How to Use a Correlation vs. Causation Worksheet to Analyze Data
Using a correlation vs. causation worksheet to analyze data is a useful tool for determining the underlying relationship between variables. The worksheet can help researchers identify potential causal relationships and distinguish them from correlations.
When using the worksheet, it is important to begin by clearly defining the variables being examined and the type of relationship being sought. This will help to ensure that any correlations or causal relationships are identified accurately.
Once the variables have been identified, the next step is to begin analyzing the data. The worksheet provides several steps for conducting the analysis. First, the worksheet allows for the identification of any potential correlations between the variables. It also allows for the calculation of the correlation coefficient, which is used to measure the strength of the relationship between the variables.
[toc]
Once correlations have been identified, the worksheet then provides guidance on how to determine whether the correlations are actually causal. This involves examining how changes in one variable can affect the other. If the changes are significant, then it is likely that a causal relationship exists.
Finally, the worksheet provides an analysis of the results and offers suggestions for further research. This can be used to strengthen the existing relationships or to identify any potential causal relationships that may have previously been overlooked.
By following the steps provided in the correlation vs. causation worksheet, researchers can quickly and accurately identify any causal relationships between variables. This can help to ensure that any results are accurate and reliable.
5 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Working With Correlation Vs. Causation
1. Assuming that correlation implies causation: correlation often implies a relationship between two variables, but it does not always indicate causation.
2. Overlooking confounding variables: confounding variables are other factors that may be influencing the relationship between two variables and should be considered when interpreting the results of a correlation analysis.
3. Ignoring sample size: a larger sample size is typically more reliable than a smaller sample size.
4. Assuming causation from a single correlation: correlations should not be interpreted in isolation, as they may be related to other factors.
5. Misinterpreting correlation as causation: correlation does not always imply causation. It is important to consider other factors that may play a role in the relationship between two variables.
Understanding the Difference Between Correlation and Causation with a Worksheet
Correlation and causation can often be difficult to distinguish from each other. To help elucidate the difference between the two, we have created the following worksheet.
Part One: Understanding Correlation
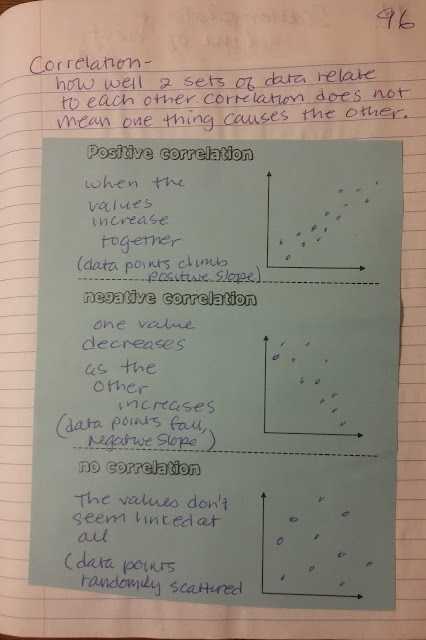
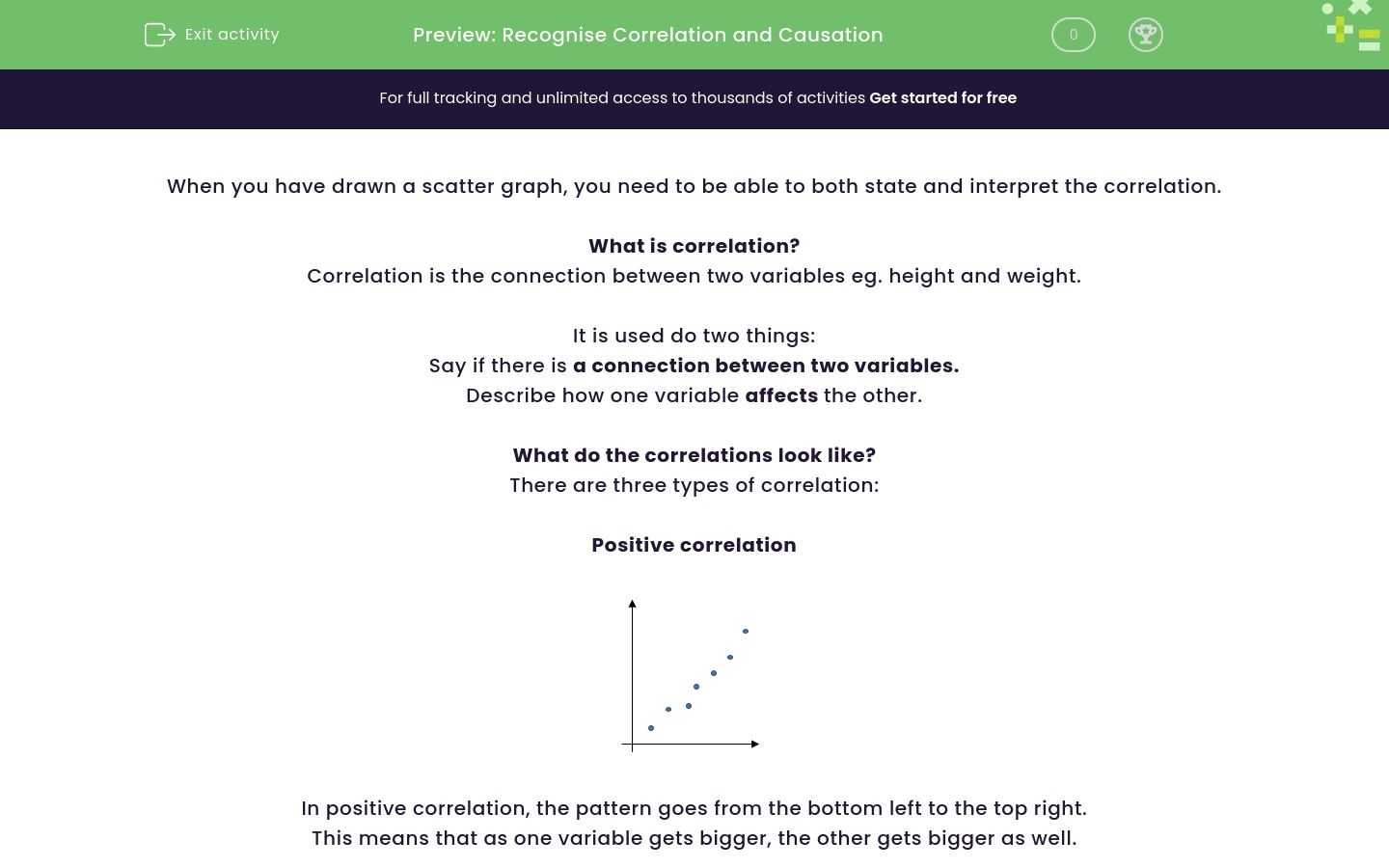
