Exploring X-Linked Genetic Inheritance: A Step-by-Step Guide
X-linked genetic inheritance is a type of inheritance pattern that is transmitted by genes located on the X chromosome. It is responsible for a wide range of genetic conditions, including some types of color blindness, hemophilia, muscular dystrophy, and Fragile X Syndrome. Understanding the basics of X-linked inheritance can help you determine your risk of passing on a genetic condition to your children.
Step 1: Understand the Basic Principles of X-Linked Inheritance
X-linked inheritance is a type of inheritance pattern that is transmitted by genes located on the X chromosome. A gene on the X chromosome is referred to as an X-linked gene. It is important to note that not all traits or conditions are X-linked. Some traits are inherited in a different pattern, such as autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive.
[toc]
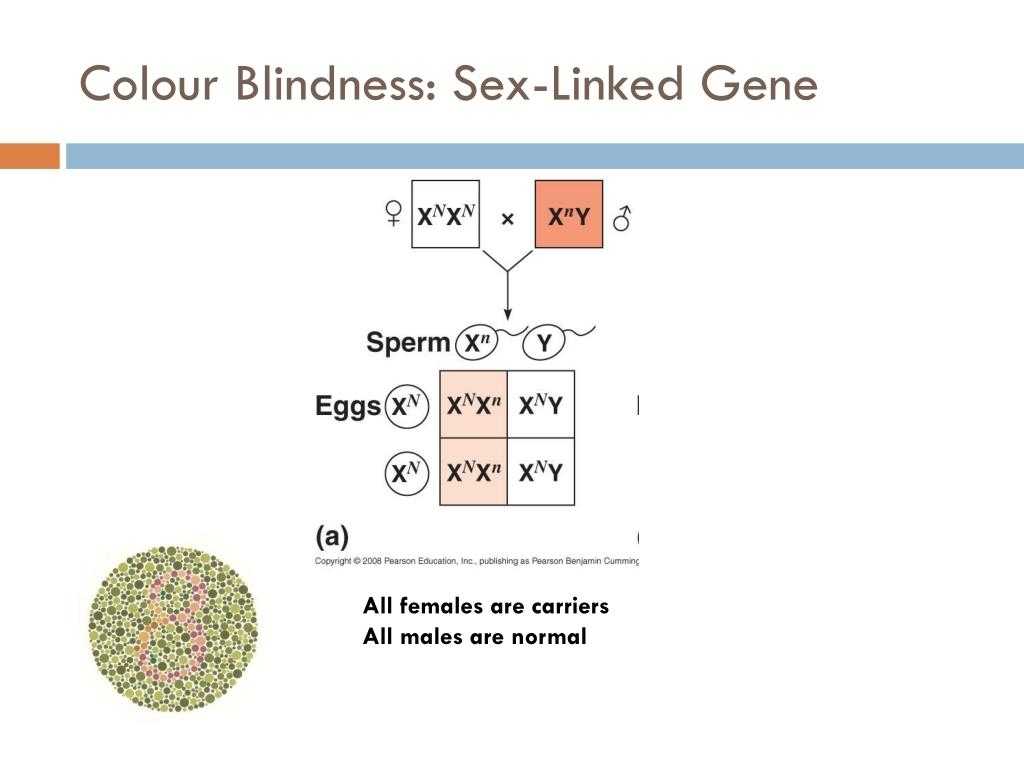
In X-linked inheritance, the gene is only passed on from mother to son. This is because the father contributes an X chromosome to his son, while the mother contributes an X chromosome to both her sons and her daughters. Thus, if the mother carries an X-linked gene, she will pass it on to all of her children.
Step 2: Understand the Symptoms of X-Linked Conditions
X-linked conditions can cause a wide range of symptoms, depending on the type of condition. Some of the most common X-linked conditions include color blindness, hemophilia, muscular dystrophy, and Fragile X Syndrome.
Color blindness is a condition in which a person is unable to distinguish certain colors. Hemophilia is a condition in which the clotting of blood is impaired, leading to increased bleeding. Muscular dystrophy is a condition in which the muscles weaken over time, leading to muscle wasting and eventually paralysis. Fragile X Syndrome is a condition in which there is an increased risk of intellectual disability, autism, and epilepsy.
