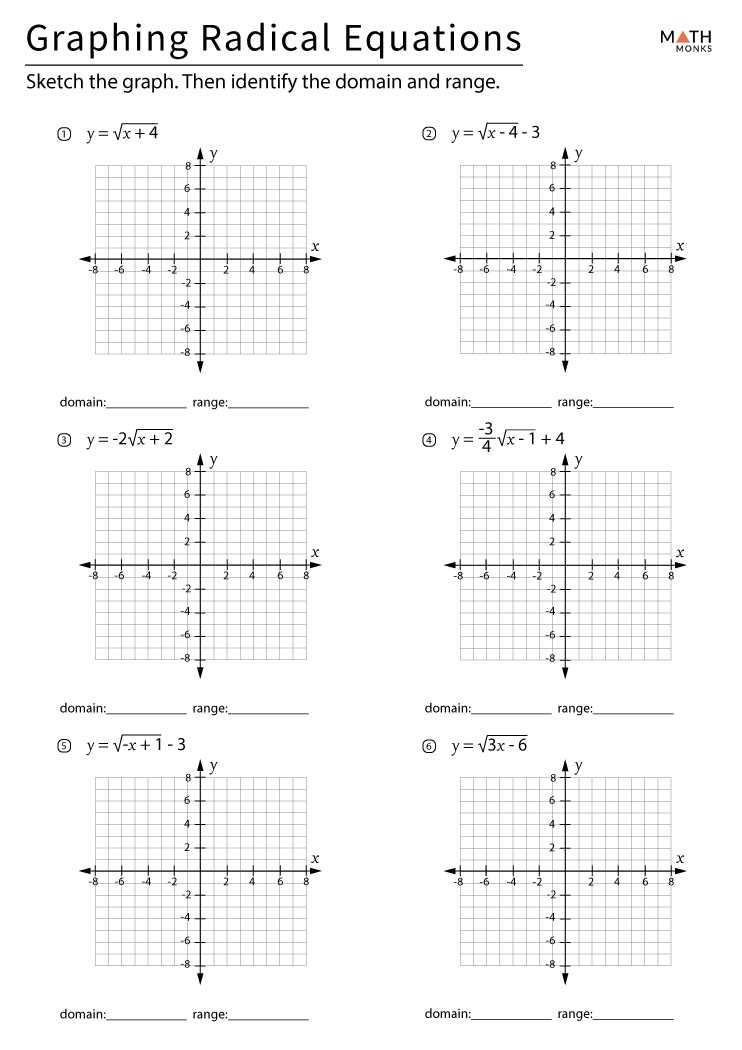
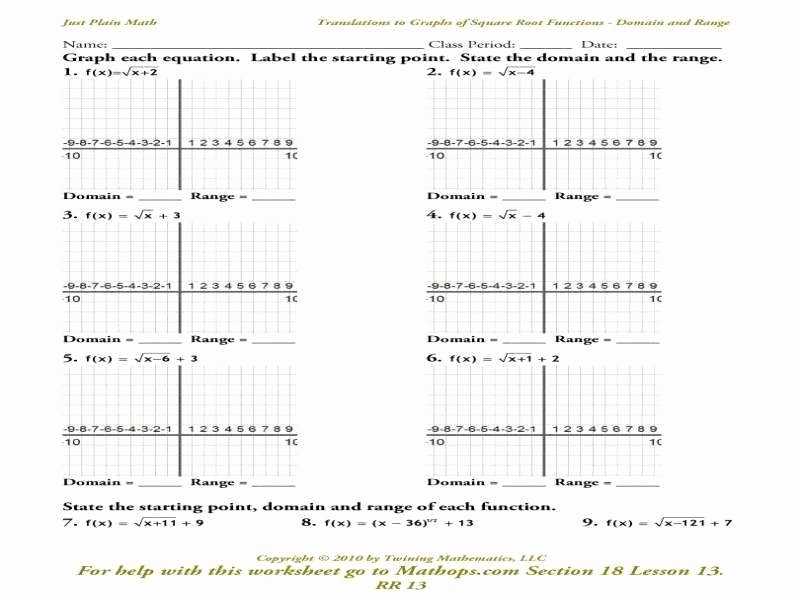
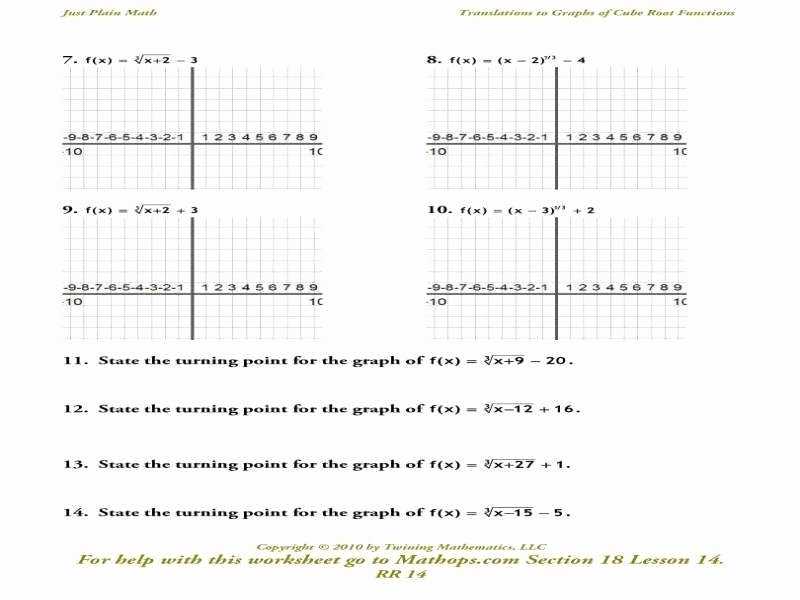
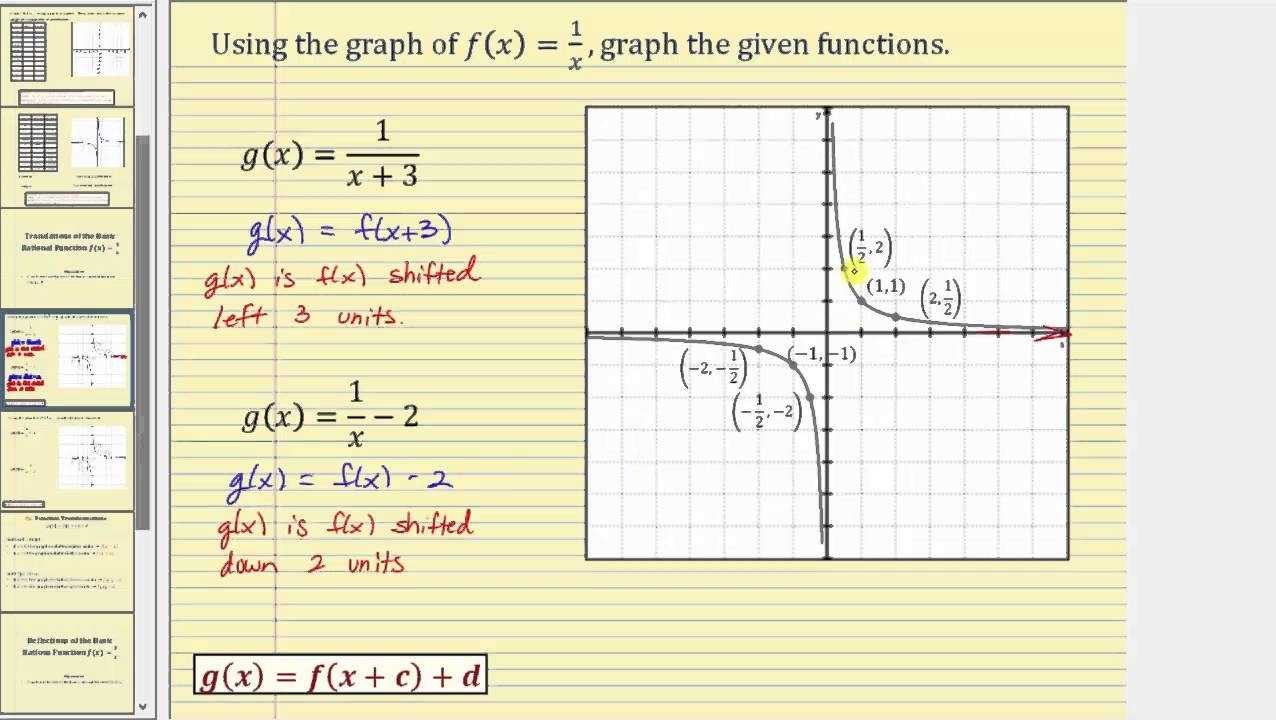
How to Graph a Rational Function: A Step-by-Step Guide Using a Graphing Rational Functions Worksheet
Graphing rational functions can be a challenging task for any student. However, with some practice and guidance, students can learn to graph these functions with ease. This step-by-step guide will use a graphing rational functions worksheet to help students understand the process.
