Unpacking the Structure of the Atom Worksheet: A Step-by-Step Guide
The structure of the atom is an essential concept to understand in the study of chemistry. This worksheet provides a step-by-step guide to unpacking this complex structure and will help to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the atom.
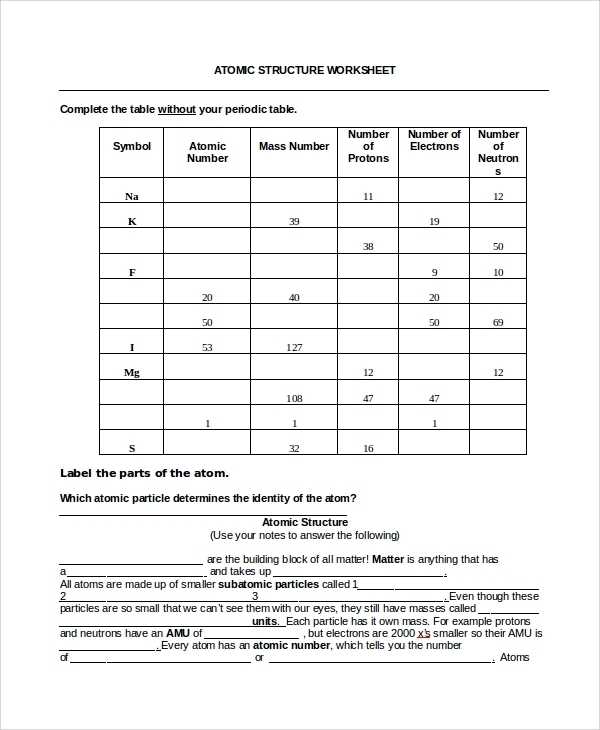
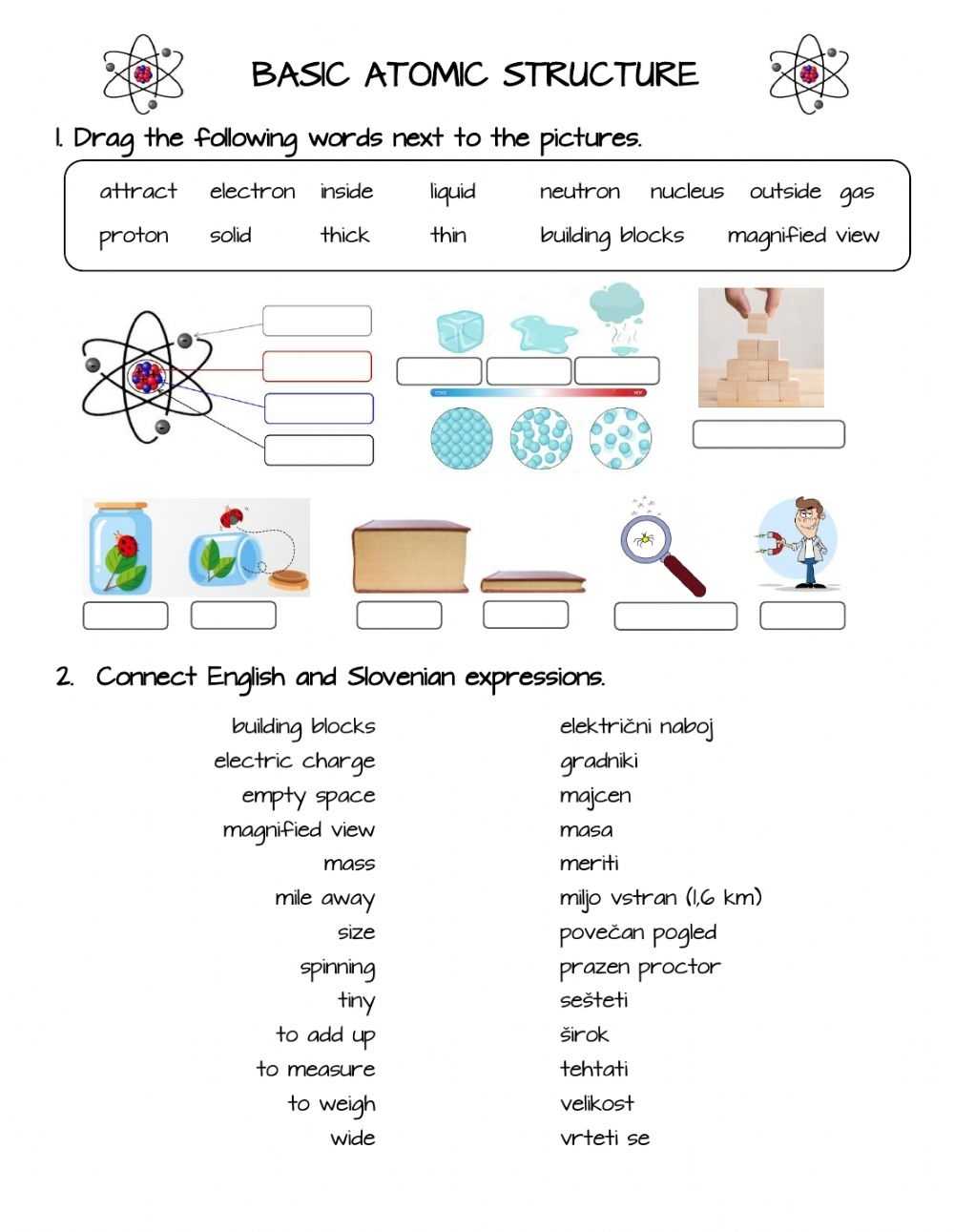
First, it is important to remember that the atom is composed of three main particles: the proton, the neutron, and the electron. Protons are positively charged particles, neutrons are neutral particles, and electrons are negatively charged particles. The protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, while the electrons orbit around the nucleus at varying distances.