Step 3: Determine Your Risk of Passing on an X-Linked Condition
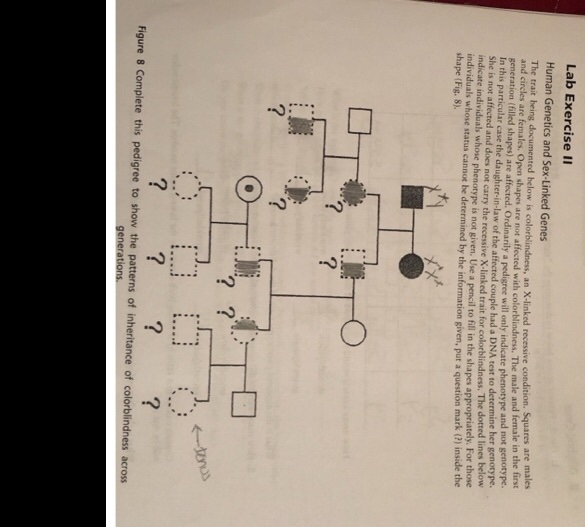
If you have a family history of any X-linked conditions, it is important to determine your risk of passing on one of these conditions to your children. If you are a woman, you can determine your risk by looking at the X chromosomes that you inherited from your mother. If you are a man, you can determine your risk by looking at the X chromosome that you inherited from your mother and the Y chromosome that you inherited from your father.
If you determine that you have an X-linked gene, it is important to remember that you may not have any of the associated symptoms. However, you will still have a 50% chance of passing on the gene to your children.
Step 4: Seek Genetic Counseling
If you are concerned about your risk of passing on an X-linked condition to your children, it is important to seek genetic counseling. A genetic counselor can provide you with information about the risks of passing on an X-linked gene and help you make informed decisions about your reproductive choices.
How X-Linked Genes Work: A Comprehensive Overview
X-linked genes are a type of gene located on the X chromosome, one of the two sex chromosomes in humans. These genes are responsible for a wide range of developmental, physiological, and behavioral traits. In this article, we will provide an overview of how X-linked genes work, including their inheritance patterns and their role in sex determination and various genetic disorders.
X-linked genes are inherited in a unique way due to their location on the X chromosome. Unlike other chromosomes, which can be inherited from either parent, the X chromosome is only inherited from the mother. This is because the father’s sperm only contains either an X or Y chromosome, depending on the sex of the baby. As a result, males only inherit one X chromosome, while females inherit two.
This has an important effect on how X-linked genes are inherited. If a father carries a mutation on his X chromosome, all of his daughters will inherit the mutation, but none of his sons will. Similarly, if a mother carries a mutation on her X chromosome, half of her sons and half of her daughters will inherit the mutation.
X-linked genes also play an important role in sex determination. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. During the development of an embryo, the Y chromosome triggers the development of male sex organs, while the presence of two X chromosomes triggers the development of female sex organs.
Finally, X-linked genes are also responsible for a wide range of genetic disorders. These disorders are caused by mutations on the X chromosome, and can range from mild to severe. Examples of X-linked disorders include color blindness, hemophilia, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
In conclusion, X-linked genes are a type of gene located on the X chromosome that play an important role in sex determination and various genetic disorders. They are inherited in a unique way due to their location on the X chromosome, and half of all sons and daughters of a parent with a mutated X chromosome will inherit the mutation. Understanding how X-linked genes work is key to understanding the genetic basis of many disorders and traits.
Genetic Counseling and X-Linked Disorders: What You Need to Know
Genetic counseling is an important part of understanding and managing inherited diseases, especially those that are X-linked. X-linked inherited disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome. These disorders can affect both men and women, but they are usually more severe in men due to their lack of a second X chromosome, which can act as a backup.
Genetic counselors can help individuals and families understand the risk of passing on X-linked disorders in their family. They can also provide information about available testing and potential treatments. Genetic counselors can also provide counseling and support to help families cope with the diagnosis and/or management of an inherited disease.
For individuals with a family history of an X-linked disorder, genetic counseling is often recommended. The goal of genetic counseling is to provide information about the risk of an X-linked disorder and the available options for management and prevention. During a genetic counseling session, a counselor will review the family’s medical history, discuss available testing options, and provide information about the risks associated with passing on the disorder.
Genetic counselors can also provide counseling to address any emotional concerns families may have about a diagnosis or management of an inherited disorder. They can provide resources to help families cope with their diagnosis and can provide support during this difficult time.
Genetic counseling is an important part of understanding and managing inherited X-linked disorders. It can provide individuals and families with important information about the disorder and available testing and management options. It can also provide emotional support and resources to help families cope with any diagnosis or management of an inherited disorder.
