Exploring the Basics of Cellular Transport: An In-Depth Analysis of the Answers in a Cellular Transport Worksheet
Cellular transport is a fundamental process that is essential for the functioning of all living organisms. It is a complex process through which molecules, ions, and other materials are moved in and out of the cell. To better understand the basics of cellular transport, an in-depth analysis of the answers in a cellular transport worksheet can provide valuable insights.
At the most basic level, cellular transport is a process that is driven by the concentration gradient of a given molecule or substance. In other words, the cells move molecules or ions from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration. This process is facilitated by membrane proteins, which act as gateways for the movement of molecules and ions. Depending on the type of molecules or ions being transported, the process is classified as either active transport or passive transport.
Active transport requires the expenditure of energy, typically in the form of ATP, to move molecules or ions from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. Examples of active transport include the movement of glucose across the cell membrane and the transport of certain types of ions, such as sodium and potassium.
[toc]
Passive transport, on the other hand, does not require energy and relies on the concentration gradient to move molecules or ions from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Examples of passive transport include the diffusion of oxygen and other gases across the cell membrane and the diffusion of water across the cell membrane.
The answers to a cellular transport worksheet can also help to explain the specific processes involved in the movement of molecules and ions across the cell membrane. Endocytosis is a process that involves the engulfment of larger molecules, such as proteins, and their movement into the cell. Exocytosis is the opposite process, whereby materials are moved out of the cell. Both of these processes require the use of membrane proteins to move the molecules or ions across the cell membrane.
In conclusion, a thorough analysis of the answers in a cellular transport worksheet can provide valuable insights into the basics of cellular transport. By understanding the difference between active and passive transport, the types of molecules and ions that can be moved across the cell membrane, and the specific processes involved in the movement of molecules and ions, it is possible to gain a greater understanding of how cells work and how they interact with their environment.
The winter morning was frigid and still. A thin layer of frost blanketed the ground, glinting in the dim light of dawn. The trees, their leaves long gone, stood in silent sentry, their stark branches reaching into the sky like fingers. The air was so cold that it seemed to press against the skin and sting the lungs with each breath. It was a beautiful, peaceful morning, and the world was a study in shades of gray and blue.
The sun began to rise over the horizon, its golden light casting a warm glow over the landscape. The frost began to melt, and a thin mist hung like a curtain in the air. The light sparkled off the dew-covered grass, making the entire world seem to sparkle. The birds began to chirp, their songs a delightful counterpoint to the quiet of the morning.
All around, nature was slowly coming to life. The world was slowly being transformed from a hushed and still landscape to one alive with beauty and sound. It was a stunning sight that spoke of the power of nature and the wonders of the world.
Unlocking the Secrets of Cellular Transport with a Comprehensive Review of Cellular Transport Worksheet Answers
Cellular transport is a fundamental process in the life of all living organisms, and an understanding of how it works can unlock many of the mysteries of life. This comprehensive review of cellular transport worksheet answers will provide a detailed explanation of the various mechanisms of cellular transport, as well as the principles that govern them.