Step 1: Identify the Rational Function
Before anything else can be done, students must first identify the type of rational function they are dealing with. Typically, rational functions are written in the form of a fraction, where the denominator and numerator are both polynomials. It is important to understand the structure of the function in order to plot it accurately.
[toc]
Step 2: Determine the Domain of the Function
The domain of a rational function is the set of all values for which the function is defined. The domain can be determined by finding the values of x for which the denominator of the function is equal to 0. These values should be listed in a table for future reference.
Step 3: Find the Asymptotes
The asymptotes of a rational function are the lines which the graph approaches, but never crosses. To determine the asymptotes of the function, set the denominator equal to 0 and solve for x. The resulting values will be the x-intercepts of the asymptotes.
Step 4: Sketch the Graph
Now that the domain and asymptotes have been identified, it is time to begin sketching the graph. Start by plotting the x-intercepts and asymptotes of the function. Then, connect them with straight lines to form the basic shape of the graph.
Step 5: Plot the Points and Smooth the Curve
The final step is to plot additional points on the graph in order to smooth out the curve. To do this, simply choose a few x-values within the domain, plug them into the equation, and plot the resulting points. Once all the points have been plotted, connect them with a smooth curve.
By following these steps, students can easily graph rational functions using a graphing rational functions worksheet. With practice and guidance, students can become proficient in this skill and apply it to their studies.
Exploring the Different Types of Asymptotes and Their Applications in Graphing Rational Functions
An asymptote is a line that a function approaches as it reaches infinity, but never actually reaches. Asymptotes are an important tool in the field of mathematics, particularly in the graphing of rational functions. In this article, we will explore the different types of asymptotes and their applications in graphing rational functions.
There are three main types of asymptotes: horizontal, vertical, and oblique. A horizontal asymptote is a horizontal line that a function approaches as it reaches infinity. A vertical asymptote is a vertical line that a function approaches as it reaches infinity. An oblique asymptote is a slanted line, usually in the form of a diagonal, that a function approaches as it reaches infinity.
In the graphing of rational functions, asymptotes are used to define the boundaries of the graph. For example, if a rational function has a horizontal asymptote at y=5, this means that the graph of the rational function will never go beyond the y-axis at y=5. Similarly, if a rational function has a vertical asymptote at x=2, this means that the graph of the rational function will never go beyond the x-axis at x=2. Asymptotes are also used to identify the behavior of a rational function near the boundaries of the graph.
Finally, asymptotes can be used to identify the vertical and horizontal intercepts of a rational function. A vertical intercept is the point at which the graph of a rational function intersects the x-axis. A horizontal intercept is the point at which the graph of a rational function intersects the y-axis. Asymptotes can be used to identify the vertical and horizontal intercepts of a rational function, since the intercepts are located at the boundaries of the graph.
In conclusion, asymptotes are an important tool in the field of mathematics, especially in the graphing of rational functions. Asymptotes are used to define the boundaries of the graph, to identify the behavior of a rational function near the boundaries of the graph, and to identify the vertical and horizontal intercepts of a rational function.