Understanding X-Linked Diseases Through Genetics: Exploring the Causes and Treatments
X-linked diseases are genetic disorders caused by mutations on the X chromosome, which is one of the two sex chromosomes found in humans. X-linked diseases affect both males and females, although males are often more severely affected. These diseases can range from mild to severe and can cause a variety of physical, mental, and developmental problems.
In order to understand the causes of X-linked diseases, it is important to understand the structure of the X chromosome. The X chromosome carries thousands of genes, which are responsible for the production of proteins and enzymes that are necessary for normal body function. Mutations in these genes can cause a variety of different diseases. These mutations can be inherited from a parent or can occur randomly during a person’s development.
The symptoms and severity of X-linked diseases depend on the type of mutation that is present. Some mutations may cause mild symptoms while others may cause more severe symptoms. Common symptoms of X-linked diseases include intellectual disability, learning disabilities, and physical abnormalities.
The treatments for X-linked diseases depend on the type and severity of the disease. In some cases, treatments may involve medication or lifestyle changes. In other cases, treatments may involve more invasive procedures such as gene therapy or stem cell therapy. In some cases, X-linked diseases may be managed with a combination of treatments.
It is important to remember that X-linked diseases are complex and can cause a variety of physical, mental, and developmental problems. It is also important to note that X-linked diseases can be inherited from a parent or can occur randomly during a person’s development. With the help of medical professionals, those affected by X-linked diseases can receive the treatments they need to manage their symptoms and lead healthy lives.
Uncovering the Mysteries of X-Linked Genes: A Primer for Beginners
The Impact of X-Linked Genes on Human Health: An Introduction
X-linked genes are a type of gene which are located on the X chromosome, which is one of the two sex chromosomes in humans. These genes are particularly important to human health, as they can affect physical and mental development and can be responsible for a variety of inherited disorders.
X-linked genes are inherited differently from other genes. In females, the X chromosome is inherited from both parents, as females have two X chromosomes. In males, however, the X chromosome is inherited from their mothers only, as males have only one X chromosome. This means that if a mother passes on an X-linked gene which is affected by a mutation, the mutation will be present in all of the male offspring, but only half of the female offspring.
Due to their inheritance patterns, X-linked genes are responsible for a number of genetic disorders, many of which are quite serious. Examples of X-linked disorders include hemophilia, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, fragile X syndrome, and color blindness. These disorders can cause a wide range of physical and mental symptoms, ranging from mild to severe.
In addition to causing disorders, X-linked genes can also affect the normal development of a child. For example, an X-linked gene could be responsible for a child’s height, weight, hair color, or other physical characteristics. In some cases, X-linked genes can even influence a child’s behavior and personality.
It is important to remember that X-linked genes can also be beneficial. For example, some X-linked genes are responsible for providing protection against certain diseases, and can even help to prolong life expectancy.
In conclusion, X-linked genes play a vital role in human health, both in terms of causing genetic disorders, as well as influencing physical and mental development. It is important to understand how X-linked genes work in order to better understand the impact they can have on human health.
Harnessing the Power of X-Linked Genes: A Guide to Genetic Engineering
In recent years, advances in genetics have made it possible to exploit the power of X-linked genes to create novel organisms with enhanced characteristics. By manipulating the genes responsible for certain traits, it is possible to modify the characteristics of an organism, or even to create entirely new ones. This guide aims to provide an overview of genetic engineering and its potential applications in the manipulation of X-linked genes.
Genetic engineering is the intentional manipulation of an organism’s genome, typically to confer desirable traits. It is achieved through a variety of techniques, including gene cloning, gene splicing, gene knockouts, and gene expression. In X-linked gene manipulation, scientists focus on the genes located on the X chromosome, as they are inherited on a predictable pattern and can be passed down from one generation to the next.
Gene cloning involves making a copy of a gene sequence and inserting it into a different organism. This allows scientists to create organisms with desired traits. For example, by cloning a gene that codes for a particular protein, scientists can introduce the protein into an organism and confer a desired trait.
Gene splicing is a technique by which scientists can alter the genetic code of a gene, typically by removing or changing a single nucleotide. This can be used to change the expression or activity of a gene, thus altering the characteristics of an organism.
Gene knockouts are a type of genetic engineering in which one or more genes are silenced, so that they no longer produce a particular protein. This technique can be used to create organisms that lack certain traits or behaviors.
Gene expression is the process by which genetic information is translated into a functional protein. By manipulating the expression of genes, scientists can control the amount and type of proteins produced within a cell, allowing them to alter the characteristics of an organism.
