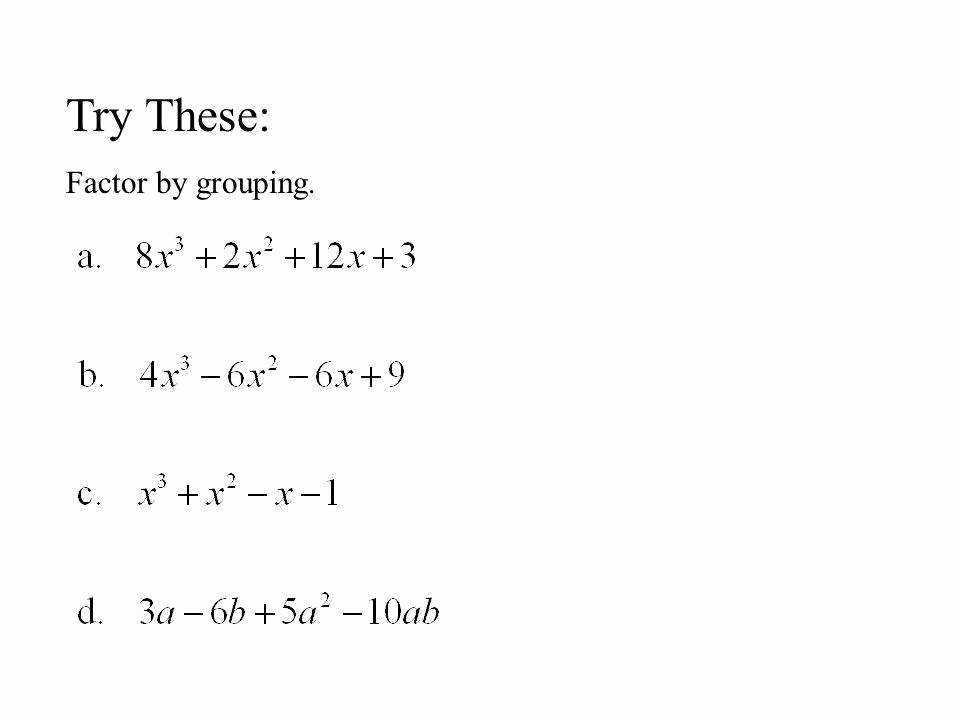How to Use a Factoring Special Cases Worksheet to Simplify Algebraic Expressions
Factoring special cases worksheets are a great tool for simplifying algebraic expressions. When used, these worksheets can help reduce lengthy and complex expressions into simpler and more manageable equations. To use a factoring special cases worksheet, first identify the type of expression that needs to be simplified. Depending on the type of expression, different strategies may be used.
For example, if the expression contains a common factor, the worksheet can help identify it. Once identified, the common factor can be factored out of the expression to reduce its complexity. Similarly, if the expression contains a difference of two squares or a perfect square trinomial, the worksheet can help identify these special cases and factors them out accordingly.
In addition, a factoring special cases worksheet can also help simplify expressions containing variables. By using a substitution method, the worksheet can help substitute the variables with numerical values, allowing the expression to be simplified. Once the expression is simplified, the worksheet can also help identify any remaining common factors that can be factored out of the equation.
[toc]
By using a factoring special cases worksheet, complex algebraic expressions can be broken down into simpler equations. This not only makes the expression easier to understand, but also simplifies the process of solving for the unknowns and finding the solutions.
Solutions and Tips for Factoring Special Cases Worksheet Questions
Factoring special cases worksheet questions can often be difficult to answer. However, with a few tips and tricks, it can be made much easier.
First, it is important to understand the basics of factoring. In general, factoring involves breaking down an expression into simpler factors. To do this, you must identify the greatest common factor and the least common multiple of the given expression. Once these are identified, you can use the distributive property to break down the expression into simpler factors.
It is also important to understand the different types of polynomials. Polynomials are divided into two categories: linear and quadratic. Linear polynomials can be factored by finding the greatest common factor and then using the distributive property to break down the expression. Quadratic polynomials, on the other hand, must be factored using the quadratic formula.
