Understanding Parent Functions and Transformations: A Comprehensive Guide
Parent functions and transformations are essential concepts of mathematics. Understanding the fundamentals of these topics can help students become more adept and proficient at problem-solving and analyzing data. This guide provides an overview of parent functions and transformations, from the basic definitions to the various types of transformations.
The concept of a parent function is relatively simple. A parent function is a basic, fundamental function from which all other related functions can be derived. For example, the parent function for a linear equation is the standard form, y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. All linear equations can be derived from this basic form.
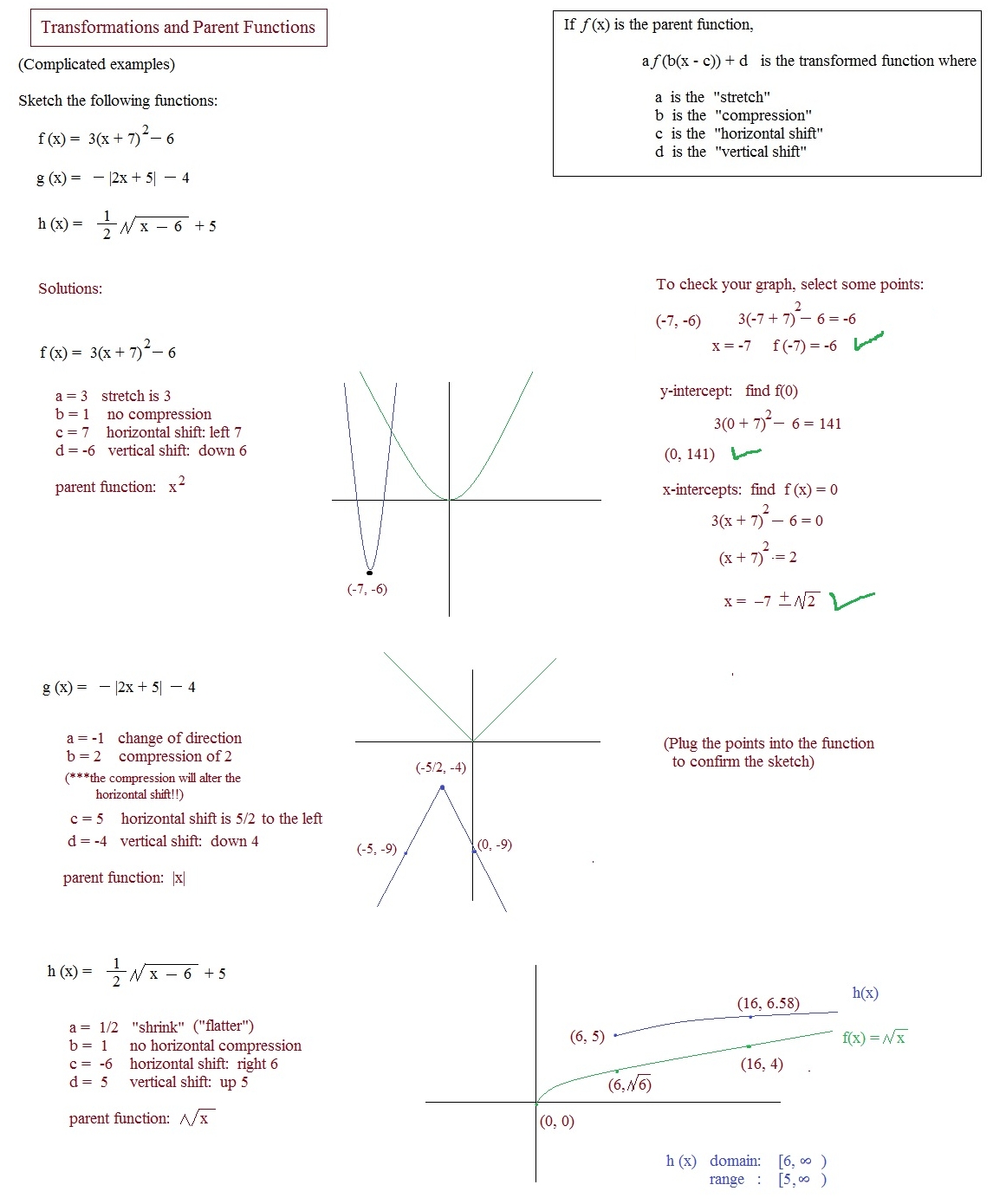
Transformations are changes made to the original, parent function to create a new, related function. These changes can be made in terms of the graph’s shape, orientation, or location. Common transformations include reflections, shifts, dilations, and rotations.