Solving a System of Equations Using a Graphing Rational Functions Worksheet
Solving a system of equations using a graphing rational functions worksheet can be a useful tool for understanding the relationship between two variables. This worksheet helps to graphically illustrate the relationships between two variables, which can then be used to determine the solution of a system of equations.
To begin, the user must first enter the two equations into the worksheet. Each equation can be represented by a graph and each variable is represented by a point on the graph. By connecting the points, the user can determine the parameters of the equation and the intersection of the two equations. This intersection will be the solution of the system of equations.
Once the equations have been entered, the user must choose the appropriate graphing method. The most common graphing method is the Cartesian graph, which uses two perpendicular axes to plot the equations. The user should be sure to select the appropriate scales for both axes so that the graph accurately illustrates the relationship between the variables.
Once the graph has been plotted, the user can now examine the relationship between the two equations. By looking at the graph, the user can determine the values of both variables at the point of intersection. The user can also identify any areas of the graph that may indicate a solution to the system of equations.
Finally, the user should review the solution to ensure accuracy. By verifying the solution, the user can be sure that the solution is correct and that the equations are correctly graphed.
Using a graphing rational functions worksheet can be a useful tool for understanding the relationship between two variables. By plotting the equations, the user can determine the solution of a system of equations and verify the accuracy of the solution. This worksheet can be used to help students gain a better understanding of the relationship between two variables and to aid in problem solving.
Analyzing the Impact of Domain and Range on Graphing Rational Functions
Graphing rational functions involves understanding the domain and range of the equation. Domain and range are two concepts of mathematics that determine the set of all possible input and output values of a function. Domain is the set of all inputs that can be used in a function, while range is the set of all outputs that the function can produce. Knowing the domain and range of a rational function can help visualize the graph and predict its behavior, as the graph will be constrained to the defined domain and range.
The domain of a rational function is determined by the denominator of the equation. The denominator must not equal zero, as this would result in division by zero, which is an undefined operation. Therefore, the domain is the set of all values that make the denominator not equal to zero. The range is determined by the numerator of the equation. The range of a rational function is all real numbers except the values that make the numerator equal to zero.
By understanding the domain and range of a rational function, it is possible to create an accurate graph. The domain of the rational function will dictate the horizontal boundaries of the graph, while the range will set the vertical boundaries. The shape and behavior of the graph will be determined by the remaining components of the equation. Therefore, it is essential to be aware of the domain and range of a rational function in order to accurately graph it.
Utilizing Technology to Enhance Graphing Rational Functions Learning with a Worksheet
In the modern classroom, utilizing technology to teach graphing rational functions can be a powerful learning tool. With the right technology and worksheet, students can quickly and efficiently learn the concepts of graphing rational functions.
When teaching rational functions, a worksheet can be a great tool to help students understand the topic. A worksheet helps to break down the concept into smaller, more manageable pieces. This allows students to focus on each part of the concept and gain a better understanding of the overall topic.
When teaching a worksheet on graphing rational functions, it is important to utilize technology. Technology can help to streamline the process and make it easier for students to comprehend and retain the material. For example, a graphing calculator can be used to quickly graph equations and help students visualize the concept in action. Other technologies, such as an online graphing tool, can also be used to quickly generate graphs with a few clicks of the mouse.
In addition to the use of technology, a worksheet can be enhanced with visual aids. This can include pictures of graphs of different functions, as well as equations with examples of how the equations are used to graph the functions. By seeing the graphs and equations in action, students can more easily grasp the concept.
Finally, a worksheet could also include practice problems or quizzes that help the students assess their understanding of the concept. This can help the students to identify areas in which they need to review or refine their understanding.
Utilizing technology to teach graphing rational functions with a worksheet can be an effective learning tool. By combining technology with visual aids and practice problems, students can gain a better understanding of the concept and be better prepared to tackle more difficult topics.
