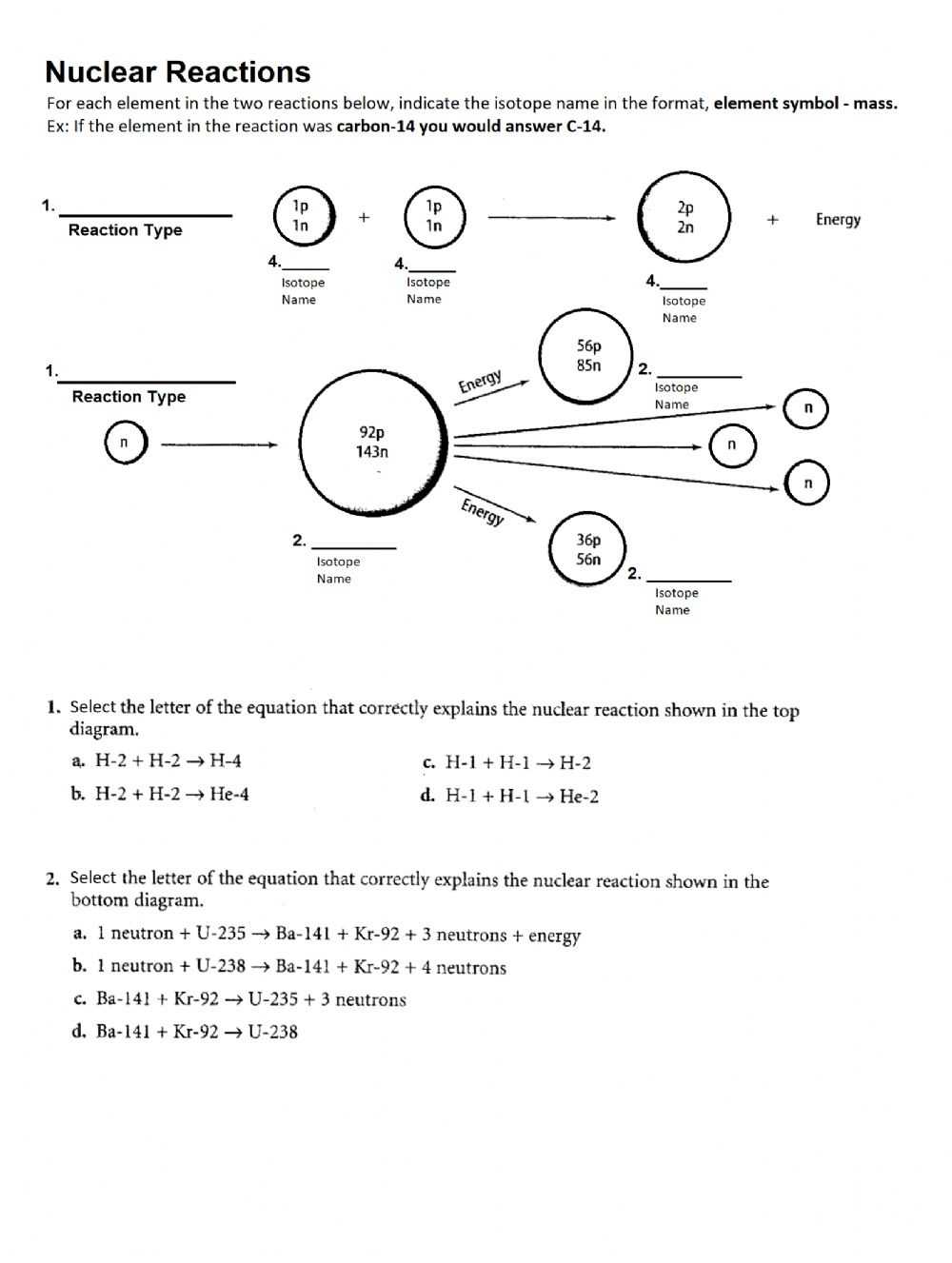
Exploring Nuclear Decay Worksheet Answers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Radioactive Decay
1. What is Nuclear Decay?
Nuclear decay is the process of a nucleus of an atom spontaneously losing energy by emitting particles such as protons, neutrons, alpha particles, beta particles, and/or gamma rays. This process is also known as radioactivity, and is a form of naturally occurring energy transformation. During nuclear decay, the nucleus of an atom decays into a different type of nucleus with a different atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus.