Correlation is the observation that two or more variables move together in relation to one another. It is a statistical measure of how two different variables interact with one another, and is represented by a coefficient ranging from -1 to +1. A correlation of +1 indicates a perfect positive correlation, while a correlation of -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation. A correlation of zero indicates that the two variables are completely unrelated.
Part Two: Understanding Causation
Causation, on the other hand, is the relationship between two or more variables where one variable causes a change in the other. It is the act of producing an effect, and is based on the idea that one variable causes a change in the other. In other words, causation suggests that a change in one variable is responsible for a change in the other variable.
Part Three: Distinguishing Correlation from Causation
While correlation and causation can appear to be similar, there are key differences between the two. Correlation does not necessarily indicate causation, and it is important to understand that correlation does not always indicate causation. Correlation simply indicates that two or more variables move together, but does not necessarily mean that one variable causes a change in the other. Causation, on the other hand, indicates that one variable causes a change in the other.
In conclusion, correlation and causation are two distinct concepts. While they may appear similar at first, it is important to note that correlation does not always indicate causation. Understanding the difference between correlation and causation can help to distinguish between the two concepts and ensure that data is interpreted correctly.
Exploring the Pros and Cons of Correlation vs. Causation Worksheets
Correlation vs. Causation Worksheets are an essential tool for data analysis. Correlation and causation are two of the most important concepts in data science. Correlation measures the degree of linear relationship between two variables, while causation looks at the cause and effect relationship between the same two variables. Both are important in data analysis, and understanding the differences between these two concepts is essential for interpreting data correctly.
The Pros of Correlation vs. Causation Worksheets is that they help data scientists to understand the relationship between two variables and make informed decisions based on their findings. With a correlation worksheet, data scientists can quickly determine the strength of the relationship between two variables and make decisions accordingly. A causation worksheet can help data scientists determine the cause and effect relationship between two variables, which can be used to make predictions about future outcomes.
The Cons of Correlation vs. Causation Worksheets is that it can be difficult to interpret the results correctly. There are many factors that can influence the strength of the relationship between two variables and if the results are interpreted incorrectly, it could lead to incorrect decisions. Additionally, correlation worksheets may not be able to capture all the factors that could influence the relationship between two variables. Causation worksheets are more complex and require more data analysis to accurately interpret the findings.
