Exploring the Benefits of Worksheet Methods of Heat Transfer for Industrial Applications
Worksheet methods of heat transfer are an important industrial application for many industries. This type of heat transfer is a reliable and cost-effective solution that can be used in a variety of applications. In this article, the benefits of worksheet methods of heat transfer will be explored in detail.
Worksheet methods of heat transfer are used to transfer heat from one source to another. This type of heat transfer is often used in industrial applications, such as in the manufacture of large components, to transfer heat from a source of high temperature to a target of low temperature. The process of worksheet methods of heat transfer involves the use of thermal insulation and a worksheet. The worksheet acts as a thermal barrier between the source and target and is designed to reduce the amount of heat that is transferred. This helps to ensure that the target temperature remains at a safe level and that the transfer of heat from the source to the target is efficient and consistent.
One of the key benefits of worksheet methods of heat transfer is that it is an efficient and cost-effective solution. The thermal insulation and worksheet used in the process are made from materials that are relatively inexpensive and easily available. This means that the cost of the process is minimal and the amount of energy required to transfer the heat is also reduced. Additionally, the worksheet helps to ensure that the heat is transferred in a controlled manner, reducing the risk of damage to the target.
[toc]
Another benefit of worksheet methods of heat transfer is that they are an environmentally friendly solution. The materials used in the process are environmentally friendly and do not have any negative impacts on the environment. Additionally, the worksheet helps to reduce energy consumption, meaning that the process is energy efficient and reduces the amount of energy required to transfer the heat. This helps to reduce the amount of energy consumed and helps to reduce energy costs.
Finally, worksheet methods of heat transfer are a reliable and consistent solution. The materials used in the process are designed to ensure that the heat is transferred in a consistent manner and that the target temperature remains at a safe level. This helps to ensure that the process is reliable and consistent, reducing the risk of damage to the target.
In conclusion, worksheet methods of heat transfer are an important industrial application for many industries. This type of heat transfer is a reliable and cost-effective solution that can be used in a variety of applications. It is an efficient and cost-effective solution, is an environmentally friendly solution, and is a reliable and consistent solution. As such, worksheet methods of heat transfer are an invaluable industrial application that can be used to transfer heat from one source to another in a safe and efficient manner.
Comparing Different Worksheet Methods of Heat Transfer in the Home Environment
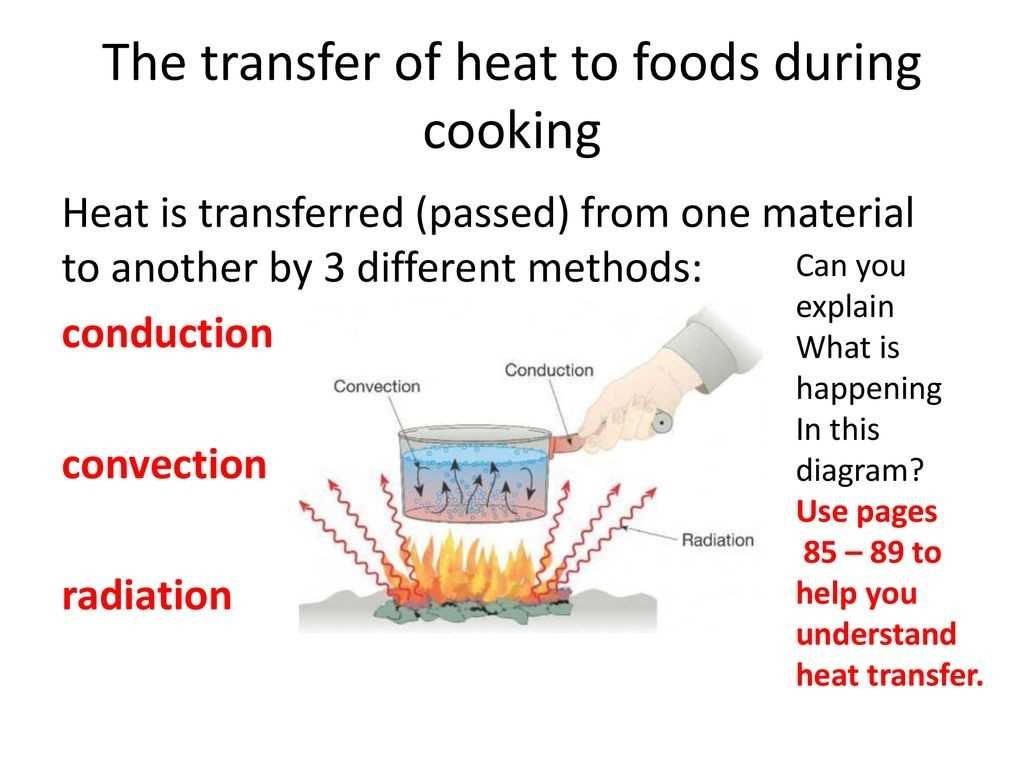
Heat transfer is an important concept in the home environment, and there are several methods by which heat can be transferred. Heat can be transferred by conduction, convection, and radiation. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and understanding how they work is essential to making informed decisions about the best heat transfer method for a given home environment.