2. What are the Different Types of Nuclear Decay?
[toc]
There are four main types of nuclear decay: alpha decay, beta decay, gamma decay, and electron capture.
Alpha decay occurs when a nucleus releases an alpha particle, which is a helium nucleus composed of two protons and two neutrons. This type of decay is the most common form of naturally occurring radioactive decay and results in a reduction of the atomic number by two and an increase in the mass number by four.
Beta decay occurs when a neutron in the nucleus of an atom decays into a proton and an electron. The number of protons in the nucleus increases by one, while the number of neutrons decreases by one.
Gamma decay occurs when a nucleus emits a high-energy photon, which is a packet of energy in the form of light. Gamma decay does not alter the atomic number or the mass number of the atom.
Finally, electron capture occurs when an electron is captured by the nucleus of an atom and combines with a proton to form a neutron. This type of decay results in a decrease of the atomic number by one and no change in the mass number.
3. What is Half-Life?
Half-life is the amount of time it takes for half of the original amount of a radioactive isotope to decay. It is an important concept in the field of nuclear physics and is used to estimate the age of materials containing radioactive isotopes. Half-life is typically expressed in terms of years, but it can also be expressed in terms of seconds or other time units. The amount of time it takes for a given radioactive isotope to decay is determined by its half-life.
Understanding Nuclear Decay Worksheet Answers: A Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Half-Lives and Decay Rates
1. What Is Nuclear Decay?
Nuclear decay is the spontaneous process in which an unstable nucleus undergoes a change in its structure, releasing energy in the form of radiation. This process is also known as radioactive decay.
2. What Are Half-Lives?
A half-life is the time it takes for half of the atoms of a given radioactive element to decay. This period does not depend on the amount of the material present, but rather on the element itself.
3. What Is the Decay Rate?
The decay rate is the speed at which a nucleus decays. It is usually expressed as the number of nuclei decaying per unit time.
4. How Is Half-Life Calculated?
Half-life can be calculated by taking the natural logarithm (ln) of the ratio of the initial number of nuclei to the number of nuclei remaining after a given time period. The half-life is then equal to the time period multiplied by the natural logarithm of two.
5. How Is Decay Rate Calculated?
The decay rate can be calculated by taking the natural logarithm (ln) of the ratio of the number of nuclei remaining after a given time period to the initial number of nuclei. The decay rate is then equal to the natural logarithm of two divided by the time period.
Analyzing Nuclear Decay Worksheet Answers: How to Interpret Results and Draw Conclusions from Complex Data
Interpreting the results from a nuclear decay worksheet can be a daunting task, particularly if the data is complex. In order to successfully draw conclusions from the data, it is important to understand the basic principles of nuclear decay and the mathematical relationships involved.
First, the nuclear decay equation must be understood. This equation states that the rate of radioactive decay is proportional to the amount of radioactive material present. This means that as the amount of radioactive material decreases, the rate of decay will also decrease. As such, the results from a nuclear decay worksheet should indicate a decrease in activity as the amount of radioactive material is reduced.
Second, the results should be interpreted in terms of the nuclear decay equation. This means that the amount of radioactive material present is determined by the rate of decay and the total amount of radioactive material present. The results should therefore show a decrease in activity as the amount of radioactive material is reduced.
Third, the results should be interpreted in terms of the nuclear decay equation. This means that the activity should decrease as the amount of radioactive material is reduced. This should also be shown in the results from the nuclear decay worksheet.
Finally, the results should be interpreted in terms of the nuclear decay equation. This means that the results should show an increase in activity as the amount of radioactive material is increased. This should also be shown in the results from the nuclear decay worksheet.
By understanding the basic principles of nuclear decay and the mathematical relationships involved, it is possible to interpret the results from a nuclear decay worksheet and draw meaningful conclusions. As such, these results can be used to understand the nature of nuclear decay and its implications for the environment and human health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Nuclear Decay Worksheet Answers provide a great way to learn about nuclear decay and the various types of radioactive materials. It is an important tool for students to understand the concepts of nuclear radioactivity and its effects on everyday life. The worksheet also helps to reinforce the understanding of the different types of radiation and the associated risks. Overall, the Nuclear Decay Worksheet Answers provide an excellent way to learn about nuclear decay and the various types of radioactive materials.
[addtoany]