Exploring the Basics of Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids Worksheet: A Guide for Educators
Metals, nonmetals and metalloids are three distinct classes of elements with different physical and chemical properties. Educators can use this worksheet to explore the basics of these three categories of elements.
The worksheet begins with a brief introduction to the three categories of elements. It explains how metals, nonmetals and metalloids differ from one another, and how they are used in everyday life. It then moves on to explore the physical and chemical properties of metals, nonmetals and metalloids. It includes questions to help students understand the differences between the three categories, and to apply this knowledge to everyday life.
Next, the worksheet introduces the concept of periodic table of elements. It explains the labeling system used to identify elements and how this system can be used to help identify metals, nonmetals and metalloids. Finally, the worksheet provides a series of questions and activities to help students understand the basics of metals, nonmetals and metalloids.
[toc]
This worksheet is designed to provide educators with a comprehensive yet concise introduction to the basics of metals, nonmetals and metalloids. It is suitable for use in elementary and secondary classrooms, and can be used to help students gain a better understanding of the physical and chemical properties of these three classes of elements.
The Benefits of Using Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids Worksheets in the Classroom
Metals, nonmetals and metalloids worksheets are a valuable tool for educators to use in the classroom. These worksheets help to provide students with a thorough understanding of the properties of each of the elements. They help to develop critical thinking skills, problem solving and the ability to apply knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Metals, nonmetals and metalloids worksheets are an excellent way to help students to understand the physical and chemical properties of each element. These worksheets provide a visual representation of the properties of each element, allowing students to better comprehend the differences between them. They also help to show students how different elements interact with each other, which further enhances their understanding of their properties.
Metals, nonmetals and metalloids worksheets can be used to reinforce concepts taught in the classroom, or to supplement current information. By providing students with a visual representation of the elements, they can better comprehend the material and gain a more comprehensive understanding of the concepts.
Metals, nonmetals and metalloids worksheets are also great for providing students with practice questions. These worksheets can be used to assess student knowledge and understanding of the material. They also provide an opportunity for students to practice their skills in a safe and secure environment, without the worry of being judged.
Metals, nonmetals and metalloids worksheets are also great for helping to facilitate team-building activities in the classroom. By having students work together on these worksheets, they can gain a better understanding of each other’s strengths and weaknesses. This can lead to increased collaboration, improved communication and a deeper appreciation of each other’s work.
