Exploring the Different Components of Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answers
1. Overview of Ecological Pyramids:
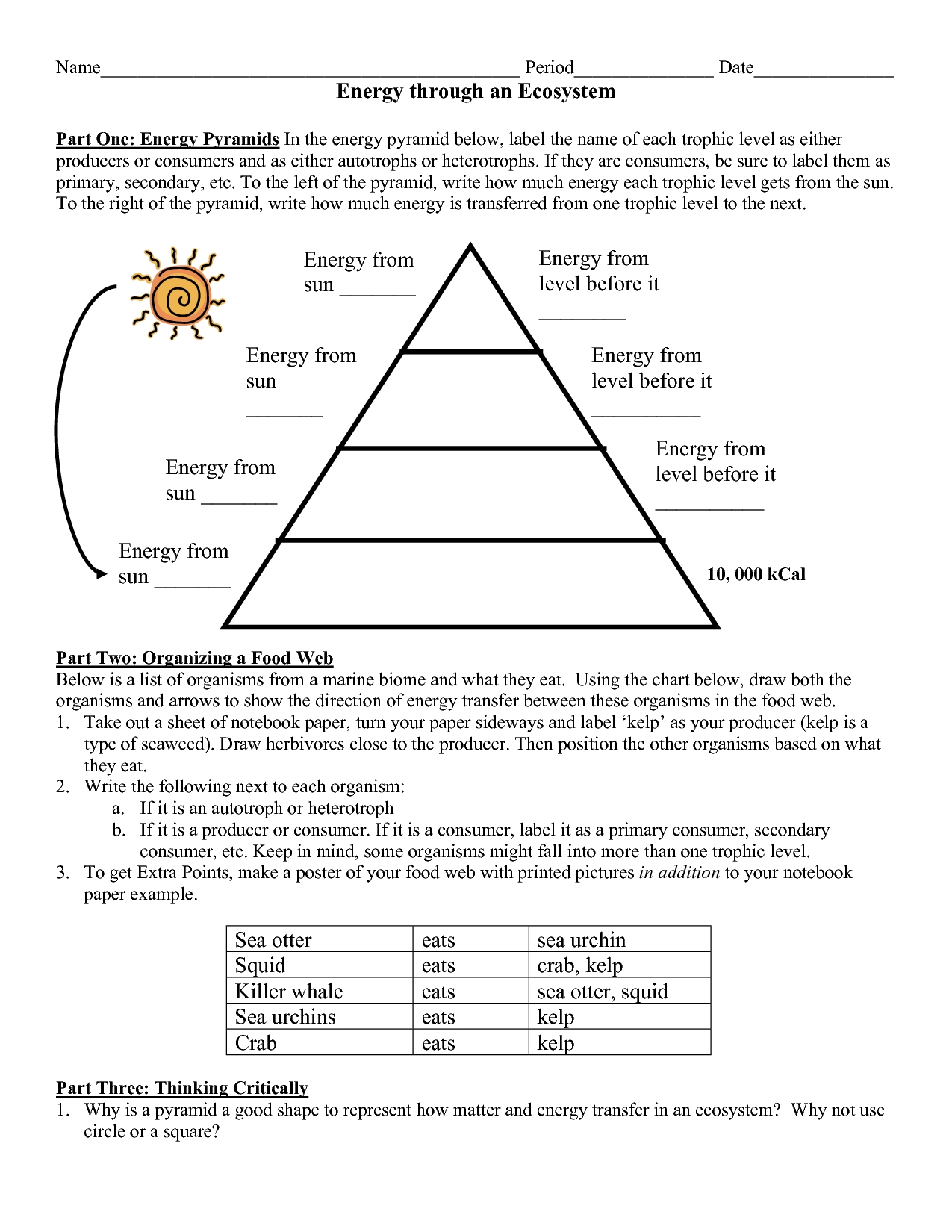
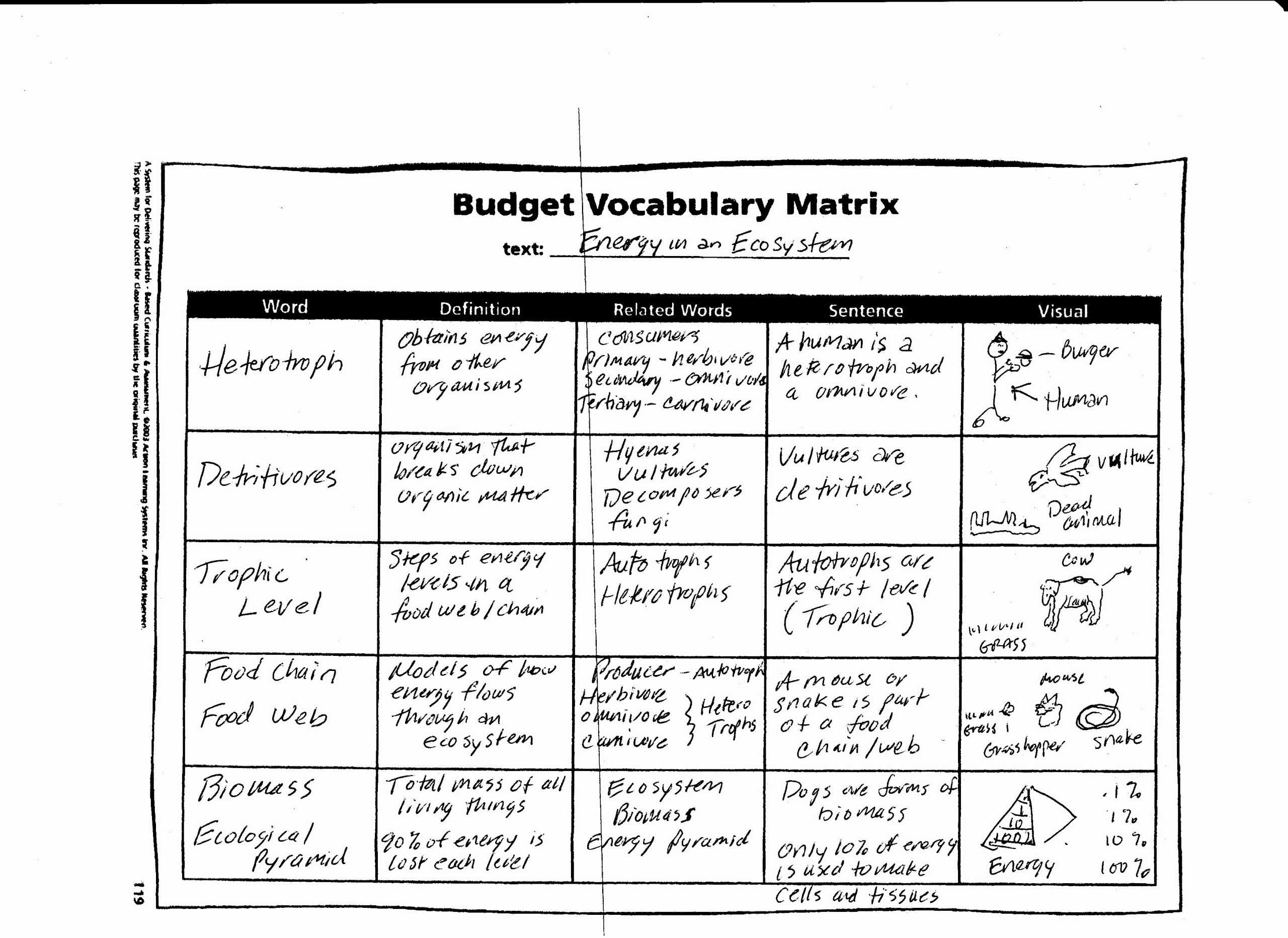
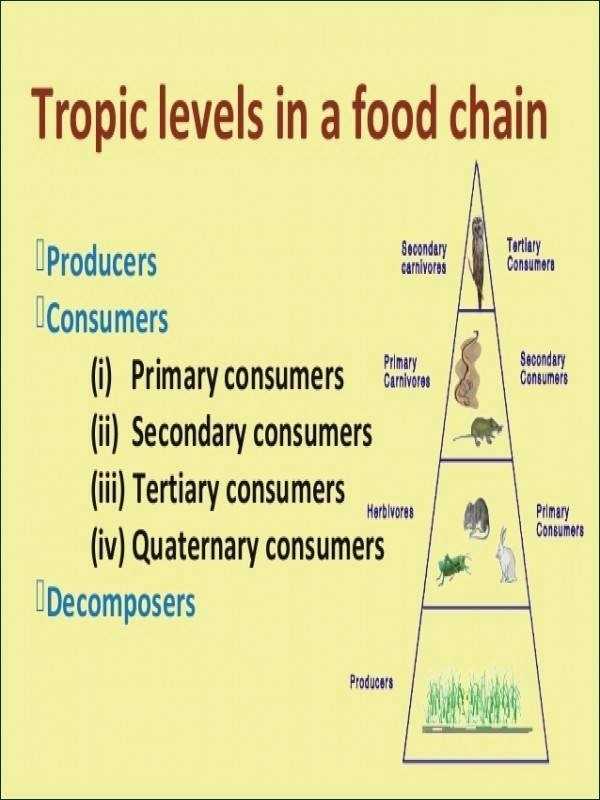
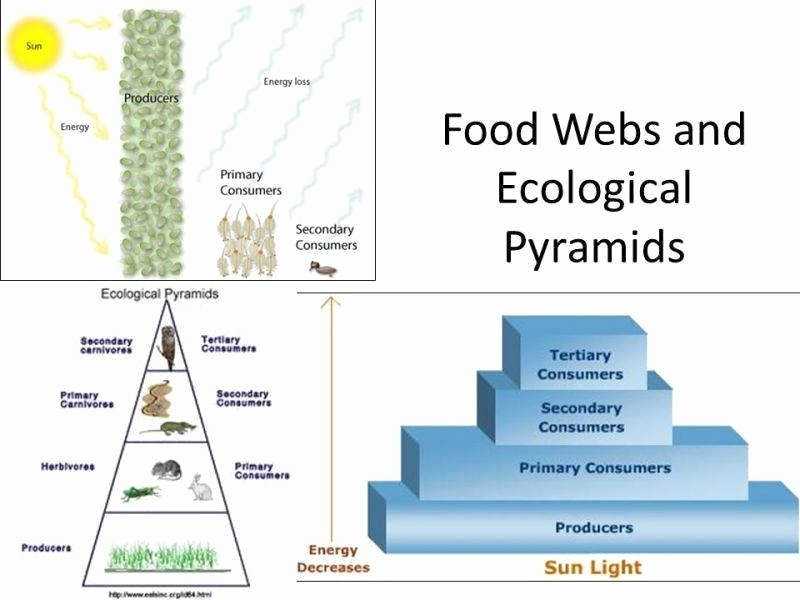
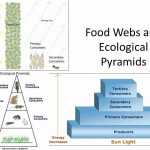
An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation of the trophic levels in an ecosystem. It is used to illustrate the relationships between the different organisms in an ecosystem and their position in the food chain. The pyramid is divided into sections, with each section representing a different trophic level. The base of the pyramid is the primary producers, followed by the primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers at the top.
2. Primary Producers:
Primary producers are the base of the ecological pyramid. These organisms, such as plants and algae, produce their own food through photosynthesis. They are the source of energy for the rest of the ecosystem and provide food for the primary consumers.