Overall, Correlation vs. Causation Worksheets are an essential tool for data analysis. They can help data scientists to understand the relationship between two variables and make informed decisions based on their findings. However, it is important to understand the differences between correlation and causation so that the results can be interpreted correctly. Additionally, correlation worksheets may not be able to capture all the factors that could influence the relationship between two variables, so it is important to use a combination of correlation and causation worksheets when analyzing data.
Exploring the Correlation Vs. Causation Debate with a Worksheet
Exploring the correlation versus causation debate can be a complex and nuanced process. To help guide this exploration, it is useful to have a worksheet that allows for the examination of the different elements at play. This worksheet can be used to evaluate the evidence and draw conclusions about the possible relationship between two variables.
The worksheet begins by considering the two variables in question. This can include details such as the type of data, the time period of observation, and any context that might be relevant. The next step is to evaluate the evidence that can be used to determine whether a correlation exists between the two variables. This includes looking at any quantitative or qualitative data that could provide insight into the possible relationship. The worksheet also asks for an analysis of any possible confounding variables that could be influencing the relationship.
The third step of the worksheet is to consider whether the evidence points to a cause-and-effect relationship between the two variables. This involves looking at any potential mechanisms or pathways that could explain the relationship. It also requires an examination of any potential alternative explanations that could explain the results.
The final step of the worksheet is to draw a conclusion about the evidence. This requires a consideration of all the evidence and a reasoned argument as to whether a causal relationship exists between the two variables. In some cases, it may be necessary to reassess the evidence and further investigate the potential relationship.
Exploring the correlation versus causation debate can be a challenging process. This worksheet provides a useful framework for evaluating the evidence and drawing conclusions about the possible relationship between two variables.
Correlation Vs. Causation: A Guide for Beginner Data Analysts
Correlation and causation are two terms often used in the field of data analysis that are often confused for one another. While they are closely related, they have distinct meanings that are important to understand.
Correlation is the relationship between two variables and is usually measured as a coefficient, which is a number between -1 and 1. A coefficient of -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation, meaning that as one variable increases, the other decreases. A coefficient of 1 indicates a perfect positive correlation, meaning that as one variable increases, the other increases as well. A coefficient of 0 indicates no correlation between the two variables. Correlation does not indicate causation, as it does not prove that one variable causes the other to change.
Causation is the relationship between two variables in which one variable causes a change in the other. Causation requires a cause and effect relationship and is usually determined through experiments. To demonstrate causation, the experiment must isolate the potential cause and measure the effect, while controlling for other factors.
When analyzing data, it is important to understand the difference between correlation and causation. Correlations can be used to point to potential causes, but they cannot demonstrate causation. Causation requires experiments to determine the cause and effect relationship. By understanding the difference between correlation and causation, data analysts can make the most accurate conclusions based on the data they are analyzing.
Tips for Interpreting Results from a Correlation Vs. Causation Worksheet
1. Consider the direction of the correlation: A positive correlation indicates that an increase in one variable is associated with an increase in the other variable, while a negative correlation indicates that an increase in one variable is associated with a decrease in the other variable.
2. Examine the strength of the correlation: The strength of a correlation is usually measured using the Pearson’s r coefficient. This coefficient ranges from -1 to +1, with a value close to 0 indicating a weak correlation, while a value close to 1 or -1 suggests a strong correlation.
3. Check for any confounding variables: It is important to consider any confounding variables that may be influencing the results. For example, if two variables are positively correlated, it is possible that a third variable is the real cause of the relationship.
4. Consider the context of the results: It is important to consider the context in which the results were obtained. The results may not be applicable to different contexts, and therefore care should be taken when making generalizations from the results.
5. Remember that correlation does not equal causation: Correlation does not necessarily indicate causation. Therefore, it is important to consider other factors, such as the direction of the correlation, the strength of the correlation, and any confounding variables that may be influencing the results.
Examples of Real-Life Correlation Vs. Causation Analysis Using a Worksheet
Correlation vs. causation analysis is a valuable tool used to analyze data and draw conclusions in a variety of fields, including business, finance, economics, and science. A correlation-causation analysis worksheet is a great way to organize and evaluate data. It helps to identify any correlations between different variables and then assess whether or not there is a causal relationship between them.
To illustrate this concept, consider the following two examples of correlation vs. causation analysis using a worksheet.
