Exploring the Properties of Atoms: An Overview of Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
The properties of atoms are explored through the study of atomic structure. This worksheet will provide an overview of the components of atomic structure, and explore the various ways in which these components interact to form the atoms we observe in our universe.
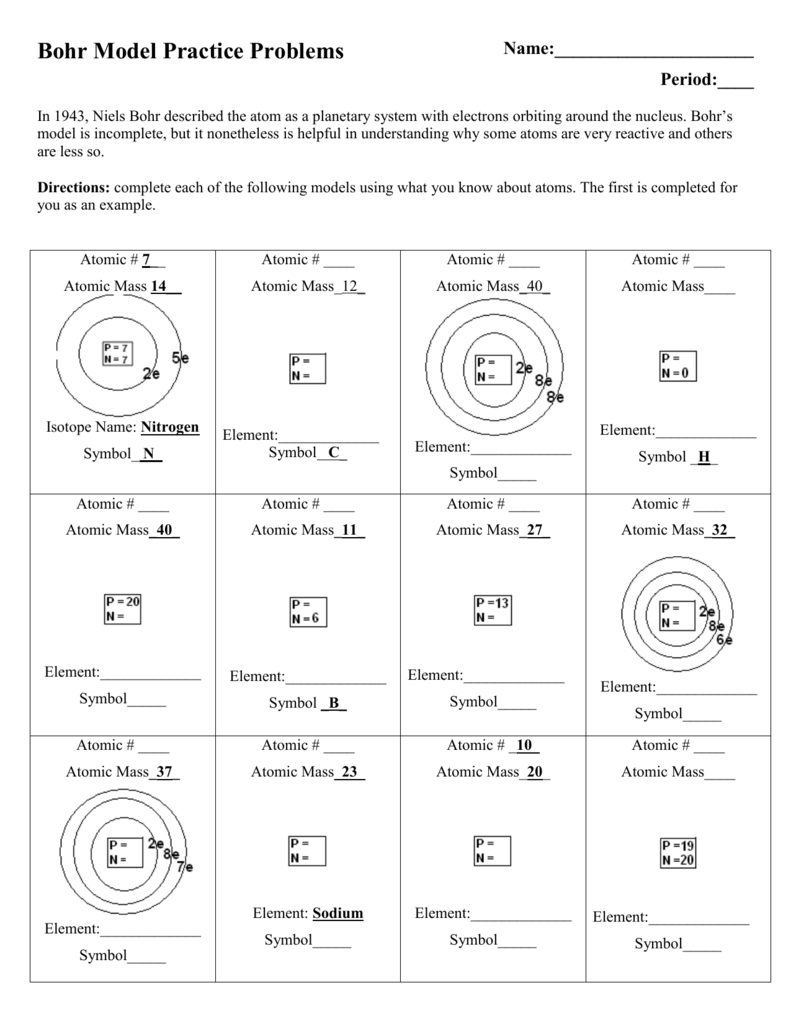
At the most basic level, an atom is composed of a nucleus, surrounded by electrons. The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons, which have a positive and neutral charge, respectively. These protons and neutrons are held together by a strong nuclear force, and the electrons are bound to the nucleus by an electromagnetic force.