3. Primary Consumers:
Primary consumers are the organisms that feed on the primary producers. These organisms, such as insects, herbivores, and other small animals, are the first link in the food chain. They provide a source of energy for the secondary and tertiary consumers.
[toc]
4. Secondary Consumers:
Secondary consumers are the organisms that feed on the primary consumers. These organisms, such as carnivores and omnivores, are the second link in the food chain. They provide a source of energy for the tertiary consumers.
5. Tertiary Consumers:
Tertiary consumers are the top predators in the food chain. These organisms, such as large predators, feed on the secondary consumers and are the last link in the food chain. They provide a source of energy for the organisms at the top of the pyramid.
Comparing Ecological Pyramids Worksheets Answers from Different Ecosystems
The ecological pyramid is an essential tool for understanding the complexity of the food chain and the relationships between different species in an ecosystem. Comparing ecological pyramids from different ecosystems can be an enlightening exercise, as it allows us to observe and understand the differences in the interactions between different species within different habitats.
When comparing ecological pyramids from different ecosystems, it is important to consider the various factors that can influence the pyramid’s structure and the number of organisms at each level. For instance, the amount of energy available in the environment, the type of food chain present, and the interactions between consumers and producers all have an effect on the structure of an ecological pyramid. Additionally, the amount of competition between species and the number of predators and prey within the habitat are also key factors to consider when comparing pyramids from different ecosystems.
When comparing pyramids, it is also important to consider the different types of organisms that can be found at each level. For example, the producer level in a grassland ecosystem is often dominated by small plants such as grasses and mosses, while the producer level in a forest ecosystem may be dominated by larger plants such as trees. Additionally, the consumer levels may contain different types of animals in different ecosystems, such as herbivores and predators.
By comparing ecological pyramids from different ecosystems, we can gain a better understanding of the interactions between species in different habitats, as well as the effects of human activities on the environment. Through this comparison, we can begin to understand the complexity of the food chain and the importance of preserving and protecting different ecosystems.
Understanding the Role of Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answers in Conservation Practices
Ecological pyramids are a visual representation of an ecosystem’s food web. They provide a powerful tool to understand the flow of energy and matter through the environment and are essential to the conservation of its biodiversity.
At the base of an ecological pyramid are the producers—organisms such as plants and algae that use sunlight and nutrients to produce energy. Next in the pyramid are the primary consumers, which are animals that feed on the producers. These are followed by the secondary consumers, which feed on the primary consumers, and so on up the pyramid.
The ecological pyramid represents the flow of energy from the producers to the top predator. It also demonstrates how energy is lost at each level of the food chain. The pyramid helps to identify the roles of different organisms in the ecosystem, how organisms interact with each other, and how energy is lost as it moves up the food web.
This information is essential for conservation practices. It helps to identify which species are key players in the ecosystem, and can help to inform conservation strategies. For example, if a species at the top of the food chain is removed or threatened, conservationists can identify which species are at risk and develop strategies to protect them.
In addition, the ecological pyramid provides a way to measure the health of an ecosystem. By monitoring changes in the pyramid, conservationists can assess the impacts of human activities on the environment, such as habitat loss and pollution. This information can then be used to develop strategies to protect and restore the ecosystem.
The ecological pyramid is an invaluable tool for conservation practices and a powerful visual tool to illustrate the complexity and interdependence of an ecosystem. It provides an understanding of the roles of different species in the food web and how energy is lost as it moves up the pyramid. This knowledge is essential for the development of effective conservation strategies, and for the protection of biodiversity and the health of our planet.
Conclusion
The Ecological Pyramid Worksheet Answers provide an important insight into the way energy and biomass are exchanged between the different levels of the food chain. It is essential to understand the concept of energy transfer to maintain a healthy ecosystem and to understand the balance between producers and consumers. By understanding the answers to the worksheet, one can gain a better understanding of how to maintain a balanced and healthy ecosystem.
[addtoany]