Exploring the Role of Transport in Cell Function and Metabolism
Transport plays an integral role in cellular function and metabolism. It is a fundamental process that enables cells to acquire vital nutrients and expel waste products. Within the cell, transport is carried out by a variety of transport proteins and organelles, allowing for the exchange of essential molecules, ions, and other substances.
Transport proteins are a group of molecules that are responsible for the movement of molecules and ions across the cell membrane. These proteins are embedded within the membrane and function as gates, allowing certain molecules to enter or leave the cell. Examples of these proteins include ion channels, which control the movement of ions, and transporters, which facilitate the transport of molecules such as amino acids and glucose. In addition to proteins, organelles such as endosomes, lysosomes, and vacuoles also play a role in transport.
The transport of molecules and ions is essential for a variety of cellular processes. The movement of potassium and sodium ions, for example, is essential for maintaining the cell’s electrical potential. This process is known as active transport and is essential for nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction. In addition, the transport of glucose is essential for energy production, as it provides the cell with the energy it needs to function. Other molecules such as amino acids, lipids, and nucleotides are also essential for various metabolic processes.
[toc]
In conclusion, transport plays an essential role in cell function and metabolism. By allowing for the movement of essential molecules, ions, and other substances, transport enables cells to acquire vital nutrients and expel waste products. This process is achieved through transport proteins and organelles, allowing for the exchange of molecules and ions across the cell membrane. As a result, transport is essential for a variety of cellular processes, providing cells with the energy and materials they need to survive.
Understanding the Role of Active and Passive Transport in Cells
Active and passive transport are two types of cellular transport processes that occur within cells. Active transport refers to the movement of molecules across the cell membrane, against the concentration gradient, utilizing energy in the form of ATP. This process is necessary for the existence of life, as it is used to move ions and molecules that are essential for the functioning of cells and organisms. Passive transport, on the other hand, involves the movement of molecules across the cell membrane, down the concentration gradient, without the expenditure of energy.
Active transport is a vital process for cells, as it enables them to maintain an internal environment that is different from their external environment. This is especially important for cells that resist high salt concentrations outside of the cell, as it allows the cell to import essential minerals and maintain a suitable internal environment. Active transport is also used to transport molecules across the cell membrane, such as proteins, amino acids, and nucleic acids, which are essential for the functioning of cells.
Passive transport is a less energy-demanding process than active transport and is used to move molecules and ions down their concentration gradient. This process occurs spontaneously and does not require any energy expenditure. It is used to move molecules and ions across the cell membrane, such as water, carbon dioxide, and oxygen, which are essential for the existence of life.
Active and passive transport play a crucial role in the survival of cells and organisms. Active transport is necessary for the maintenance of an internal environment that is different from the external environment, while passive transport is used to move molecules and ions down the concentration gradient, without the expenditure of energy. Both processes are essential for the functioning of cells and organisms, and they are necessary for the survival of life.
Examining the Impact of Diffusion and Osmosis on Cell Transport
Cell transport is a process that is essential to the survival of many organisms. It involves the movement of molecules across the cell membrane, allowing for the exchange of nutrients, waste, and other materials. In particular, the diffusion and osmosis of molecules play a significant role in cell transport.
