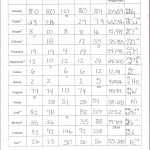
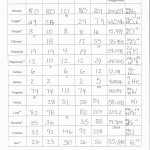
Unpacking the Atom: An Exploration of Atomic Structure Practice Worksheet Answers
The atom is the basic building block of all known matter. Its structure can be broken down into smaller, more fundamental components that help us better understand its complex physical and chemical properties. By unpacking the atom, we can gain insight into the fundamental principles of matter and energy.
At the most basic level, the atom is composed of three main particles: the proton, the neutron, and the electron. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of the atom, while electrons are located in a cloud around the nucleus.
Protons are positively charged particles that make up the majority of an atom’s mass. Neutrons are neutral particles that provide stability to the nucleus. Together, protons and neutrons form the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are negatively charged particles that are much smaller and lighter than protons and neutrons. They are found in orbitals around the nucleus and are responsible for most of an atom’s chemical activity.
[toc]
An atom’s structure can be further broken down into subatomic particles. These particles, such as quarks, gluons, and leptons, are even smaller than electrons and provide insight into the fundamental forces of nature.
By unpacking the atom, we can gain a better understanding of the structure of matter and how it interacts with energy. We can see how its components interact and how they contribute to the properties of an atom. By understanding the atom’s structure, we can better understand the universe and how it works.
A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Atomic Structure Practice Worksheet Answers
1. What is the atomic structure?
Atomic structure is the arrangement of particles that make up an atom. Atoms are composed of a nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons, and electrons that orbit the nucleus. The nucleus is composed of positively charged protons and neutrons that have no charge. Electrons are negatively charged and are found in different energy levels surrounding the nucleus.
2. How do protons and neutrons differ?
Protons and neutrons both have mass, but protons have a positive charge while neutrons have no charge. Protons are found in the nucleus of an atom and neutrons are found in the nucleus as well. Protons and neutrons are both responsible for the atom’s mass, but because protons have a positive charge, they interact with other particles such as electrons and other protons to form bonds. Neutrons, on the other hand, are neutral and do not interact with other particles.
3. What are the different energy levels of electrons?
Electrons occupy different energy levels that are located around the nucleus of an atom. These energy levels are called shells, and each shell is further divided into sub-shells called orbitals. Electrons in different shells have different energies, and they can move between energy levels. The energy level closest to the nucleus is the lowest energy level and is called the ground state. The higher energy levels are further away from the nucleus.
Unlocking the Secrets of Atomic Structure Practice Worksheet Answers: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. The basic building blocks of all matter are atoms. Atoms are made up of three components: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons make up the nucleus of an atom and are found in the center. Electrons orbit the nucleus in shells and are responsible for chemical bonding.
2. Protons are positively charged particles and have an atomic number of one. Neutrons are neutral particles and have an atomic number of zero. Protons and neutrons are held together by a strong nuclear force.
3. Electrons are negatively charged particles. The number of electrons determines the type of atom it is. For example, hydrogen has one electron, while carbon has six electrons. Electrons orbit the nucleus at various distances, which is dependent on their energy level.
4. Atoms are held together by chemical bonds that form when electrons are shared between them. The sharing of electrons creates a strong bond that is difficult to break. Different types of bonds form depending on the type of atom, the number of electrons, and the arrangement of electrons.
5. Atoms are constantly moving and vibrating due to their energy levels. They also can interact with other atoms, forming compounds. Compounds are made up of two or more different types of atoms held together by chemical bonds.
6. The structure of atoms can be determined through a variety of methods such as X-ray crystallography, electron microscopy, and nuclear magnetic resonance. By studying the arrangement of atoms, scientists can learn about the properties of different materials and develop new technologies.
Conclusion
The Atomic Structure Practice Worksheet Answers provides an excellent way to understand the basics of atomic structure. It is a great tool for students to gain an understanding of how elements interact with each other and how electrons move around the nucleus of an atom. With the answers, students can see how the behavior of atoms can be predicted, and how the structure of an atom can affect its properties. By understanding the answers to the practice worksheet, students can gain a better understanding of atomic structure and its importance in the world around them.
[addtoany]