By harnessing the power of X-linked genes, scientists are able to modify an organism’s characteristics, or create entirely new organisms. This guide has provided an overview of genetic engineering and its potential applications in X-linked gene manipulation. With the right knowledge and resources, scientists can use these techniques to create novel organisms with enhanced traits.
X-Linked Genetics in the Animal World: Exploring the Possibilities
X-linked genetics are a fascinating and complex topic in the animal world. X-linked genetic traits occur when the gene responsible for a trait is located on the X chromosome, as opposed to traits found on other chromosomes such as the Y chromosome. X-linked traits are of particular interest to researchers because the inheritance of these traits is different from those of autosomal traits.
In mammals, X-linked genetic traits are often inherited from the mother, as males only have one X chromosome and females have two X chromosomes. In these cases, a female will pass on either her dominant or recessive X chromosome to her offspring, while a male will always pass on his single X chromosome. This means that any recessive traits on the X chromosome will be expressed in male offspring but not in female offspring.
X-linked genetic traits can also be inherited from the father, but this occurs in a different manner. In this case, a male passes on his single X chromosome to either a son or a daughter, and the daughter will then express the trait. In this way, X-linked genetic traits in mammals can be passed onto future generations.
X-linked genetic traits are not limited to mammals, however. Many species of birds, reptiles, and fish also possess X-linked traits. In some species, X-linked traits are inherited in the same manner as in mammals, while in other species the inheritance is more complicated. For example, in some species of birds, a male will pass on his X chromosome to both sons and daughters, while in other species only a daughter will express the trait.
The possibilities for exploring X-linked genetics in the animal world are endless. Studying the inheritance patterns of X-linked genetic traits can provide invaluable insight into the evolution of species and the genetic factors that influence their behavior and physical characteristics. Through further research, the mysteries of X-linked genetics may one day be fully understood.
The Role of X-Linked Genes in Plant Genetics: What You Need to Know
X-linked genes are an important part of plant genetics. These genes are located on the X chromosome and are responsible for a variety of traits and characteristics. X-linked genes play a crucial role in genetic diversity, providing the building blocks for new and unique varieties of plants.
X-linked genes are responsible for a variety of characteristics in plants. These genes are responsible for the size and shape of leaves, as well as the number of flowers a plant produces. Furthermore, X-linked genes are responsible for the color of many flowers, and also play a role in resistance to disease.
X-linked genes are also important in terms of genetic diversity. When two plants with different X-linked genes mate, the result is a plant with a unique genetic combination. This allows for the production of new and interesting varieties of plants. In addition, X-linked genes can be used to create hybrid plants that are resistant to disease or pests.
X-linked genes are an important part of plant genetics and offer a great deal of potential. From creating unique varieties of plants to providing resistance to disease, X-linked genes are an essential part of understanding and manipulating plant genetics. Furthermore, understanding how X-linked genes work can help researchers create new varieties and hybrids that can benefit both the environment and humanity.
Genetic Testing and X-Linked Disorders: A Comprehensive Guide
Genetic testing is a powerful tool for diagnosing and managing inherited genetic disorders. X-linked disorders, in particular, are a group of conditions which are caused by a mutation in a gene located on the X chromosome. These conditions are typically more common in males than females and can be passed from mother to son, or from father to daughter.
The purpose of genetic testing for X-linked disorders is to identify the presence of the mutated gene and determine if an individual is a carrier of the disorder. Genetic testing for X-linked disorders can help identify those at increased risk for developing the disorder, as well as those who may be carriers.
Genetic testing for X-linked disorders typically involves DNA analysis. This type of testing requires a sample of the individual’s blood, saliva, or cheek swab. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The laboratory will look for the presence of the mutated gene in the individual’s DNA.
The results of the genetic testing can provide important information to help inform medical decisions. For example, if a person is found to be a carrier, their family members may need to be tested to determine their risk for developing the disorder. If a person is found to have the mutated gene, the healthcare provider can consider appropriate treatment options.
Genetic testing for X-linked disorders can be a valuable tool for diagnosis and management. It is important for individuals to understand the risks and benefits associated with genetic testing in order to make an informed decision. Individuals should consult with their healthcare provider to discuss their options and understand the implications of genetic testing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the X-linked Genes worksheet is an important tool for understanding the ways in which genetics affects our health and development. It provides an overview of the different types of X-linked genes and how they work, as well as a variety of examples that demonstrate the effects of these genes on individuals and their families. This worksheet can be used to help individuals and families better understand genetic disorders and the potential risks associated with them, as well as helping to identify which family members may be at risk for certain conditions. Understanding X-linked genes can help us make more informed decisions about our own health and the health of our loved ones.
[addtoany]