Conduction is the transfer of heat through the direct contact of two objects. Heat is transferred when two objects of different temperatures come into contact with one another, and the warmer object will transfer its heat to the cooler object. In a home environment, conduction is most often used to transfer heat through metal surfaces, such as a radiator or a stovetop. The metal surface acts as a conductor, allowing the heat to pass from one object to another. The advantage of conduction is that it is relatively inexpensive and easy to implement, and it can be used in a wide range of home environments. The disadvantage of conduction is that it is less efficient than other methods of heat transfer, and it can take a long time for the heat to be evenly distributed.
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids. Heat is transferred when a fluid is heated, and the warmer fluid will move away from the cooler fluid, allowing the heat to be transferred to the cooler area. In a home environment, convection is most often used to transfer heat through the air, such as in a forced-air heating system. The advantage of convection is that it is relatively efficient and can quickly heat a space. The disadvantage of convection is that it requires more energy to operate and can be more expensive than other methods of heat transfer.
Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic radiation. Heat is transferred when an object emits electromagnetic radiation, and the radiation will be absorbed by other objects in the environment. In a home environment, radiation is most often used to transfer heat through the sun. The advantage of radiation is that it is relatively efficient and can quickly heat a space. The disadvantage of radiation is that it can be difficult to control and can be more expensive than other methods of heat transfer.
Overall, each method of heat transfer has its own advantages and disadvantages, and understanding how each method works is essential to making informed decisions about the best heat transfer method for a given home environment.
Understanding the Role of Insulation in Improving Heat Transfer with Worksheet Methods
Insulation is an important component in improving heat transfer. It is used to slow down the rate at which heat moves through a material, thus reducing the amount of energy needed to heat or cool a given space. Insulation also helps to reduce the amount of energy lost through convection, conduction, and radiation, thus making a building or home more energy efficient.
The ability of insulation to improve heat transfer can be quantified and evaluated using worksheet methods. In this process, the thermal resistance (R-value) of the insulation is calculated. The R-value is a measure of how well the insulation resists the transfer of heat, and is determined by the type and thickness of the insulation material. Higher R-values indicate better insulation, and there are specific R-values for different types of insulation materials.
Worksheet methods also consider the thermal characteristics of the building envelope or home, such as the wall and ceiling construction. This includes the type of materials used, their thickness, and the airtightness of the envelope. This information is then used to calculate the total thermal resistance of the building or home, which is the sum of the thermal resistances of the walls, ceiling, and other components of the envelope.
The R-values of the insulation and the total thermal resistance of the building envelope are then compared to determine the effectiveness of the insulation in improving heat transfer. If the insulation has an R-value that is greater than the total thermal resistance of the envelope, it is considered to be effective in improving heat transfer.
Worksheet methods are a powerful tool for understanding and evaluating the role of insulation in improving heat transfer. They provide a simple, yet accurate way of calculating the R-value of insulation, as well as the total thermal resistance of a building envelope, in order to determine the effectiveness of insulation in improving heat transfer.
Conclusion
Worksheet Methods Of Heat Transfer is an effective way for students to learn about the different ways heat is transferred and how it affects their everyday lives. Through this worksheet, students can gain a better understanding of how heat is transferred in their environment and how it impacts their daily lives. With this knowledge, students can be better prepared to make informed decisions related to the use of energy and its impact on the environment.
[addtoany]