Understanding Vertical and Horizontal Shifts when Graphing Rational Functions
When graphing rational functions, vertical and horizontal shifts can have a significant effect on the overall graph. A vertical shift refers to a movement of the graph up or down along the y-axis. This can be caused by a change in the constant, or c-value, of the function. If the c-value is increased, the graph will shift up, and if the c-value is decreased, the graph will shift down. A horizontal shift, on the other hand, refers to a movement of the graph left or right along the x-axis. This can be caused by a change in the coefficient, or a-value, of the function. If the a-value is increased, the graph will shift to the left, and if the a-value is decreased, the graph will shift to the right. Understanding the effect of vertical and horizontal shifts when graphing rational functions can help to more accurately represent the data and draw meaningful conclusions.
Investigating the Properties of Graphing Rational Functions with a Worksheet
This worksheet is designed to help students investigate the properties of graphing rational functions. The worksheet contains three sections which are designed to help students gain an understanding of how a rational function is graphed and how it can be manipulated.
The first section of the worksheet consists of a series of questions and examples related to the graphing of rational functions. It begins by introducing the student to the concept of a rational function and its graph. This section then provides examples of graphing simple rational functions, as well as questions related to the manipulation of the graph of the function.
The second section of the worksheet focuses on the concept of a rational function’s intercepts and asymptotes. It begins by introducing the student to the intercepts and asymptotes of a graph and how they are determined. This section then provides examples of graphing rational functions with specified intercepts and asymptotes. Finally, questions are included to help students recognize how the intercepts and asymptotes will change when the coefficients of the function are changed.
The third section of the worksheet is designed to help students gain an understanding of how the graph of a rational function is affected by changes in its coefficients. This section begins by introducing the student to the concept of a coefficient and how it affects the shape of the graph. This section then provides examples of how the graph of a rational function can be manipulated by changing its coefficients. Finally, questions are included to help students recognize how the graph of the function is affected by changes in its coefficients.
Overall, this worksheet is designed to help students gain an understanding of the properties of graphing rational functions. Through a series of questions and examples, students will learn how to graph rational functions, recognize their intercepts and asymptotes, and manipulate the shape of the graph by changing the coefficients of the function.
Exploring the Impact of Multiplicity and End Behavior on Graphing Rational Functions
Rational functions are mathematical expressions that involve the division of two polynomials. They are used to model a variety of real-world phenomena, such as population growth and the dynamics of a business cycle. As such, it is important to have a thorough understanding of their behavior in order to properly interpret their relevance. This article will explore the impact of multiplicity and end behavior on the graphing of rational functions.
Multiplicity is an important factor to consider when graphing rational functions. The multiplicity of a root of a rational function is the number of times the root is repeated. This can have a significant impact on the shape of the graph. For instance, if a root has a multiplicity of two, the graph of the rational function will have a point of inflection at the root. In other words, the graph will appear to dip down and then up again at the root. On the other hand, if the root has a multiplicity greater than two, the graph will appear to form a loop around the root.
The end behavior of a rational function also has an impact on its graph. End behavior is the behavior of the graph of a rational function as the domain value tends to either positive or negative infinity. If the degree of the numerator is greater than that of the denominator, the graph will approach positive infinity as the domain value tends to positive infinity and negative infinity as the domain value tends to negative infinity. Conversely, if the degree of the numerator is less than that of the denominator, the behavior will be reversed.
In conclusion, multiplicity and end behavior are both important factors to consider when graphing rational functions. The multiplicity of a root can affect the shape of the graph, while the end behavior can determine the direction the graph will tend towards as the domain value tends to infinity. Understanding these concepts is essential for interpreting the meaning of a graph of a rational function.
Conclusion
The Graphing Rational Functions Worksheet provides a comprehensive guide for students to understand how to graph rational functions. It gives them step-by-step instructions on how to identify the domain, intercepts, asymptotes, and vertical and horizontal lines. By understanding how to graph rational functions, students are able to visualize the mathematical equations and interpret them in a meaningful way. With this worksheet, students are better equipped to solve problems involving rational functions.
[addtoany]