Analyzing Macromolecules Worksheet 2: Overview and Key Takeaways
Macromolecules Worksheet 2 provides an overview of the different types of macromolecules and their functions in living organisms. It begins by introducing the four major macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It then goes on to discuss the structure and function of each macromolecule, as well as the role they play in metabolism.
The worksheet also provides an overview of the different kinds of macromolecules, such as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. It also discusses the differences between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, the formation of proteins and their role in metabolism, and the structure of nucleic acids.
The key takeaways from Macromolecules Worksheet 2 include:
[toc]
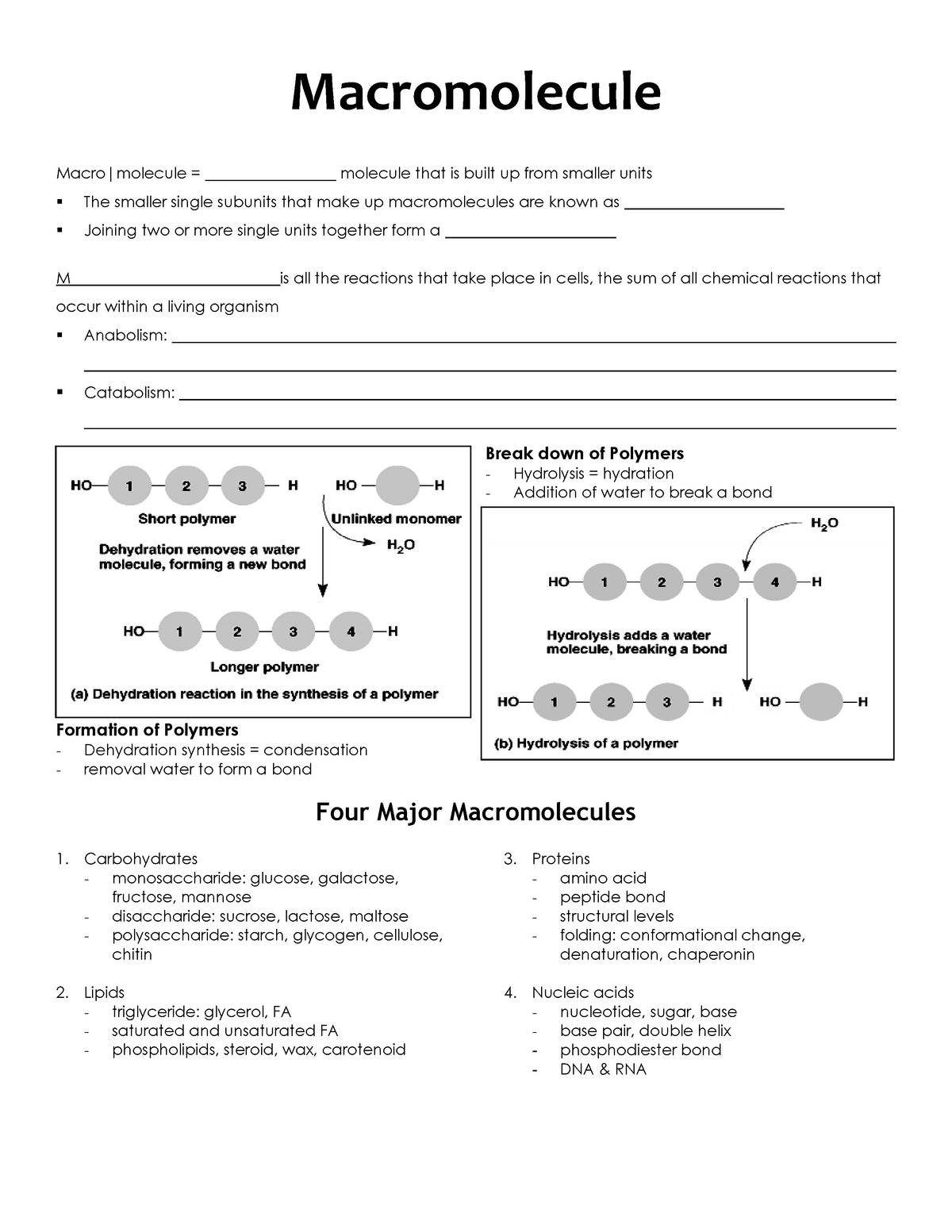
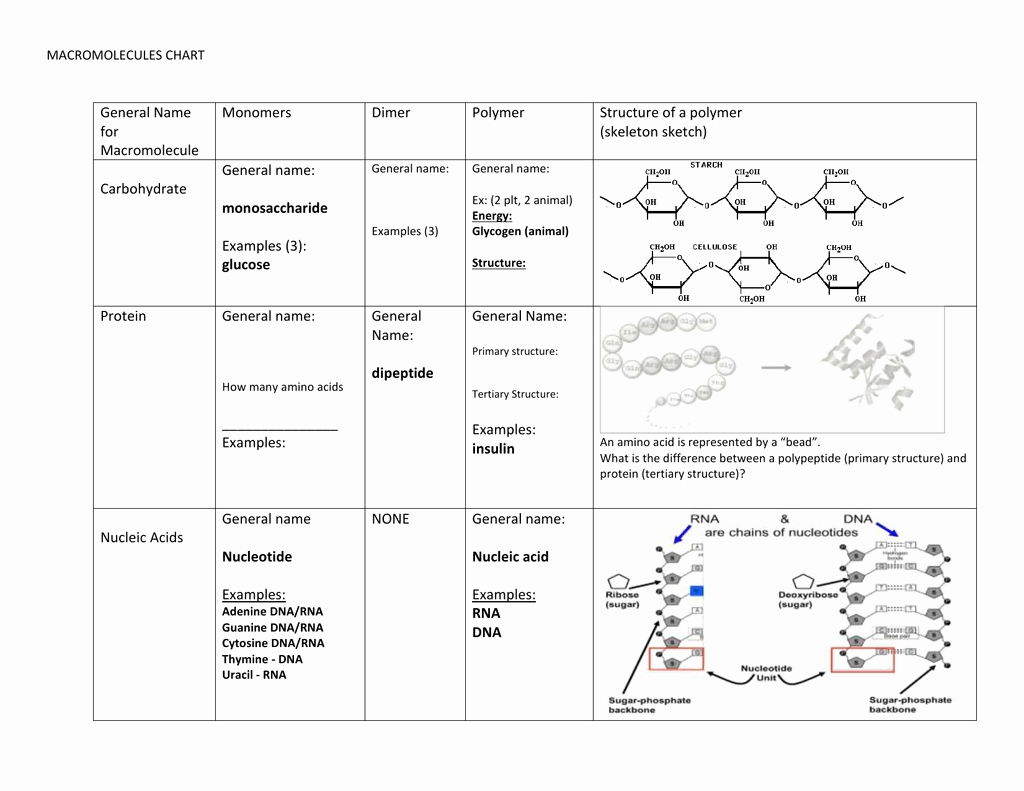
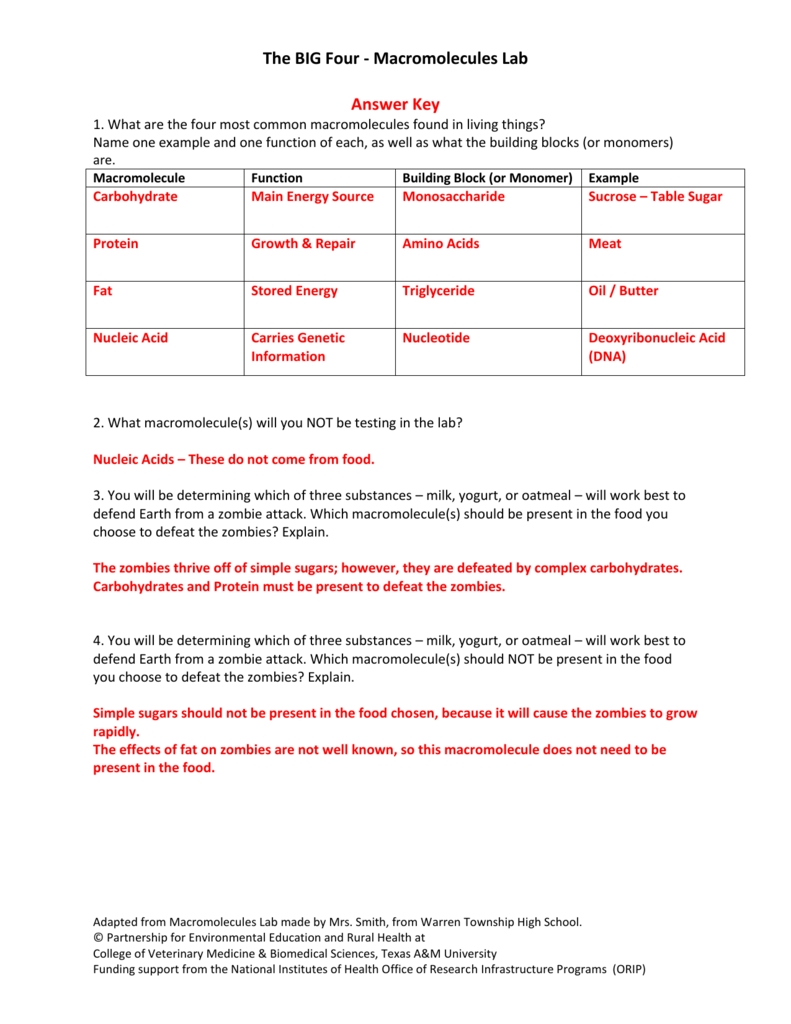
• Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are the four major macromolecules that form the essential building blocks of life.
• Monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides are the different kinds of carbohydrates.
• Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids are the different kinds of lipids.
• Proteins are formed from the combination of amino acids and play a role in metabolism.
• Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, have a specific structure and play a role in genetics and heredity.
Overall, Macromolecules Worksheet 2 provides an overview of the different kinds of macromolecules and their functions in living organisms. It is an important resource for anyone studying biochemistry and biology.
Exploring the Different Types of Macromolecules in Worksheet 2
Macromolecules are large molecules composed of smaller units. These molecules are essential for life, as they form the structural materials of cells and form the basis of all biochemical processes. Worksheet 2 explores the different types of macromolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Carbohydrates are an important class of macromolecules, and they are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Carbohydrates include sugars, starches, and cellulose. They provide the energy needed for cellular processes and serve as a source of energy for the body.
Lipids are another type of macromolecule. They are composed of fatty acids, glycerol, and other components. Lipids are important for forming cellular membranes and for storing energy. Fats are a type of lipid, and they are used for insulation and for providing energy.
Proteins are complex macromolecules composed of amino acids. Proteins are important for processes such as metabolism, transport, and cell signaling. They are also used to make enzymes, hormones, and other molecules.
Nucleic acids are macromolecules composed of nucleotides. Nucleic acids include DNA and RNA, which carry genetic information and control the expression of genes.
Worksheet 2 explores the different types of macromolecules and their importance in living systems. By understanding the different types of macromolecules, we can better understand how life works and how organisms function.
Examining the Complexity of Macromolecules in Worksheet 2
The complexity of macromolecules is an important factor to consider when studying biology. Macromolecules are large molecules that are composed of smaller molecules or atoms. They are essential for life and are found in all living organisms. Macromolecules are composed of four main classes: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Each class of macromolecule has its own unique structure and function.
Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are an important source of energy for cells and are also used in a variety of other roles, including structure and recognition. Carbohydrates are composed of monosaccharides, which are single sugar molecules, and polysaccharides, which are chains of sugar molecules.
Proteins are composed of amino acids and are important for structure and function. Proteins are involved in many different processes such as transport, enzymatic activity, and cell signaling. Protein structure is extremely complex and can be organized into primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures.
Lipids are composed of fatty acids and are important for cellular structure and energy storage. They are also involved in many other processes such as cell signaling and recognition. Lipids can be organized into three main categories: phospholipids, glycolipids, and steroids.
Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides and are the genetic material of all living organisms. They are involved in the storage and replication of genetic information. Nucleic acids can be organized into two main categories: DNA and RNA.
The complexity of macromolecules is an essential factor to consider when studying biology. Each class of macromolecule has its own unique structure and function, and all of these molecules are essential for life. By studying the complexity of macromolecules and understanding their structure and function, we can gain a better understanding of the biological processes that take place in living organisms.
Working Through the Unique Challenges of Macromolecules Worksheet 2 Answers
1. Describe the unique challenge of macromolecules:
The unique challenge of macromolecules is that they are composed of multiple, smaller molecules or atoms that must be arranged in a specific and precise manner in order to fulfill their biological role. As macromolecules are composed of many smaller units, it can be difficult to accurately predict their behavior and interactions, as well as how they will react with other molecules. Additionally, macromolecules can be complex and highly organized, making them difficult to study and fully understand. Such complexity requires advanced analytical techniques such as x-ray crystallography and mass spectrometry in order to accurately determine the structure and function of macromolecules.
Conclusion
The Macromolecules Worksheet 2 Answers provide a thorough overview of the four main macromolecules – carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. It helps to explain the structure and function of each macromolecule and how they are related to one another. This knowledge can help us to better understand how these molecules function in our bodies, how they are incorporated into our diets, and how they may be manipulated to benefit our health.
[addtoany]