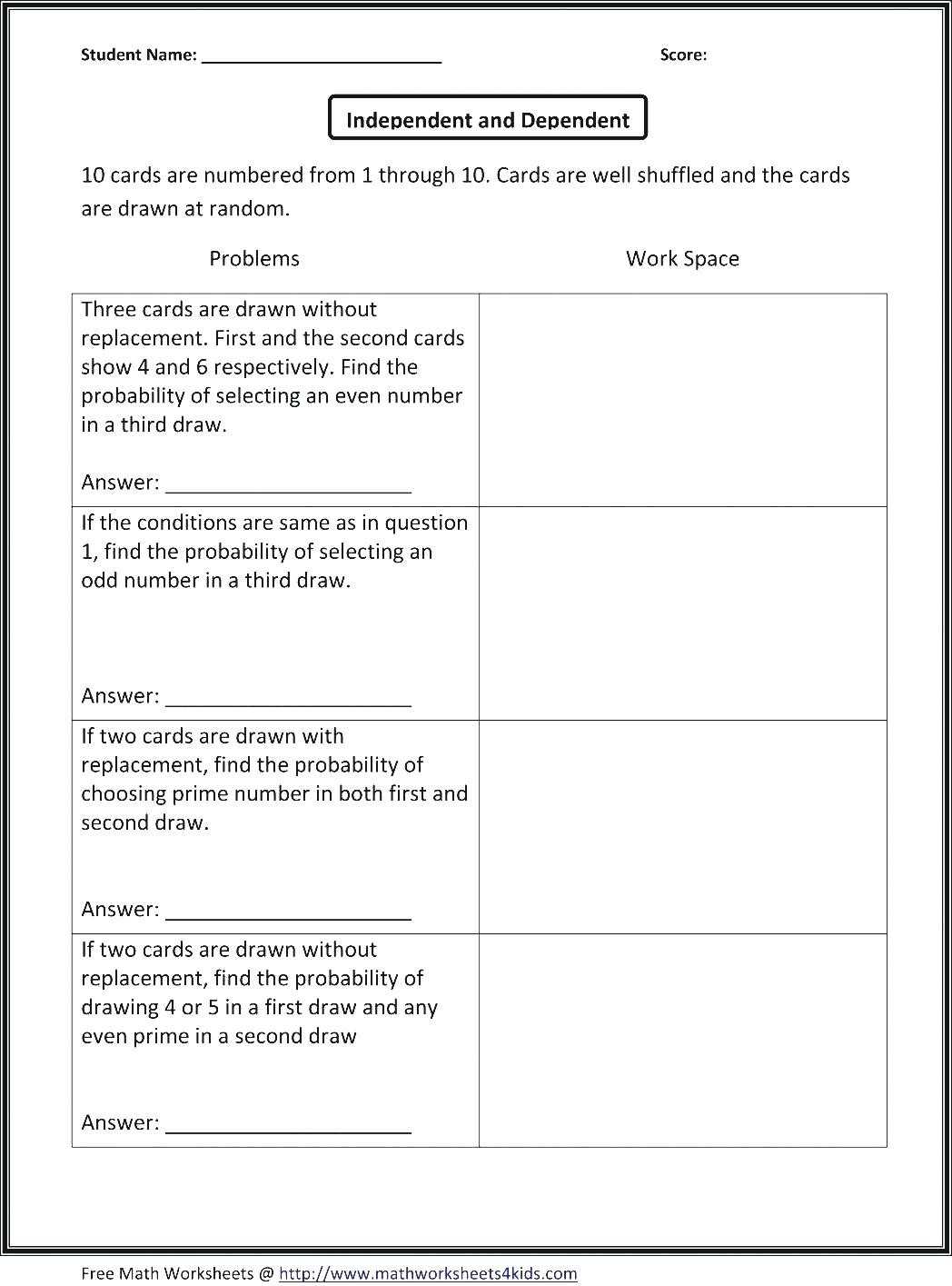
Exploring the Journey of Direct and Inverse Variation: Uncovering the Basics of the Relationship
Direct and inverse variation are two of the most fundamental relationships in mathematics. They provide a way of understanding how two variables are connected in an equation. In a direct variation, the two variables are related in such a way that when one changes, the other changes in a proportional manner. For example, if the price of a product increases, the quantity of the product decreases. In an inverse variation, the two variables are related in such a way that as one increases, the other decreases in a proportional manner. For example, if the speed of a car increases, the time it takes to reach a certain destination decreases.
These two variations can be expressed in a mathematical equation. In a direct variation, the equation is written in the following form: y = kx. In this equation, y is the dependent variable and x is the independent variable. The constant k is the ratio between the two variables, and it shows how the variables are related. In an inverse variation, the equation is written as xy = k. In this equation, x is the dependent variable and y is the independent variable. Again, the constant k is the ratio between the two variables and it shows how they are related.
It is important to understand that direct and inverse variation are not the same as linear or exponential equations. In a linear equation, the variables are related in a linear fashion. This means that if one variable increases, the other will increase proportionally. In an exponential equation, the variables are related in an exponential fashion. This means that if one variable increases, the other will increase exponentially.
[toc]
Direct and inverse variation are useful for understanding how two variables are related in an equation. Understanding how the two variables are related can help to solve problems and make predictions about the future. It can also be used to analyze data and make decisions based on the data. By understanding the basics of direct and inverse variation, one can better understand the relationships between variables and use this information to make better decisions.