In conclusion, metals, nonmetals and metalloids worksheets are a great tool for educators to use in the classroom. They help to provide students with a thorough understanding of the properties of each element and the ability to apply that knowledge to real-world scenarios. Additionally, they help to foster teamwork and collaboration, which can lead to a stronger understanding of each other’s abilities.
Understanding the Different Properties of Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids: A Comprehensive Overview
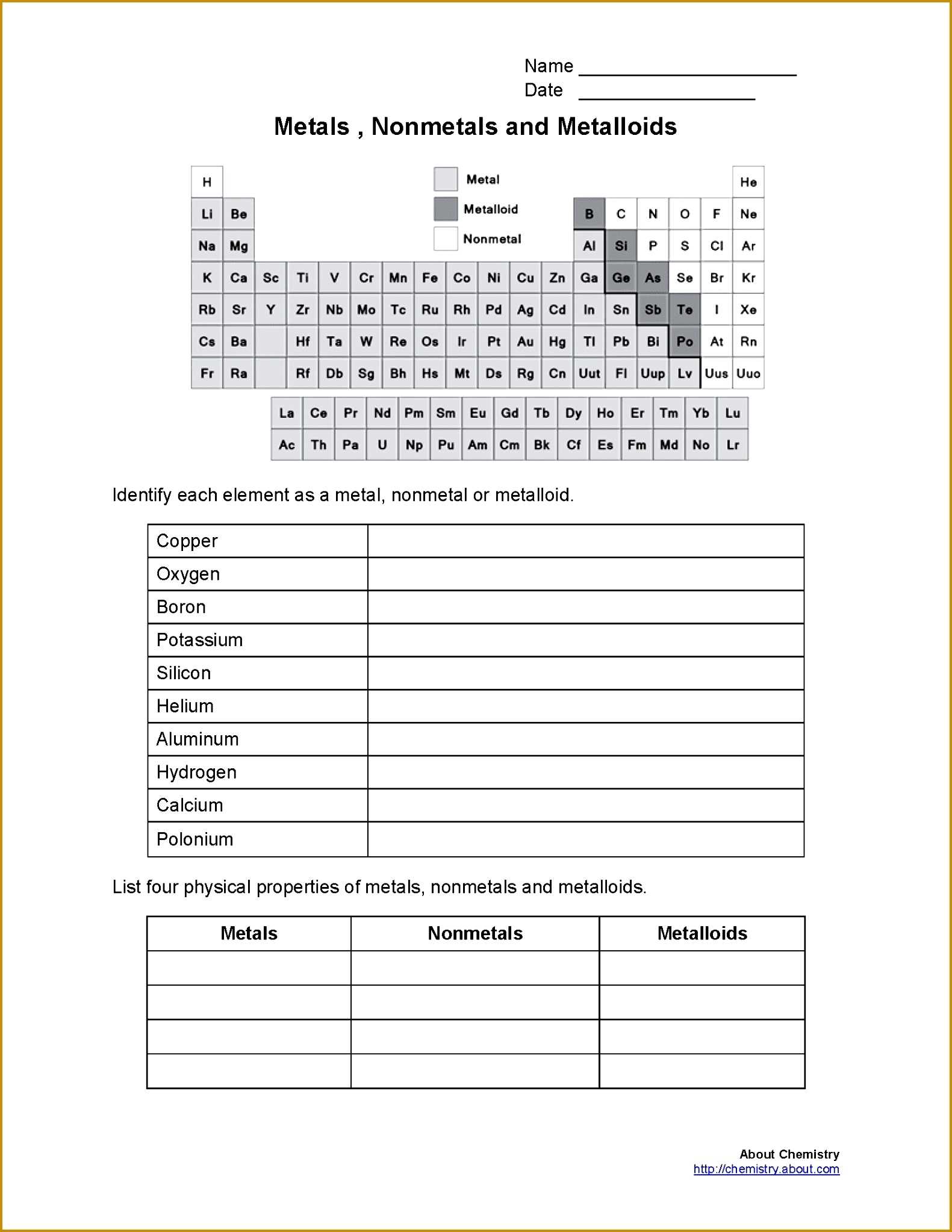
Metals, nonmetals and metalloids are the three main classifications of elements found on the periodic table. They each have distinct properties that make them unique. Understanding these properties is essential for correctly identifying and categorizing elements.
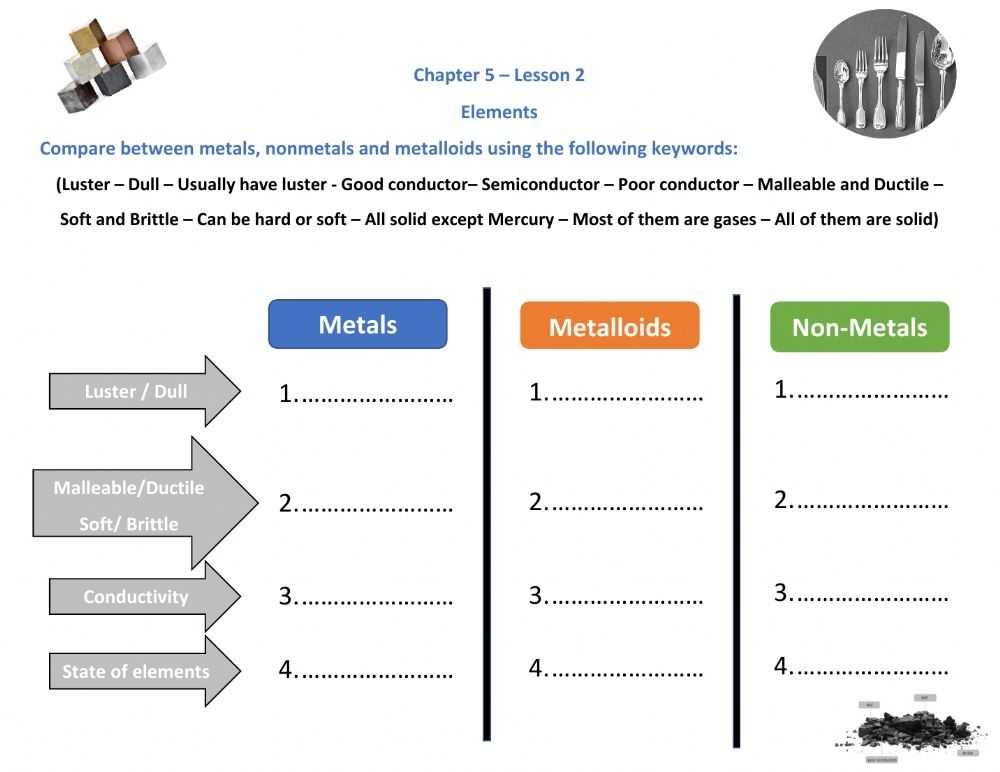
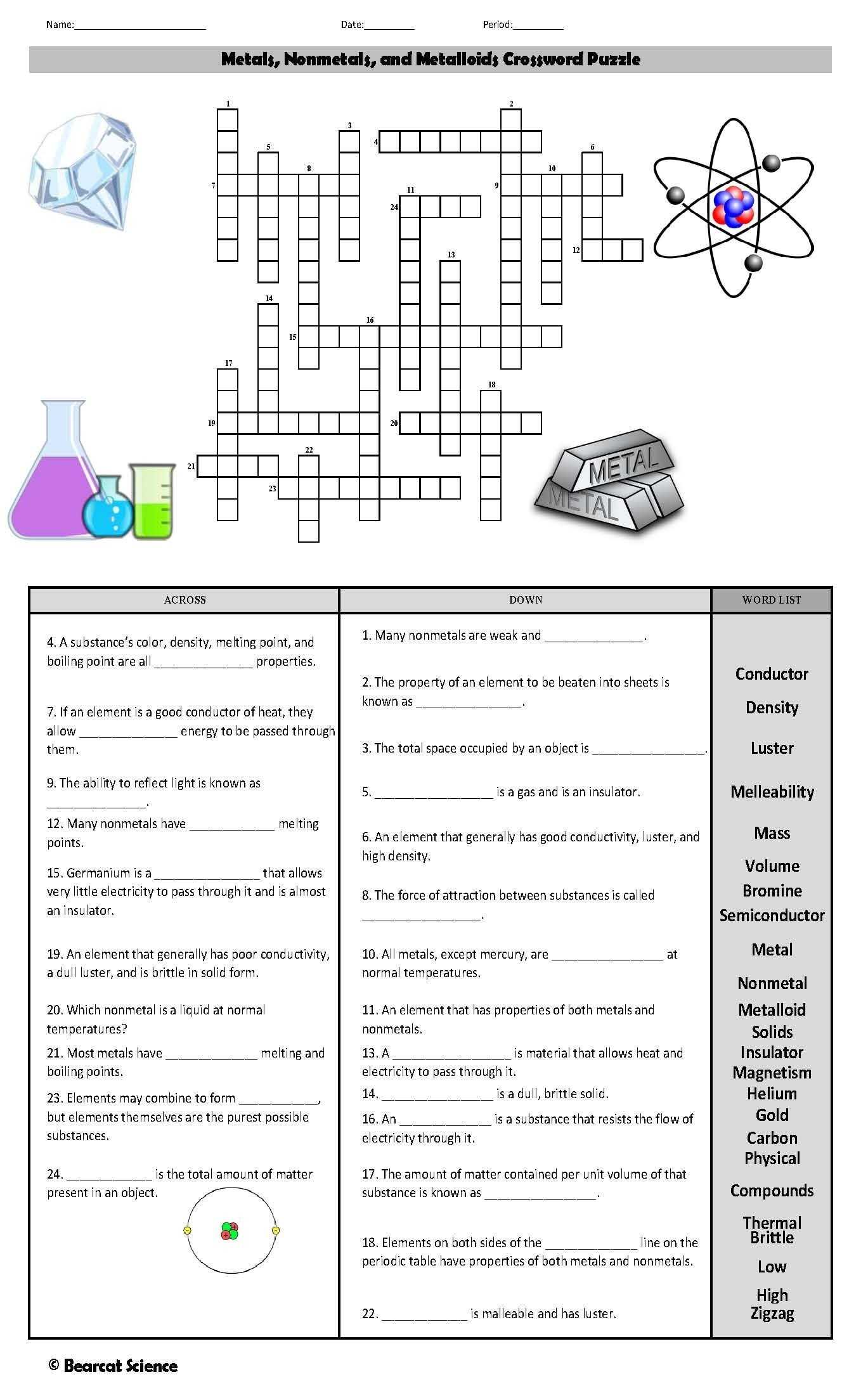
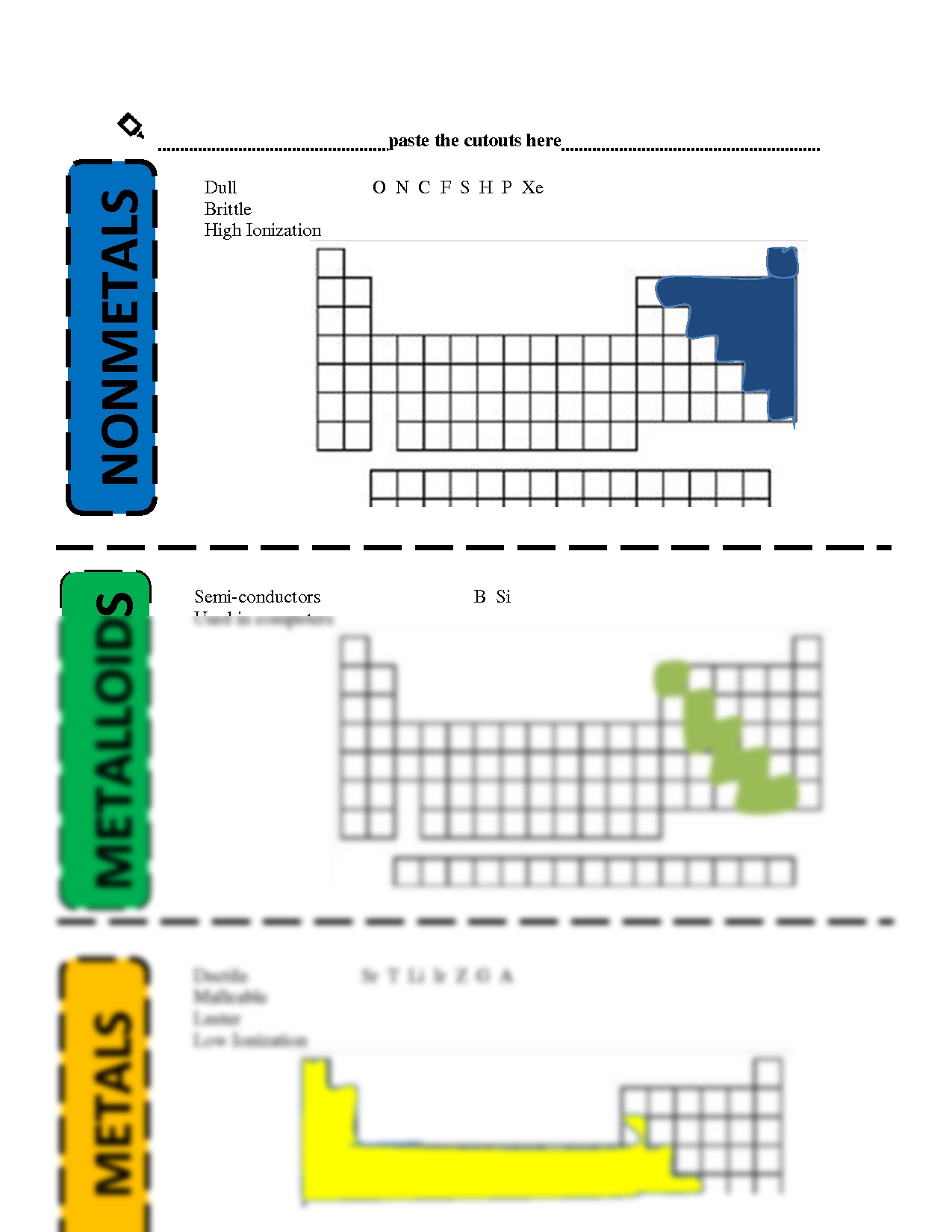
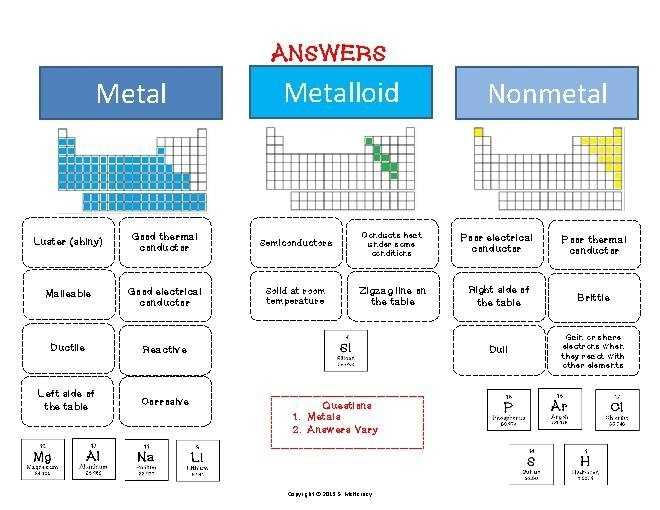
Metals are elements that are generally characterized by their malleability and ductility, as well as their ability to conduct heat and electricity. Common examples of metals include iron, copper, aluminum, and gold. Metals are also typically characterized by their luster. When a metal is scratched, it will usually leave a shiny streak on the surface.
Nonmetals are elements that are not malleable or ductile and do not conduct heat or electricity as well as metals. Examples of nonmetals include carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur. Nonmetals are generally characterized by their dull appearance and lack of luster.
