A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing Your First Geometry Proof
1. Understand the basics: Before beginning a geometry proof, it is important to understand the basics of geometry. This includes learning the definitions of basic terms, such as line, angle, triangle, and circle. It also includes understanding the basic postulates and theorems that are used in geometric proofs.
2. Gather information: Before you begin writing your proof, you should gather all of the information you will need. This includes the given information, or assumptions, as well as any definitions or postulates that you will need to use in the proof.
3. Draw a diagram: Drawing a diagram is an important step in writing a geometric proof. This will help you to visualize the proof and make it easier to understand.
[toc]
4. State the goal: Once you have gathered the necessary information, you should state the goal of your proof. This is the conclusion that you will be trying to prove.
5. Make a plan: Once you have stated the goal of your proof, you should come up with a plan of how you will go about proving it. This plan should be organized in a logical order that will make it easier to follow.
6. Write the proof: After you have developed a plan, you can begin the process of writing the proof. This should include writing out each step in the proof in a clear, concise manner. Each step should be supported by a definition, postulate, or theorem.
7. Check the proof: After you have written the proof, you should check it for accuracy. You should also check that each step follows logically from the previous one.
Following this step-by-step guide will help you to write your first geometry proof in a clear, organized manner. With practice, you will become more comfortable with the process and be able to create proofs more quickly and efficiently.
10 Tips for Mastering Geometry Proofs
1. Read the problem carefully: Before you begin attempting to solve a geometry proof, take time to read the entire statement and be sure you understand exactly what you are being asked to prove.
2. Draw a diagram: Once you have a good understanding of the problem, draw a diagram that accurately reflects the given information. This will help you visualize the problem and assist in forming a plan of attack.
3. Identify given facts: Make a list of all the facts that you know to be true. This will help you keep track of what is given in the problem and what needs to be proven.
4. Make a plan: Creating a plan of attack will help you stay organized and focused while working on the proof.
5. Utilize theorems: Take advantage of theorems, postulates, and definitions that are applicable to the problem. This can help you make connections and move forward in the proof.
6. Construct logical arguments: Ensure that your proof includes logical arguments and is easy to follow.
7. Stay organized: As you work on the proof, be sure to keep track of your work and conclusions. This will help you stay focused and organized.
8. Check your work: Once you’ve completed the proof, go back and check all of your work to ensure that everything is correct.
9. Ask for help: If you are stuck or struggling, don’t be afraid to ask for help from a teacher or more experienced classmate.
10. Practice: Practice makes perfect! The more you practice, the more comfortable you will become with geometry proofs.
Exploring the Various Types of Geometry Proofs and Their Applications
Geometry proofs are the process of using logical reasoning to establish the truth behind a mathematical statement. Geometry proofs are used to prove theorems, postulates, and other mathematical statements. They are an essential part of geometry and are used in a variety of applications.
There are several types of geometry proofs. Direct proofs are the most straightforward and involve using the given information to logically prove a statement. Indirect proofs or proof by contradiction are an effective way of proving a statement by assuming the opposite to be true and deriving a contradiction. Proof by contradiction is often used when direct proof is difficult or impossible.
Two-column proofs are another type of geometry proof. This type of proof is used to organize the given information and the logical steps used to deduce the conclusion. The two columns are labeled “Given” and “Prove” and are used to organize the information. The “Given” column contains the known facts about the statement, and the “Prove” column contains the logical steps used to prove the statement.
Flow proofs are used to prove statements by organizing the information into a flowchart. This type of proof is visual in nature and is used to break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. Flow proof is often used to prove theorems involving multiple steps.
Geometry proofs are essential in mathematics and have a variety of applications. They are used to prove theorems, postulates, and other mathematical statements. They are also used in engineering and architecture to ensure the accuracy of designs and calculations. Geometry proofs are used in everyday life to solve problems and develop solutions.
In conclusion, geometry proofs are an essential part of mathematics and have a variety of applications. There are several types of geometry proofs, such as direct proofs, indirect proofs, two-column proofs, and flow proofs. Geometry proofs are used to prove theorems and postulates, as well as to solve everyday problems.