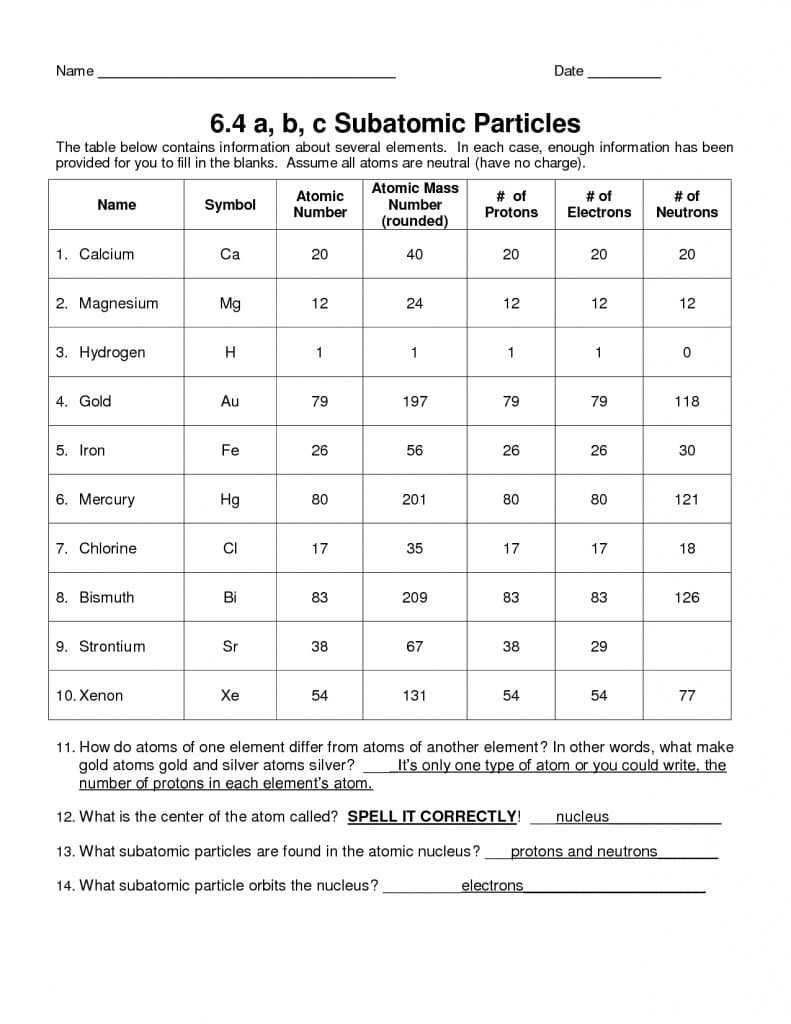
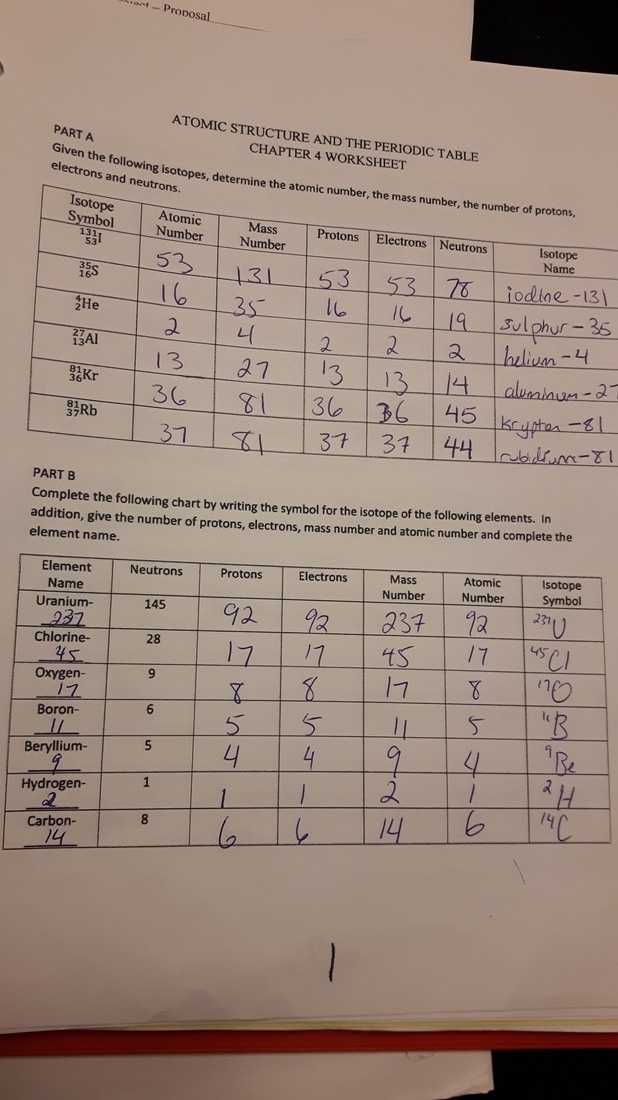
The number of protons in the nucleus determines the element to which the atom belongs. For instance, all hydrogen atoms have one proton in their nucleus, while all oxygen atoms have eight protons. Furthermore, the number of electrons in an atom’s orbit can vary, depending on how many protons the atom has. This is known as an atom’s atomic number.