Metalloids are elements that possess properties of both metals and nonmetals. They are characterized by their shiny appearance and ability to conduct electricity, but are not as malleable or ductile as metals. Examples of metalloids include silicon, boron, arsenic, and germanium.
Overall, metals, nonmetals and metalloids each have distinct properties that make them unique. Knowing these properties is essential for correctly identifying and categorizing elements. Understanding the differences between these three categories of elements can help in many different areas, from chemistry to engineering.
Investigating the Role of Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids In Everyday Life: An Interactive Worksheet Activity
Metals, nonmetals, and metalloids are all essential elements of life and play a major role in various everyday activities. Metals are malleable, ductile, and have a luster that makes them perfect for many applications. Nonmetals are the opposite of metals and are brittle, non-ductile, and generally lack a metallic luster. Metalloids are elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals.
Metals are used in many everyday items, from the metal frames of buildings and vehicles to smaller items such as coins and jewelry. Steel, aluminum, and copper are some of the most popular metals used in everyday life. Steel is a strong, durable metal that is widely used in construction, transportation, and manufacturing. Aluminum is a light metal that is often used in automotive and aerospace applications. Copper is a malleable metal that is often used in electrical wiring and plumbing.
Nonmetals are important for their insulative properties. They are used in products such as insulation for wires and buildings, and for the fabrication of plastics and rubber. Carbon, sulfur, and oxygen are some of the most important nonmetals. Carbon is used to make diamond and graphite, and is also a key component of many plastics and rubber materials. Sulfur is used in the production of fertilizers, dyes, and medicines. Oxygen is essential for life, as it is needed for combustion, respiration, and oxidization.
Metalloids are elements that are hard to classify as either a metal or a nonmetal due to their unique properties. Some of the most important metalloids are silicon, germanium, and arsenic. Silicon is used in the production of semiconductors, which are the basis of modern electronics. Germanium is used to make transistors that are used in computers and other electronic devices. Arsenic is used in a variety of applications such as glassmaking and metallurgy.
Overall, metals, nonmetals, and metalloids are all essential elements of life and play a major role in various everyday activities. From the construction of buildings to the production of electronics, these elements are essential for modern life. By understanding the properties and uses of these elements, we can better appreciate their importance in our everyday lives.
Conclusion
The Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the properties and characteristics of these three categories of elements. It is important to understand the differences between the three, as they can help to determine the potential uses and applications of each individual element. Understanding the properties and characteristics of each element can also be beneficial when it comes to researching and developing new technologies. By understanding how these elements interact with each other and their environment, we can ensure that our future is safe and secure.
[addtoany]