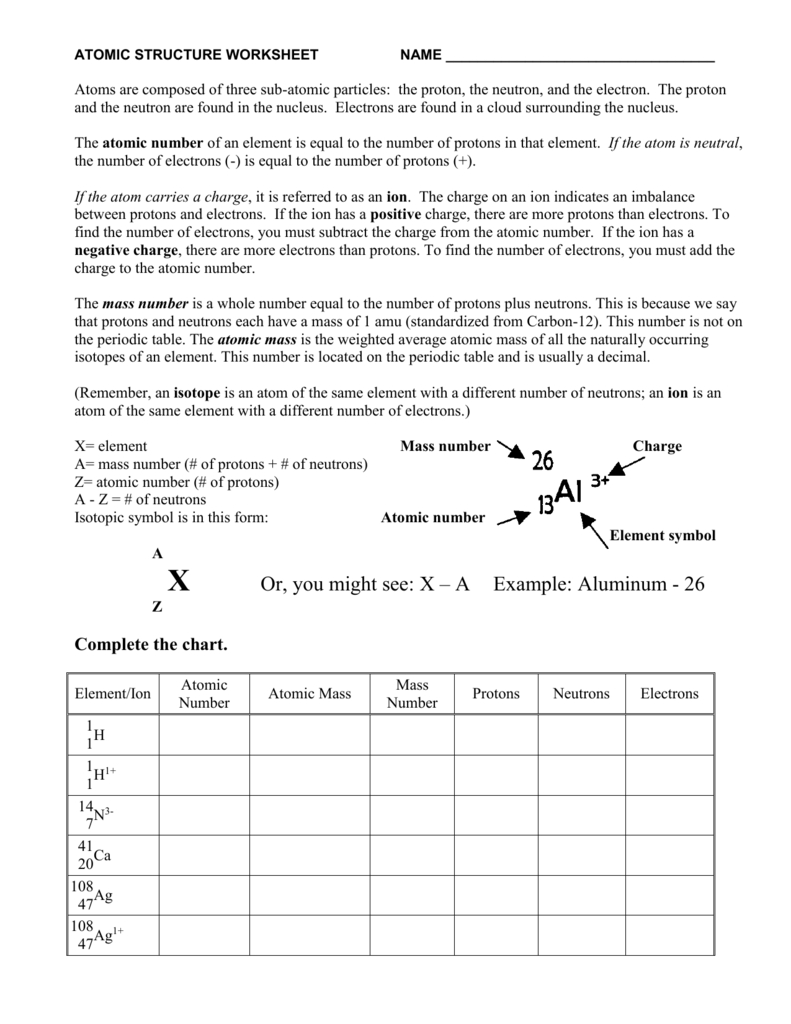
Second, it is important to understand how the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons varies within an atom. This number is determined by the atomic number of the element, which is the number of protons in the atom. The mass number of the atom is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom. The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons, as the positive and negative charges need to remain in balance.
[toc]
Third, it is important to understand how the electrons are arranged in an atom. Electrons are arranged in different energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus. The highest energy level is the valence shell, where the outermost electrons are found. As electrons become more distant from the nucleus, they have lower energy levels.
Fourth, it is important to understand how elements interact with each other. Chemical elements interact with each other based on their valence electrons, or the number of electrons in the outermost energy level. Elements with the same valence electrons have similar properties and will often bond with each other.
By following this step-by-step guide, students will gain a comprehensive understanding of the structure of the atom. This knowledge will be essential for furthering their studies in chemistry.
Exploring the Building Blocks of the Atom: A Comprehensive Overview of the Structure of the Atom Worksheet
Atoms are the smallest particles of matter that make up all physical objects. They are the fundamental building blocks of the world we know, and a thorough understanding of their structure is essential to comprehending the physical universe. This worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the structure of the atom and its constituent parts.