[toc]
Atoms can also be classified according to their mass. Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes can be either stable or unstable, depending on the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
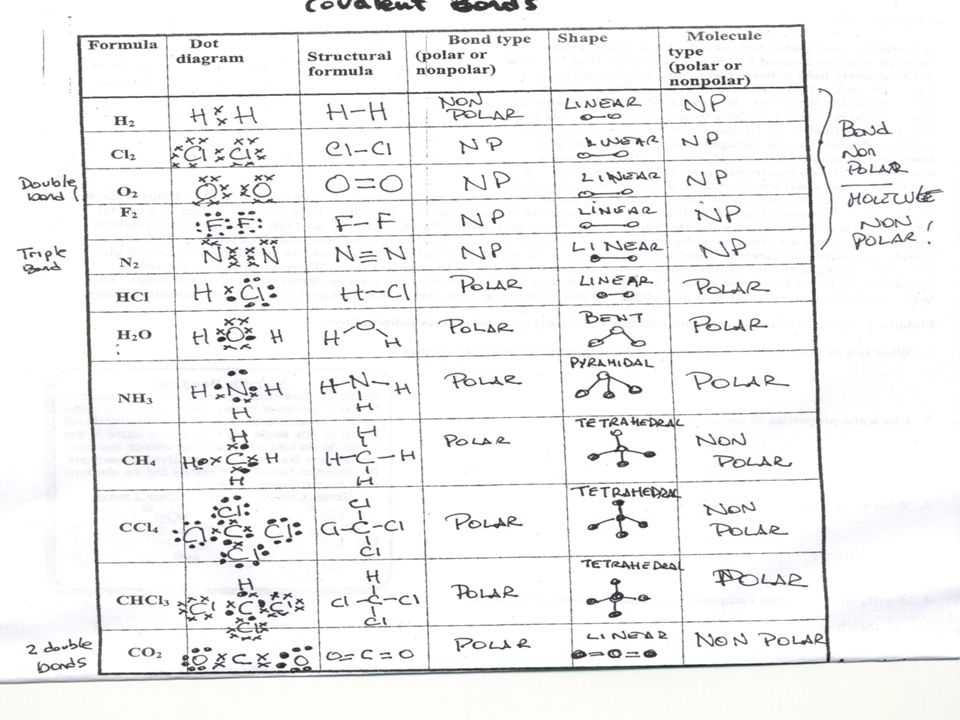
Atoms can also interact with each other in various ways. Atoms can bond with each other to form molecules, or they can be part of reactions that involve the transfer of electrons. Furthermore, atoms can form ionic bonds, in which one atom gives up some of its electrons to another atom.
In conclusion, the properties of atoms are explored through the study of atomic structure. This worksheet has provided an overview of the components of atomic structure and explored the various ways in which these components interact to form the atoms we observe in our universe. By understanding the components of atomic structure, scientists can better understand the behavior of atoms and the universe as a whole.
Understanding Nuclear Reactions: A Guide to Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
I. Introduction
Nuclear reactions are a complex and fascinating field of study, but they can be difficult to understand. This worksheet is designed to help readers gain a better understanding of nuclear reactions by exploring the fundamentals of atomic structure. By the end of this worksheet, readers should have a better understanding of the basics of nuclear reactions, including what they are, how they work, and the role of the atomic nucleus in such reactions.
II. What is a Nuclear Reaction?
A nuclear reaction is a process that involves the transformation of one element into another element, or one isotope into another isotope, through the release or absorption of energy. This energy can come in the form of gamma rays, neutrons, or other particles. Nuclear reactions are responsible for many of the most important processes in the universe, from generating energy in nuclear power plants to powering the sun and stars.
III. How Do Nuclear Reactions Work?
Nuclear reactions involve the transformation of the atomic nucleus, which is the center of the atom and contains most of its mass. During a nuclear reaction, the nucleus can be either split (fission) or fused (fusion).
In fission, the nucleus splits into two or more smaller nuclei, releasing energy in the form of gamma rays, neutrons, or other particles. In fusion, two or more nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus, again releasing energy in the form of gamma rays, neutrons, or other particles.
IV. The Role of the Atomic Nucleus
The atomic nucleus is the center of the atom and contains most of its mass. It is composed of protons and neutrons, and the number of protons determines the type of element. During a nuclear reaction, the nucleus can be either split (fission) or fused (fusion).