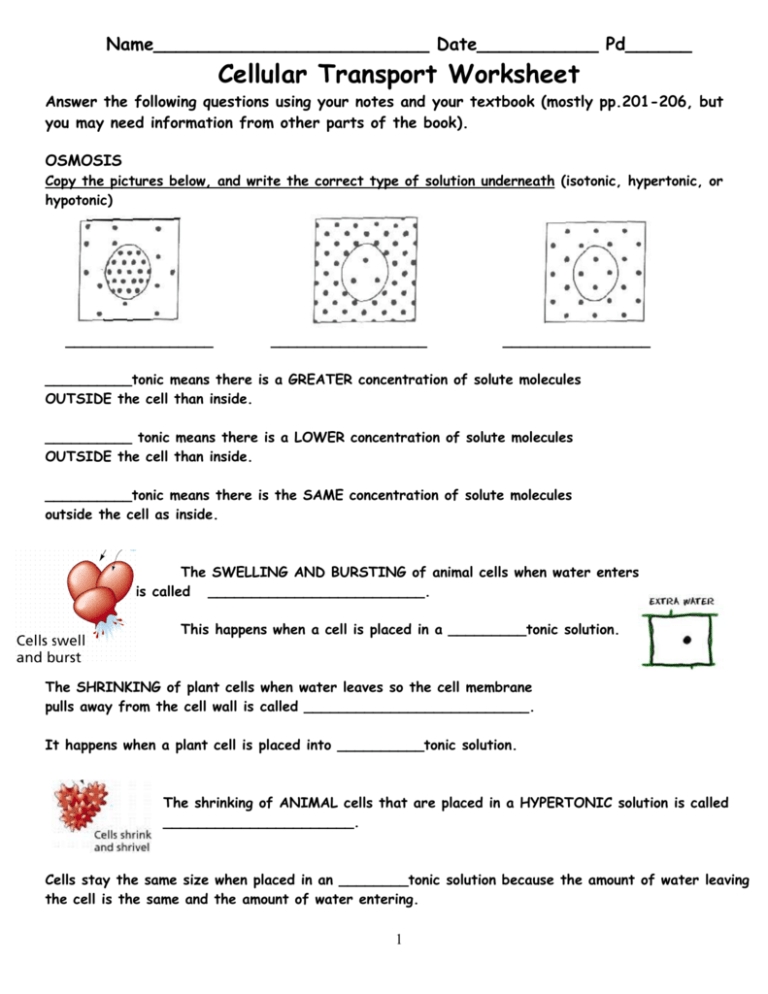
Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This occurs until the concentrations of molecules on both sides become equal. Osmosis is similar to diffusion, but it specifically involves the movement of water molecules. Osmosis occurs when water molecules move from an area with a higher concentration of water to an area with a lower concentration of water.
The impact of diffusion and osmosis on cell transport is significant. Diffusion and osmosis allow the cell to acquire nutrients and other essential materials, as well as to rid itself of waste. Without the ability to diffuse and osmose molecules, the cell would not be able to survive. Additionally, diffusion and osmosis are responsible for maintaining an optimal balance of ions, proteins, and other molecules within the cell.
Diffusion and osmosis also play a role in maintaining a cell’s internal environment. By regulating the movement of molecules across the cell membrane, diffusion and osmosis help to keep the cell’s internal environment stable and free from harmful materials. Furthermore, diffusion and osmosis are instrumental in transporting materials to and from the cell.
In conclusion, diffusion and osmosis are essential to the process of cell transport. Through their ability to regulate the movement of molecules across the cell membrane, diffusion and osmosis enable the cell to acquire essential materials and rid itself of waste. Additionally, diffusion and osmosis help to maintain the cell’s internal environment and to transport materials to and from the cell.
Investigating the Role of Transport Proteins in Cell Signalling and Regulation
Cell signalling and regulation involve complex processes that involve the transfer of information from one cell to another. One of the most important components of these processes is the transport proteins, which serve as the mediators of cellular communication. Transport proteins are responsible for transporting molecules and ions across the cell membrane, thus allowing for the transfer of information and the regulation of cell metabolism.