[toc]
A reflection occurs when the graph is flipped over either the x- or y-axis. This creates a mirror image of the original graph. A shift is when the graph is moved without any alteration to its shape. This can be done along either the x- or y-axis, or both. A dilation is a change in size, where the graph is either shrunk or enlarged. Lastly, a rotation is when the graph is turned around a point.
It is important for students to understand the basics of parent functions and transformations. By doing so, they can become more adept at problem-solving and analyzing data. This guide provides an overview of these concepts, from the basic definitions to the various types of transformations.
How to Identify Parent Functions and Transformations: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
Step 1: Identifying a Parent Function
A parent function is a basic function that describes the overall shape of a graph. It is the simplest form of a function and does not have any transformations applied to it. To identify a parent function, it is important to look at the equation of the function. The most common parent functions are linear, quadratic, absolute value, cubic, exponential, and rational functions.
Step 2: Identifying Transformations
Transformations are changes to the parent function that affect the graph of the function. These changes can include shifts in the x or y direction, stretches or compressions of the graph, or reflections across the x or y axis. To identify transformations, it is important to look for any changes to the equation of the function.
Step 3: Applying Transformations
Once the transformations have been identified, they can be applied to the parent function to create a new graph. This can be done by adding or subtracting constants to the equation, multiplying or dividing by constants, or adding or subtracting variables. It is also important to consider the order of the transformations; some transformations must be applied before others in order to achieve the desired effect.
Step 4: Analyzing the Graph
Once the transformations have been applied to the parent function, the resulting graph can be analyzed. It is important to look at the shape of the graph and note any changes that have been made by the transformations. Additionally, it is helpful to consider the domain and range of the graph, as this can help to determine the type of transformation that was applied.
By following these steps, it is possible to accurately identify parent functions and transformations. Doing so can help to gain a better understanding of the behavior of a function and the effects of various transformations.
Exploring the World of Parent Functions and Transformations: A Beginner’s Guide to Working With Worksheets
Parent functions and transformations are important concepts for students to understand in mathematics. They can be used to describe a wide variety of mathematical relationships and can even be applied to real-world problems. This guide will provide an introduction to the world of parent functions and transformations and help beginners become familiar with the worksheets that can help them learn more about these topics.
Parent functions are the most basic form of a function family. These functions are the simplest forms of equations and can be used to represent a variety of relationships. Examples of parent functions include linear, quadratic, exponential, logarithmic, and trigonometric functions. Each of these functions has its own unique characteristics, which can be studied in more detail with the help of worksheets.
Transformations are the changes that can be made to parent functions. These changes can include shifting the graph left or right, stretching or shrinking the graph, and reflecting the graph across different axes. With the help of worksheets, students can practice applying transformations to parent functions, helping them understand how these changes affect the graph’s overall shape.
Worksheets are a useful tool for exploring parent functions and transformations. They can be used to practice and review key concepts, such as the different types of parent functions and the effects of transformations on a graph. Worksheets can also be used to examine more complex problems, such as finding the inverse of a function or determining the equation of a circle.
By studying parent functions and transformations with the help of worksheets, students can gain a deeper understanding of these topics. This guide provides a basic introduction to the world of parent functions and transformations and the worksheets that can help beginners learn more about these concepts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Parent Functions And Transformations Worksheet is a great tool for helping students understand how to identify and manipulate parent functions and their corresponding transformations. It encourages them to explore the different types of functions and transformations and helps them gain a better understanding of the overall concept. With practice, students will become more confident in their abilities to identify and transform parent functions and will be better prepared for future math courses.
[addtoany]
![Access Free Transformations Of Parent Functions Worksheet [Pdf] - Vcon With Parent Functions And Transformations Worksheet](https://worksheet1.wp-json.my.id/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/access-free-transformations-of-parent-functions-worksheet-pdf-vcon-with-parent-functions-and-transformations-worksheet.png)
![Access Free Transformations Of Parent Functions Worksheet [Pdf] – Vcon With Parent Functions And Transformations Worksheet](https://worksheet1.wp-json.my.id/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/access-free-transformations-of-parent-functions-worksheet-pdf-vcon-with-parent-functions-and-transformations-worksheet-150x150.png)