In fission, the nucleus splits into two or more smaller nuclei, releasing energy in the form of gamma rays, neutrons, or other particles. In fusion, two or more nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus, again releasing energy in the form of gamma rays, neutrons, or other particles. These reactions are responsible for many of the most important processes in the universe, from generating energy in nuclear power plants to powering the sun and stars.
V. Conclusion
This worksheet has provided readers with a better understanding of the fundamentals of nuclear reactions. By exploring the basics of atomic structure, readers should now have a better understanding of the role of the atomic nucleus in such reactions and how a nuclear reaction works.
Exploring the Building Blocks of Chemistry: An Introduction to Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
1. What is an atom?
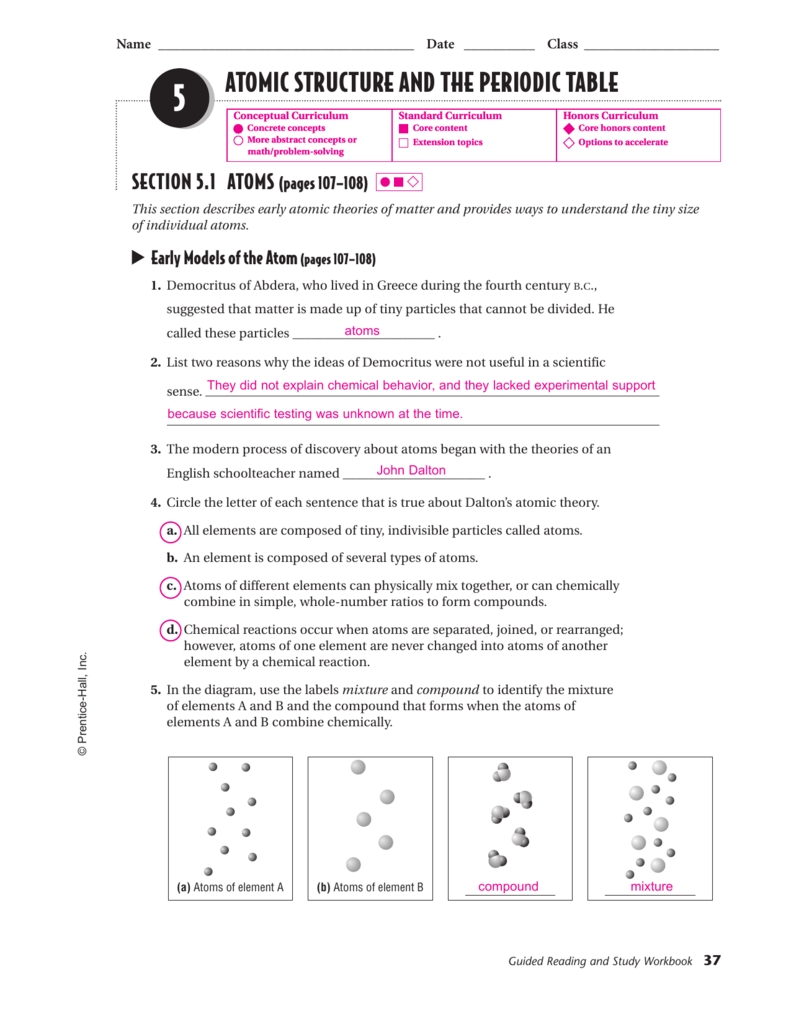
An atom is the basic unit of matter, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus of an atom is made up of protons and neutrons, while the electrons orbit around the nucleus in different energy levels. Atoms are the building blocks of all matter in the universe.
2. What is the nucleus?
The nucleus is the central part of an atom that contains protons and neutrons. It has a positive charge and is the source of most of the atom’s mass. It is held together by the strong nuclear force and is surrounded by a cloud of electrons.
3. What is the atomic number?
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom. It is also used to represent an element on the periodic table. It is equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
4. What is the mass number?
The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. It is represented by the symbol A and is used to calculate the relative atomic mass of an element.
5. What is an isotope?
An isotope is an atom of an element with a different number of neutrons from the standard form of the element. Isotopes are important for studying the properties of atoms and elements.
Conclusion
The Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key provides a comprehensive overview of the structure of atoms and how they interact with each other. This key provides a great resource for students, allowing them to understand the basics of atomic structure and how different elements are formed. Through the use of this key, students can gain a better understanding of the elements and the way they interact with each other, providing them with a better grasp of the fundamentals of chemistry.
[addtoany]