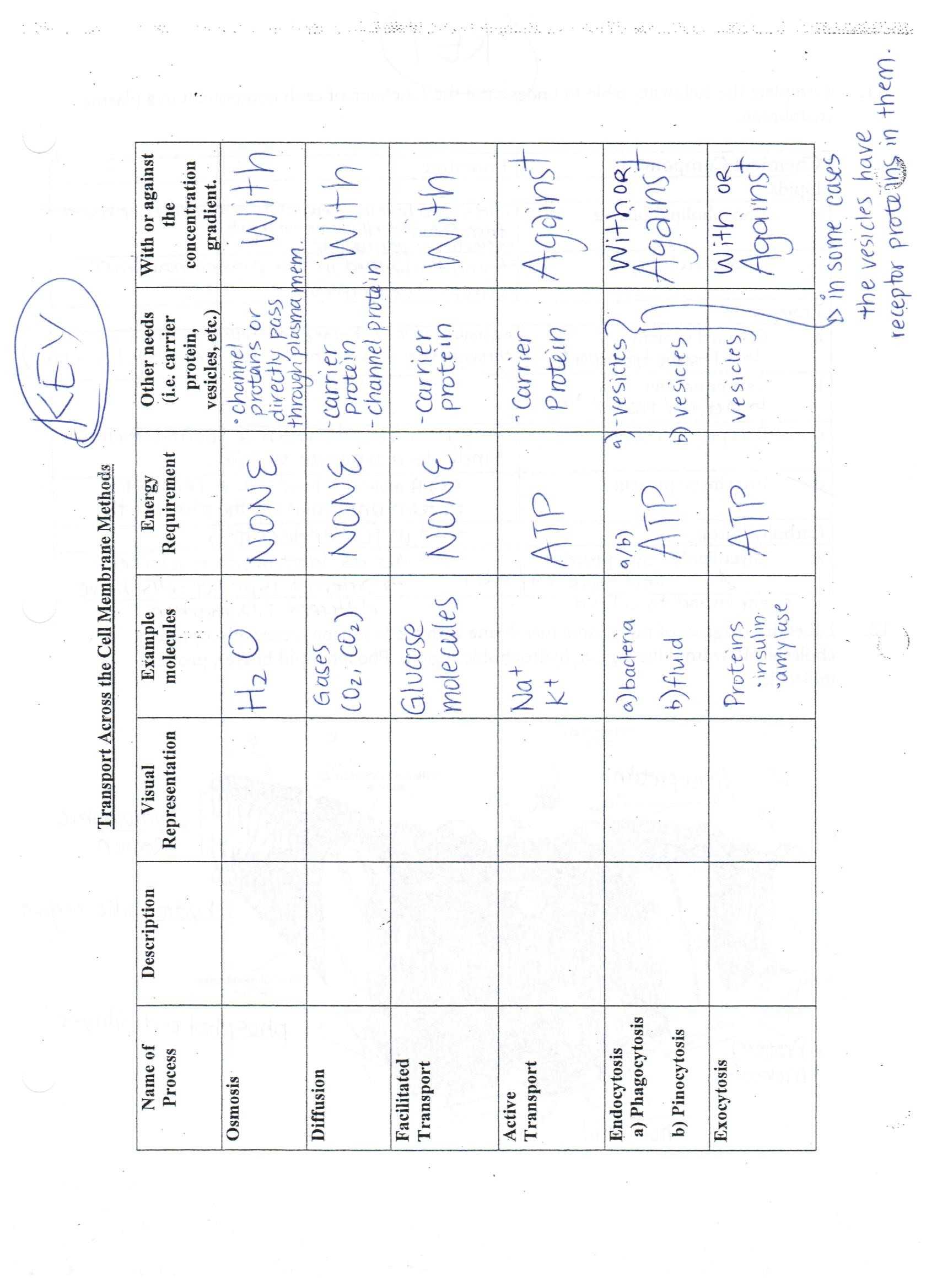
Transport proteins, also known as carriers, are integral membrane proteins that are embedded in the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. These proteins are responsible for the movement of molecules and ions across the cell membrane, either by facilitated diffusion or active transport. In facilitated diffusion, molecules pass through the protein channels passively, while active transport requires the protein to use the energy of ATP to move molecules and ions across the cell membrane.
Transport proteins play a crucial role in cell signalling and regulation. They are responsible for transporting signal molecules such as hormones and neurotransmitters across the cell membrane. These signal molecules bind to receptors in the cell membrane, which triggers a cascade of cellular responses. Transport proteins also play a role in the regulation of cell metabolism. They are responsible for transporting nutrients, such as glucose and amino acids, across the cell membrane, and for transporting waste products, such as carbon dioxide and urea, out of the cell.
In addition to their roles in cell signalling and regulation, transport proteins have been shown to play a role in diseases such as cystic fibrosis and cancer. Mutations in transport proteins can lead to an imbalance in the transport of molecules and ions across the cell membrane, thus disrupting the normal functioning of the cell. In the case of cystic fibrosis, mutations in a transport protein known as CFTR lead to an accumulation of mucus in the lungs, which can lead to serious respiratory problems. In cancer, mutations in certain transport proteins can lead to an unregulated growth of cells, resulting in tumour formation.
In conclusion, transport proteins are essential components of cell signalling and regulation. They are responsible for the movement of molecules and ions across the cell membrane, allowing for the transfer of information and the regulation of cell metabolism. Mutations in transport proteins can lead to serious diseases, such as cystic fibrosis and cancer. As such, understanding the role of transport proteins in cell signalling and regulation is essential for understanding and treating these diseases.