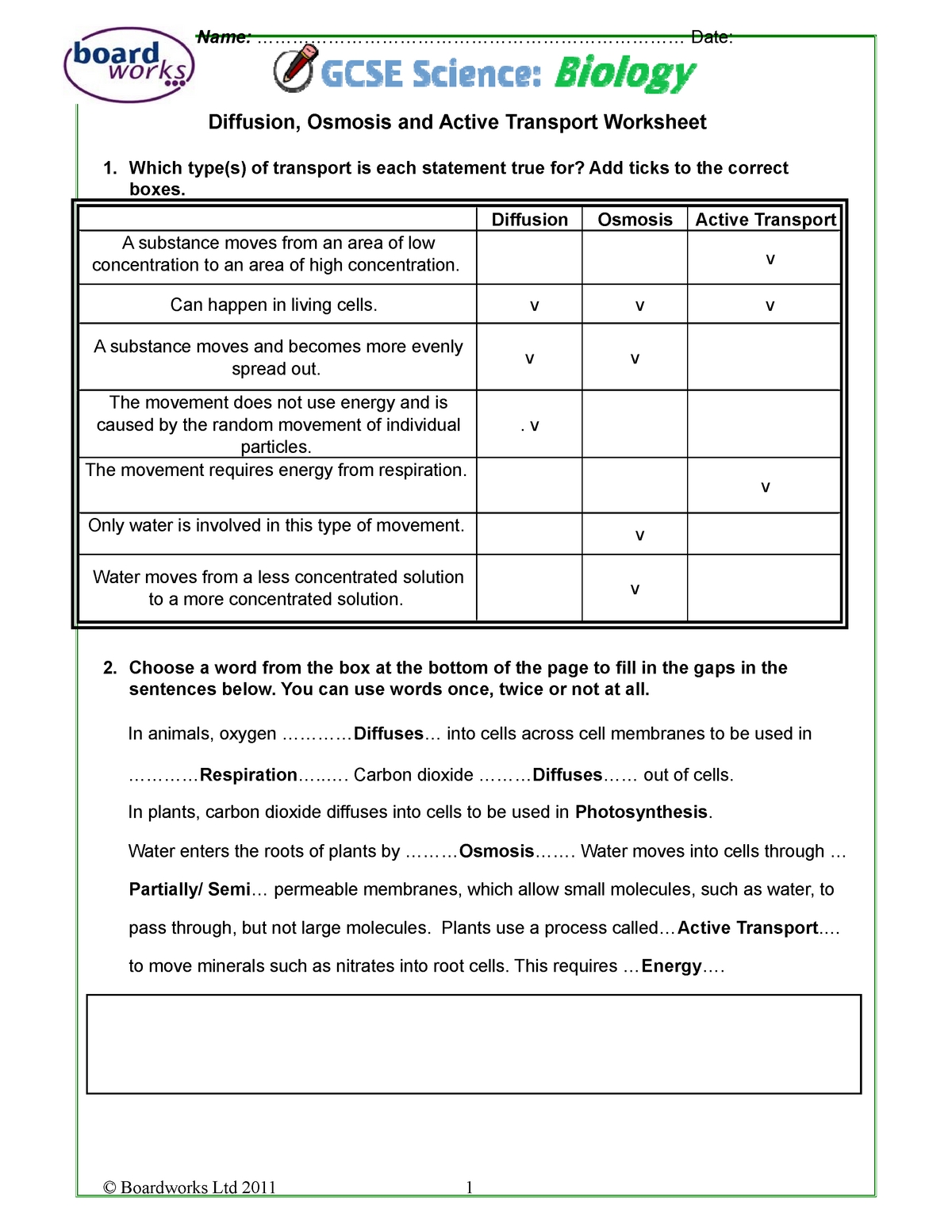
The worksheet begins by examining the basic principles of passive transport. This mechanism involves the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This occurs without the expenditure of energy and is commonly referred to as diffusion. The worksheet explains that diffusion is governed by the concentration gradient, the difference in concentration between two areas. It further explains that the rate of diffusion depends on the permeability of the membrane, the surface area of the membrane, and the size of the molecule.
Next, the worksheet discusses active transport, which is the movement of molecules against a concentration gradient. This requires the expenditure of energy and is therefore referred to as an “energy-dependent” process. The worksheet explains that active transport is driven by specific proteins, known as carriers, and is facilitated by the presence of a molecule known as an ion. The worksheet also explains how active transport can be used to move molecules that are too large for passive transport.
