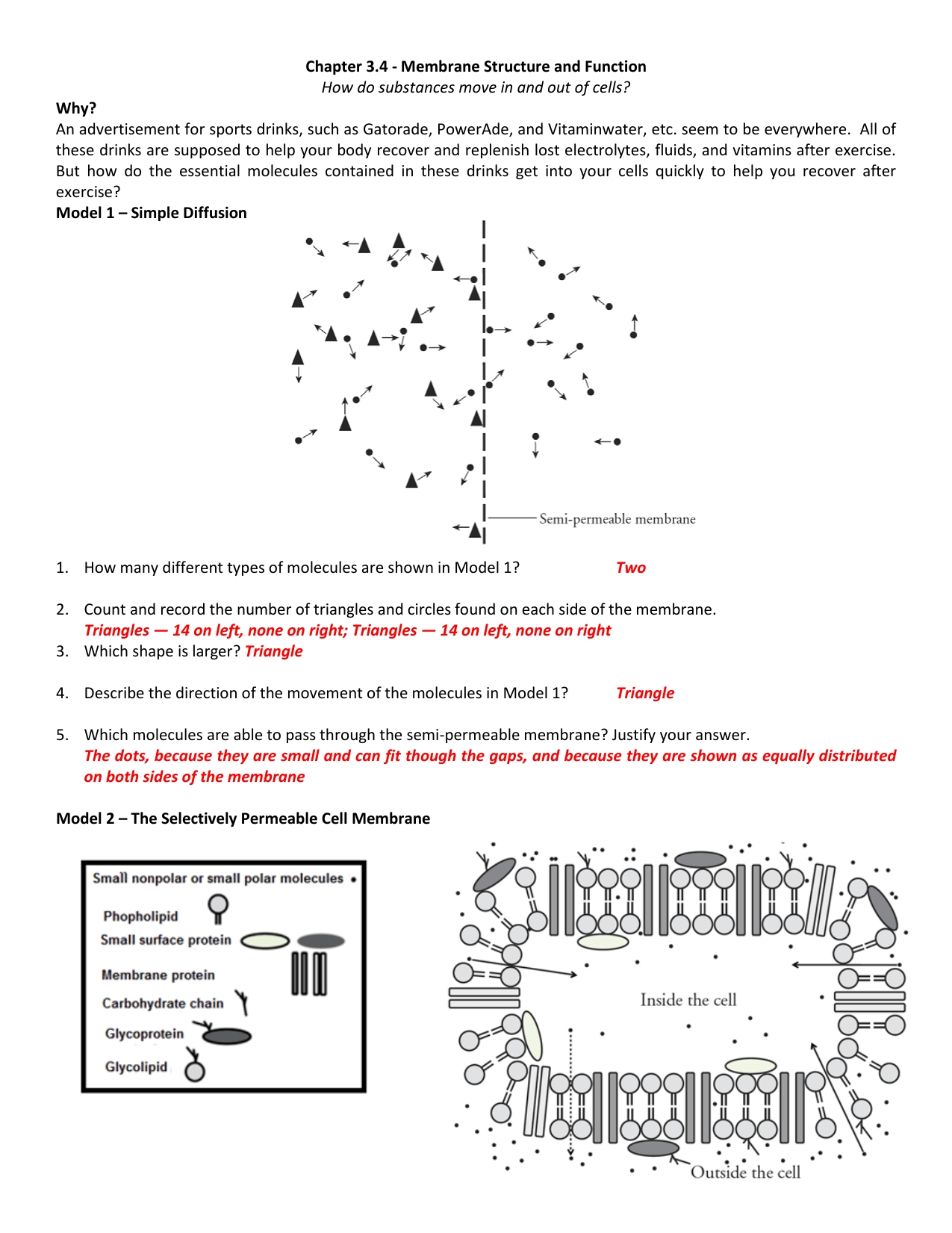
The structure of the cell membrane is complex. It is composed of two layers of lipid molecules, known as a phospholipid bilayer, which acts as a barrier, keeping substances inside and outside the cell separate. In between the two layers are proteins, which act as transporters and receptors, allowing chemicals and other substances to move in and out of the cell. Additionally, the cell membrane also contains other molecules, such as cholesterol and glycoproteins, which help to stabilize the membrane and control the flow of substances across it.
The function of the cell membrane is just as important as its structure. It acts as the gatekeeper of the cell, regulating what substances enter and exit the cell. It also helps to maintain the internal environment of the cell, by providing a barrier against toxins and other potentially harmful molecules. Furthermore, it is also responsible for cell signaling, allowing communication between different cells, and providing a platform for cell-to-cell recognition.
In conclusion, the cell membrane is an essential part of a cell. Its structure and function are both critical to its role within the cell, allowing it to protect and regulate the cell’s environment, while also communicating with other cells. An understanding of its structure and function is key to gaining a better understanding of how cells work.
Investigating Osmosis and Diffusion with Cell Membrane Worksheet Answers: How Does the Process Affect Cell Function?
The process of osmosis and diffusion is essential for the functioning of cells. Osmosis and diffusion both involve the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. In the case of osmosis, water molecules are the moving particles, while in diffusion, the particles can be any type of molecule.
Osmosis is vital for the functioning of cells because it allows for the movement of water molecules from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. This is important because water molecules can transport essential nutrients and waste products in and out of cells, allowing them to survive and thrive in their environment.
Diffusion is also important for cell functioning, as it allows for the movement of molecules other than water. For example, when molecules of oxygen or carbon dioxide diffuse across the cell membrane, they can be used by the cells for energy production. Similarly, molecules of glucose can enter the cell and be used as fuel.
Overall, the process of osmosis and diffusion is vital for cell functioning, as it allows for the movement of molecules in and out of the cell, allowing cells to survive and function properly. Without these processes, cells would be unable to obtain the essential nutrients and waste products they need to survive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cell Membrane Worksheet Answers provides a comprehensive overview of the structure and function of the cell membrane. It provides a detailed explanation of the different components of the cell membrane, as well as the various processes that take place at the membrane level. By understanding the answers to the worksheet questions, students are better equipped to understand the complex relationships between the cell membrane and other components of the cell.
[addtoany]