When it comes to factoring special cases, it is important to identify the type of expression being factored. If it is a linear polynomial, then you can use the methods described above. If it is a quadratic polynomial, then you must first use the quadratic formula to solve for the unknowns. Once the unknowns have been solved for, you can then use the distributive property to break down the expression into simpler factors.
Finally, it is important to remember that some expressions cannot be factored. If a given expression cannot be factored, then it is often best to leave it in its current form. This can be done by simplifying the expression and then writing the result as an equation.
By following these tips, factoring special cases worksheet questions can be made much easier. With a little practice and patience, factoring special cases can become second nature.
Working Through the Steps of Factoring Special Cases Worksheet Problems
Factoring is a mathematical process that involves breaking a number or expression down into its component parts. It can be used to solve complicated equations and to simplify more complex expressions. Special cases of factoring can be used to help solve equations more quickly and accurately. In this worksheet, we will look at some of these special cases and learn how to factor them.
The first special case is factoring by grouping. This is when an expression has two sets of terms that are related to each other in some way. To factor by grouping, you must group the terms together into two separate groups. After doing this, you can then factor out the common factors from each group.
The second special case is factoring trinomials. A trinomial is an expression that has three terms. To factor a trinomial, you must first identify the common factors between the terms. After this, you can factor out the common factors and then solve the equation.
The third special case is factoring by substitution. This is when an expression has two variables that are related to each other. To factor by substitution, you must substitute one of the variables with the other and then factor out the common factors.
The fourth special case is factoring by difference of squares. This is when an expression has two terms that are related to each other in that they are squares of the same number or expression. To factor by difference of squares, you must factor out the common factors and then solve the equation.
Finally, the fifth special case is factoring by completing the square. This is when an expression has two terms that are related to each other in that they are squares of each other. To factor by completing the square, you must complete the square for one of the terms and then factor out the common factors.
By understanding these special cases of factoring, you can quickly and easily solve equations and simplify more complex expressions. With some practice and patience, you can master the art of factoring and use it to make your math problems easier to solve.
Exploring Complexity in Factoring Special Cases Worksheet Exercises
This worksheet explores various special cases in factoring polynomials. By understanding how to factor special cases, students can learn useful techniques for factoring other polynomials.
The first exercise deals with factoring polynomials of degree 2, often referred to as quadratic equations. This exercise discusses how to factor quadratics that have a coefficient of one on the x^2 term. To solve this type of equation, students can use the method of completing the square. This involves taking half of the coefficient of the x term, squaring it, and then adding it to both sides of the equation. This will create a perfect square on the left side of the equation which can then be factored.
The second exercise concerns factoring polynomials of degree 3, also known as cubic equations. This exercise explains how to factor a cubic equation with a coefficient of one on the x^3 term. To factor this type of equation, students will need to use the method of grouping. This involves splitting the equation into two trinomials and then factoring each trinomial. After the trinomials are factored, the equation can be written as a product of two binomials.
The third exercise focuses on factoring polynomials of degree 4, often referred to as quartic equations. This exercise explains how to factor a quartic equation with a coefficient of one on the x^4 term. To solve this type of equation, students can use the method of grouping. This involves splitting the equation into two binomials and then factoring each binomial. After the binomials are factored, the equation can be written as a product of two trinomials.
The fourth exercise addresses factoring polynomials of degree 5, also known as quintic equations. This exercise discusses how to factor a quintic equation with a coefficient of one on the x^5 term. To factor this type of equation, students will need to use the method of grouping. This involves splitting the equation into two trinomials and then factoring each trinomial. After the trinomials are factored, the equation can be written as a product of two binomials.
By exploring these special cases in factoring, students can gain a better understanding of the techniques used to factor polynomials of any degree. Through practice, students can become proficient in factoring special cases and apply that knowledge to other polynomials.
Conclusion
The Factoring Special Cases Worksheet is an excellent resource for any student wanting to learn more about factoring special cases. By working through the questions and answers on the worksheet, students can gain a better understanding of how to factor special cases and build their skills in this area. With practice and patience, students can become more confident in their ability to factor special cases and use this knowledge to solve more complex problems.
[addtoany]