Conclusion
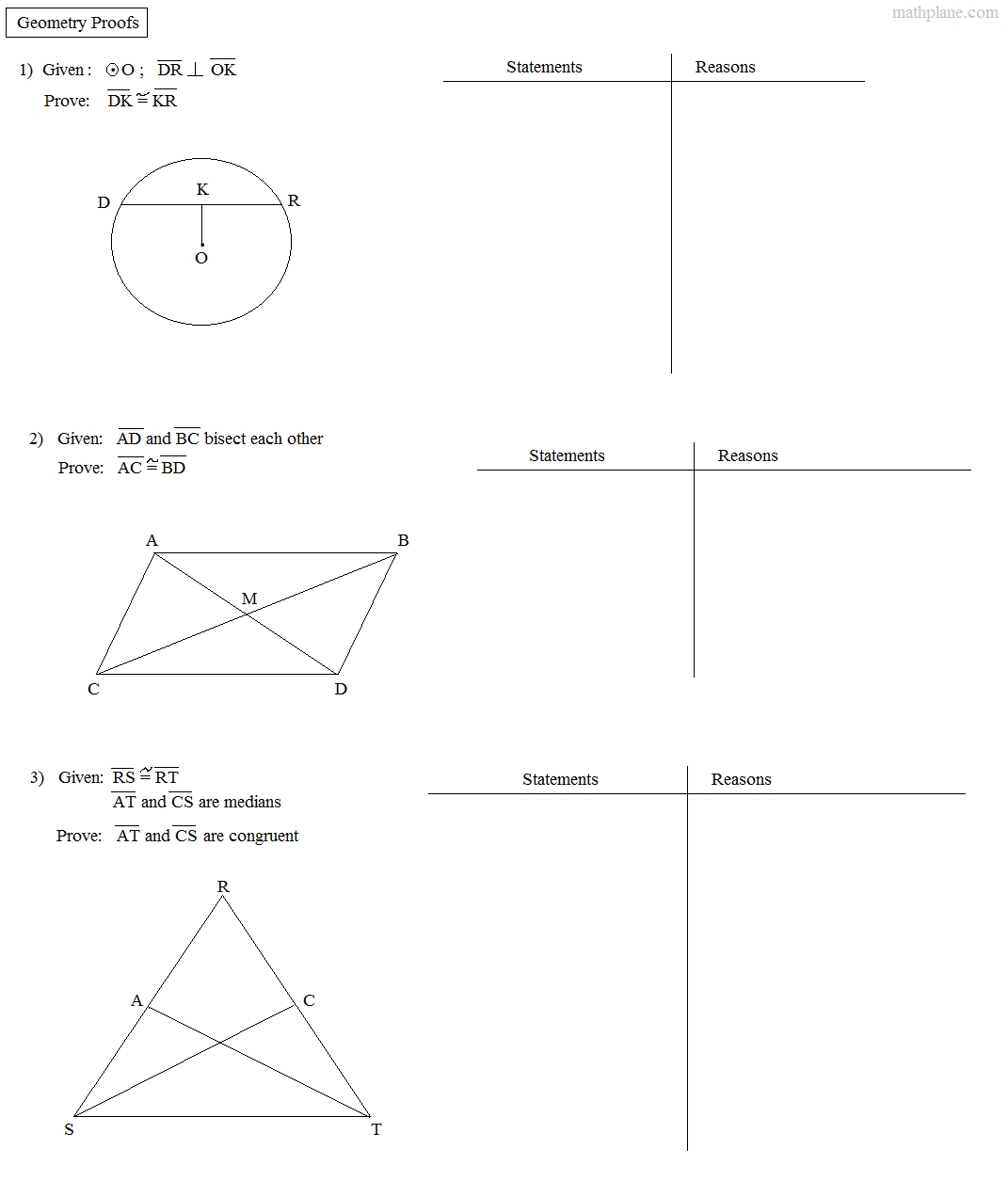
The Geometry Worksheet Beginning Proofs provides students with a great introduction to the world of proofs. It teaches the basics of writing and manipulating statements, as well as how to make logical deductions from given statements. Through this worksheet, students will gain a better understanding of how to construct a valid proof, and how to use the various tools of geometry to do so. This worksheet is a great way to introduce students to the world of proofs, and to help them develop the skills needed to succeed in higher-level mathematics.
[addtoany]