Example 1:
A researcher wants to analyze the relationship between the number of hours studied and a student’s final grade. The researcher begins by creating a worksheet listing the variables and their corresponding values. For example, the researcher might list the number of hours studied (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10) and the corresponding final grade (A, B, C, D, F). The researcher then plots the data points on a graph to observe the relationship between the two variables. This helps to identify any correlations between the number of hours studied and the student’s final grade.
Next, the researcher can use a correlation coefficient to measure the strength of the relationship between the two variables. If the correlation coefficient is strong, it indicates that there is a likely causal relationship between the two variables. For example, if the correlation coefficient is high, it suggests that the more hours a student studies, the higher their final grade will be.
Example 2:
A company wants to analyze the relationship between the number of hours an employee works and their job performance. The company begins by creating a worksheet listing the variables and their corresponding values. For example, the company might list the number of hours worked (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10) and the corresponding job performance rating (1, 2, 3, 4, 5). The company then plots the data points on a graph to observe the relationship between the two variables. This helps to identify any correlations between the number of hours worked and job performance rating.
Next, the company can use a correlation coefficient to measure the strength of the relationship between the two variables. If the correlation coefficient is strong, it indicates that there is a likely causal relationship between the two variables. For example, if the correlation coefficient is high, it suggests that the more hours an employee works, the higher their job performance rating will be.
By using a correlation-causation analysis worksheet, researchers and organizations can more effectively analyze data and draw meaningful conclusions about the relationships between different variables. It helps to identify any correlations and determine whether or not there is a causal relationship between the variables.
Analyzing Correlation Vs. Causation in the Social Sciences with a Worksheet
Correlation and causation are two of the most important concepts in the social sciences, as they provide insight into the underlying mechanisms behind social behavior. Understanding the difference between correlation and causation is essential for accurately interpreting research findings and making decisions based on evidence. This worksheet is designed to help social scientists analyze the relationship between correlation and causation.
First, consider the following scenario: Jane is a student and she notices that when she studies more, her grades improve.
In this scenario, Jane has observed a correlation between studying more and improved grades. Correlation is a statistical measure of the relationship between two variables; in this case, it is the relationship between studying more and improved grades. Correlation does not necessarily imply causation; that is, the fact that Jane studied more does not necessarily mean that it caused her grades to improve.
To determine if there is a causal relationship between studying more and improved grades, it is important to consider other factors that could be influencing the result. For example, perhaps Jane’s improved grades are a result of her teacher providing additional support or assistance, or perhaps other students in her class are more motivated to achieve good grades.
In addition, it is important to consider the strength of the correlation between studying more and improved grades. If the correlation is weak, then it is unlikely that studying more is the cause of Jane’s improved grades. On the other hand, if the correlation is strong, then it is more likely that studying more is the cause.
Finally, it is important to consider the direction of the relationship between studying more and improved grades. If studying more is causing improved grades, then this is a positive correlation; if studying more is resulting in worse grades, then this is a negative correlation.
By analyzing the relationship between correlation and causation in this scenario, social scientists can gain a better understanding of the factors that are influencing Jane’s grades. Through careful analysis, social scientists can more accurately interpret research findings and make informed decisions.
Using a Correlation Vs. Causation Worksheet to Identify Correlated Variables
Correlation vs. causation is an important distinction to make when analyzing data. It is easy to confuse the two, as they often appear in similar patterns. A correlation vs. causation worksheet can help to identify correlated variables and determine whether or not there is a cause-and-effect relationship.
First, the worksheet begins by asking questions about the data. It requires the user to consider the context of the data and the type of relationship being examined. This can help to identify the type of correlation, whether positive or negative, and the strength of the correlation.
The worksheet then asks questions to determine whether or not there is a causal relationship between the variables. It considers factors such as temporal precedence and the plausibility of a cause-and-effect relationship. It also examines whether there are any alternative explanations for the correlation.
Finally, the worksheet assesses the overall credibility of the data and the conclusions made about the correlation vs. causation. It considers factors such as the sample size of the data and the accuracy of the methods used to collect and analyze the data.
In conclusion, a correlation vs. causation worksheet is a useful tool for identifying correlated variables and determining whether or not there is a cause-and-effect relationship. By asking questions about the context of the data, the type of relationship being examined, and the possible explanations for the correlation, the worksheet provides a comprehensive analysis that can be used to make valid conclusions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correlation vs causation worksheet is a great way to understand the differences between correlational and causal relationships. It helps to understand the importance of properly analyzing both types of relationships and how to distinguish between them. This worksheet can also be used to explore the different types of relationships between variables, and to analyze and interpret the data that is collected. It is a great tool for anyone looking to better understand the complexities of relationships between variables.
[addtoany]