Conclusion
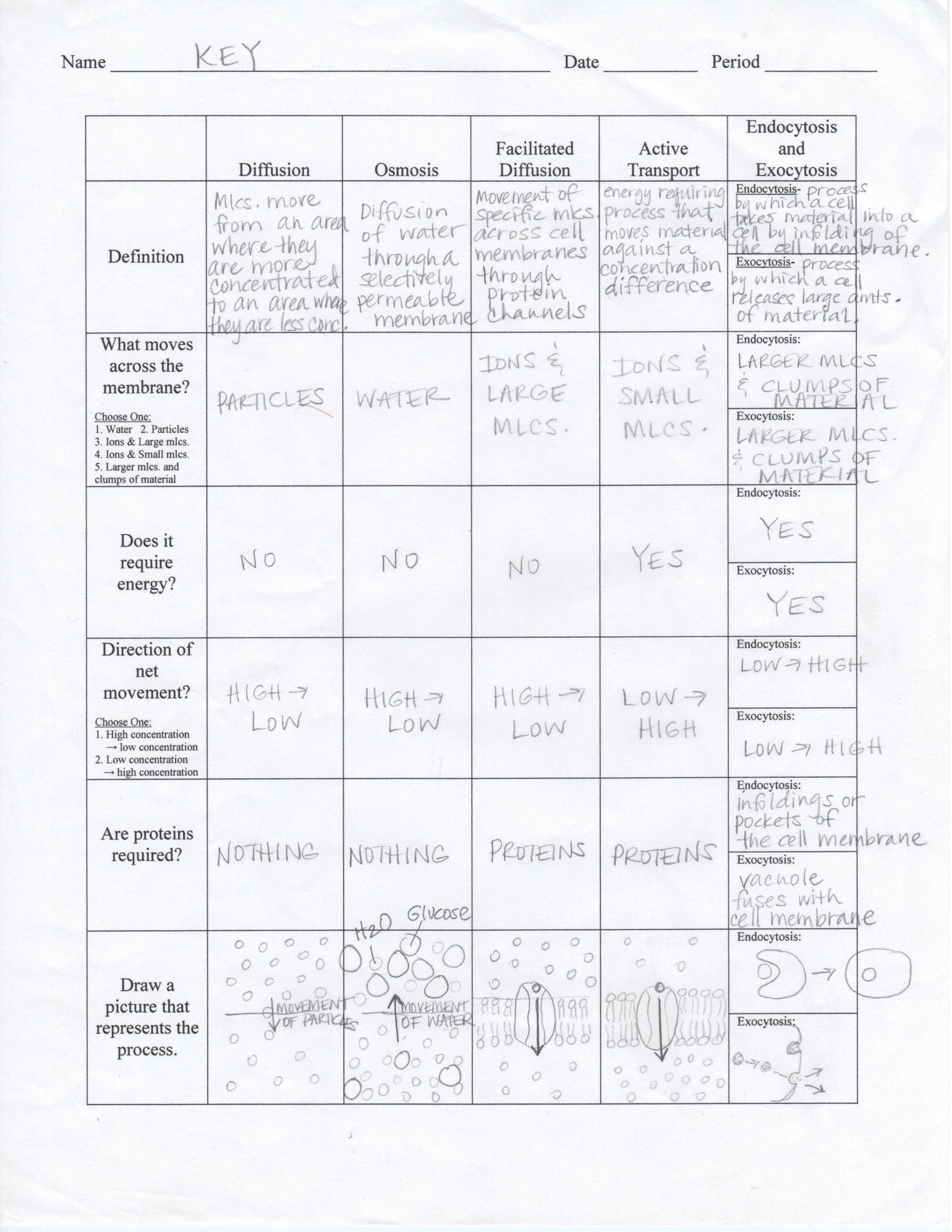
In conclusion, the Transport in Cells Worksheet is a great resource for anyone who wants to learn more about how cells transport materials across their membranes. It provides a comprehensive overview of the various types of transport, and it includes diagrams, worksheets, and questions to help students better understand the concepts. With its clear explanations and helpful visuals, this worksheet is an excellent tool for learning more about this fascinating process.
[addtoany]