Navigating the Math Maze: A Step-by-Step Guide to Solving Direct and Inverse Variation Worksheets
Navigating the math maze of direct and inverse variation worksheets can be a daunting task. However, with a few simple steps, you can easily tackle them and gain a better understanding of the concepts they represent.
The first step is to identify whether the equation is a direct or inverse variation. In a direct variation, the two variables have a proportional relationship, meaning that as one increases, the other increases as well. An inverse variation is the opposite, and it occurs when one variable increases and the other decreases.
Once you have identified the type of variation, you can begin to work on the worksheet. To solve direct variation worksheets, you will need to find the constant of proportionality, or the multiplier. This can be done by taking two points on the graph and plugging them into the equation. Then, use algebra to solve for the constant.
For inverse variation worksheets, the process is similar. First, identify two points on the graph and plug them into the equation. Then, use algebra to solve for the constant. Once you have the constant, you can then use it to solve for the other variable.
Finally, when you have solved the equation and found the constants, you can use them to answer the questions on the worksheet. In most cases, the answer to the questions will be the same as the constants.
By following these simple steps, you will have no trouble navigating the math maze of direct and inverse variation worksheets. As you become more comfortable with the concepts, you will find yourself able to tackle more complex problems with ease.
From A to Z: An Overview of the Key Terms in Direct and Inverse Variation Worksheets
A: Constant of Proportionality: The ratio between two variables that expresses their direct or inverse variation.
B: Direct Variation: A relationship between two variables where one is a constant multiple of the other.
C: Inverse Variation: A relationship between two variables where one is inversely proportional to the other.
D: Linear Equation: A mathematical expression that shows the relationship between two variables using a straight line.
E: Slope: The rate at which one variable changes with respect to the other.
F: Coefficient of Variation: A measure of the degree to which the two variables vary relative to each other.
G: Correlation: A measure of the degree to which two variables are related.
H: Scatter Plot: A graph that displays the relationship between two variables.
I: Line of Best Fit: A line that is drawn to approximate the relationship between two variables.
J: Y-Intercept: The point at which the line of best fit crosses the y-axis.
K: X-Intercept: The point at which the line of best fit crosses the x-axis.
L: Proportionality: The property of two variables that implies that one is directly or inversely proportional to the other.
M: Non-linear Equation: A mathematical expression that does not represent a linear relationship between two variables.
N: Constant of Variation: A number that expresses the degree to which two variables vary relative to each other.
O: Interquartile Range: The range of values that contain the middle 50% of the data points.
P: Outlier: A data point that is far away from the majority of the other data points.
Q: Coefficient of Determination: A measure of the strength of the linear relationship between two variables.
R: Mean: The average value of all the data points.
S: Median: The middle value of all the data points.
T: Mode: The most frequently occurring value among the data points.
U: Standard Deviation: A measure of how much the data points vary from the mean.
V: Normal Distribution: A bell-shaped graph that describes the probability of different values occurring in a set of data.
W: Skewness: A measure of how symmetrical the data points are relative to the mean.
X: Kurtosis: A measure of how peaked the data points are relative to the mean.
Y: Regression Analysis: A statistical technique used to analyze the linear relationship between two variables.
Z: Residuals: The difference between the observed values and the predicted values from a regression analysis.
Cracking the Code: Tips and Strategies for Working Through Direct and Inverse Variation Worksheets
Direct and inverse variation worksheets can be a challenging but rewarding exercise to work through. With a few tips and strategies, you can easily tackle these worksheets and find success.
Firstly, it is important to understand the basics of direct and inverse variation. Direct variation is when two variables are proportional to each other, meaning that when one increases, the other increases as well in the same ratio. Inverse variation, on the other hand, is when two variables are inversely related, meaning that when one increases, the other decreases in the same ratio.
When approaching a direct or inverse variation worksheet, it is important to read the problem carefully and identify the variables involved. Identifying the variables will help you decide which type of variation is being used. Once you have determined this, you can begin to solve the problem.
For direct variation problems, you can use the equation y = kx, where y is the dependent variable and x is the independent variable. This equation states that y is directly proportional to x. To solve the problem, you must first determine the value of k, which is the constant of proportionality. To do this, you must use the given information to set up an equation with two unknowns and solve for the value of k. Once you have the value of k, you can plug it into the equation and solve for the value of y.
For inverse variation problems, you can use the equation y = k/x, where y is the dependent variable and x is the independent variable. This equation states that y is inversely proportional to x. To solve the problem, you must first determine the value of k, which is the constant of proportionality. To do this, you must use the given information to set up an equation with two unknowns and solve for the value of k. Once you have the value of k, you can plug it into the equation and solve for the value of y.
These tips and strategies should help you easily work through direct and inverse variation worksheets. By understanding the basics of direct and inverse variation, being able to identify the variables, and determining the value of the constant of proportionality, you can easily solve these equations and find success.
Conclusion
The Direct and Inverse Variation Worksheet is a great tool for helping students understand the concept of direct and inverse variation. It provides students with an opportunity to practice and apply these concepts in a real-world setting. This worksheet also helps students identify real-world examples of direct and inverse variation, which can be beneficial when studying other math topics. With the help of this worksheet, students can gain a better understanding of how direct and inverse variation works and how to use it to solve problems.
[addtoany]