At the heart of the atom is the nucleus, a dense core comprised of two subatomic particles: protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive electrical charge, while neutrons are neutral. The nucleus of an atom contains an equal number of protons and neutrons, and together they make up the majority of the atom’s mass. Surrounding the nucleus are electrons, which are negatively charged and much lighter than the protons and neutrons. Electrons occupy orbits known as shells, which are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus.
In addition to the protons, neutrons, and electrons, some atoms also contain other subatomic particles known as quarks. These particles are present in the nucleus and are even smaller than the protons and neutrons.
To understand the structure of the atom more fully, it is important to look at the arrangement of its components. The protons and neutrons in the nucleus form a nucleus-shell structure, with protons and neutrons occupying different shells. The electrons that orbit the nucleus form a cloud-like structure known as the electron cloud. This cloud is divided into different regions, each corresponding to a different shell.
By studying the structure of the atom, we can gain insight into its properties and how it behaves. Its components, such as the protons and electrons, interact with one another to form chemical bonds. These interactions are responsible for the structure and behavior of matter, as well as the many phenomena we observe in the physical world.
This worksheet has provided a comprehensive overview of the structure of the atom. Its constituent protons, neutrons, and electrons interact with one another to form the nucleus-shell structure and the electron cloud. The understanding of the structure of the atom provides a foundation for the exploration of its properties and behavior.
Deconstructing the Components of Atoms: A Closer Look at the Structure of the Atom Worksheet
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of all matter. Understanding the components of atoms and their structure is essential for comprehending the physical world. In this worksheet, we will conduct an in-depth exploration of the components of atoms and their structure.
At the center of the atom is the nucleus, which is composed of two types of particles: protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged particles, while neutrons are neutral. The number of protons in an atom is known as the atomic number and is unique to each element. The number of neutrons in an atom is known as the mass number.
Surrounding the nucleus are the electrons, which are negatively charged particles. Electrons are much smaller than protons and neutrons and occupy a much larger space than the nucleus. Electrons are arranged in shells, or energy levels, around the nucleus. The number of electrons in each shell is determined by the element’s atomic number.
The arrangement of electrons in the shells affects the properties of the atom. For example, the electron configuration of an atom determines its reactivity. Atoms with an incomplete outer shell of electrons are more reactive than those with a full outer shell.
In addition to protons, neutrons, and electrons, atoms also contain a variety of subatomic particles such as neutrinos and muons. These particles interact with the nucleus and electrons to form molecules, which are the building blocks of physical matter.
By examining the components of atoms and their structure, we can gain a greater understanding of the physical world. Through this worksheet, we have gained an appreciation for the complexity of atoms and their role in the formation of matter.
Understanding the Basics of Nuclear Physics: A Review of the Structure of the Atom Worksheet
The atom is the basic building block of all matter and is composed of three main components: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, while electrons are located in the electron cloud surrounding the nucleus. Protons have a positive charge and are found in the nucleus, while neutrons have a neutral charge and are also located in the nucleus. Electrons have a negative charge and are located in the electron cloud.
The nucleus of an atom is composed of protons and neutrons and is held together by a strong nuclear force. The number of protons and neutrons in an atom determines the type of atom it is. For instance, atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are known as isotopes. Additionally, the number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which is used to identify an element.
The electrons in an atom orbit the nucleus at different levels, known as shells. Each shell has a specific energy level, which determines the number of electrons that can occupy each shell. The innermost shell is known as the K shell and can hold up to two electrons. The next shell is the L shell and can hold up to eight electrons. The outermost shell is known as the M shell and can hold up to eighteen electrons.
The nucleus and the electrons in an atom are held together by a strong force known as the Coulomb force. This force is the result of the attraction between the positive charges of the protons and the negative charges of the electrons. The Coulomb force also creates a binding energy, which holds the atom together.
In addition to the Coulomb force, there are also two other forces which act on the nucleus and electrons of an atom. These are the strong nuclear force, which binds the nucleus together, and the electromagnetic force, which is responsible for the attraction between the electrons and the nucleus.
Understanding the basics of nuclear physics requires an understanding of the structure of the atom. By understanding the components of the atom, including the protons, neutrons, electrons, and the forces which act on them, it is possible to gain a better understanding of how atoms interact with each other and how they interact with radiation. This knowledge can be used to gain insight into the behavior of atoms and the forces that shape the universe.
Conclusion
The Structure of the Atom Worksheet provides a great overview of the structure of the atom and its components. By completing this worksheet, students have gained a better understanding of the basic structure of the atom and how it is composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. This knowledge will help them better understand the principles of chemistry and other related science topics.
[addtoany]