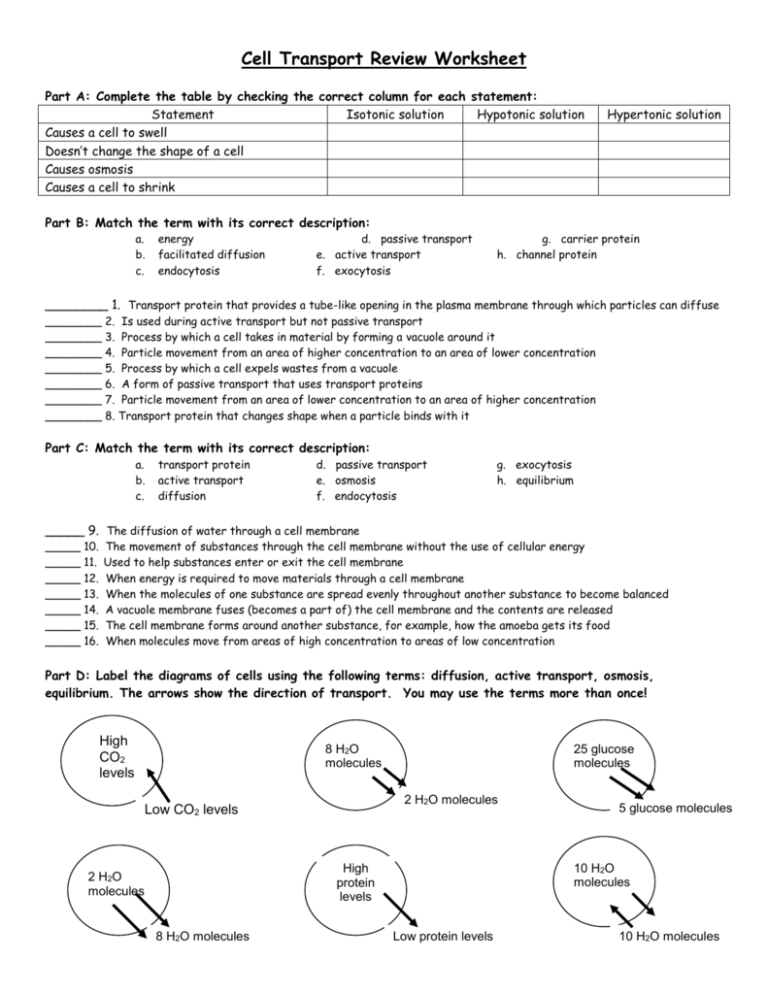
The worksheet then moves on to a discussion of the various types of cell transport, including endocytosis, exocytosis, and transcytosis. The worksheet explains that endocytosis is a form of active transport, in which a cell engulfs a substance in order to move it into the cell. Exocytosis is a form of passive transport, in which substances are released from the cell. Transcytosis is a form of active transport, in which substances are transported between cells.
The worksheet concludes with an overview of the various types of membrane transport, including facilitated diffusion, simple diffusion, and carrier-mediated transport. It explains that these mechanisms are necessary for the efficient transfer of substances across the membrane, and also explains how they interact with each other to maintain the function of the membrane.
This comprehensive review of cellular transport worksheet answers provides a detailed and comprehensive explanation of the different mechanisms of cell transport and the principles that govern them. By understanding these principles, students can gain a better understanding of how life works and unlock the secrets of cellular transport.
The Grand Canyon is an awe-inspiring sight, a vast chasm carved in the Earth by the Colorado River over millions of years. Its sheer size and beauty are truly remarkable; it stretches for 277 miles across northern Arizona, up to 18 miles wide in places and over a mile deep. Its sides are lined with multi-hued striations of red, orange and pink rock, formed by sedimentary layers of sandstone, limestone and shale.
The canyon is home to a variety of wildlife, including bighorn sheep, mountain lions, mule deer, condors and bald eagles. Its diverse landscape has been sculpted by wind and water erosion, creating a unique array of canyons, buttes, mesas and other geological features.
Visitors to the Grand Canyon can explore its depths on foot, by rafting down the Colorado River, or by taking a guided tour. From the South Rim, visitors can take in incredible views of the canyon’s walls, while the North Rim offers a more secluded experience with its cooler climate and beautiful pine forests.
The Grand Canyon is truly a sight to behold; its grandeur and beauty will remain in the hearts and minds of all who visit.
Understanding How Cell Membrane Processes Affect Cellular Transport: A Breakdown of Answers to Cellular Transport Worksheet Questions
Cellular transport is a vital process that allows cells to receive necessary nutrients, expel waste, and perform other important functions. To better understand how this process works, it is important to study the structure and function of the cell membrane, which is responsible for the movement of molecules and ions in and out of the cell.
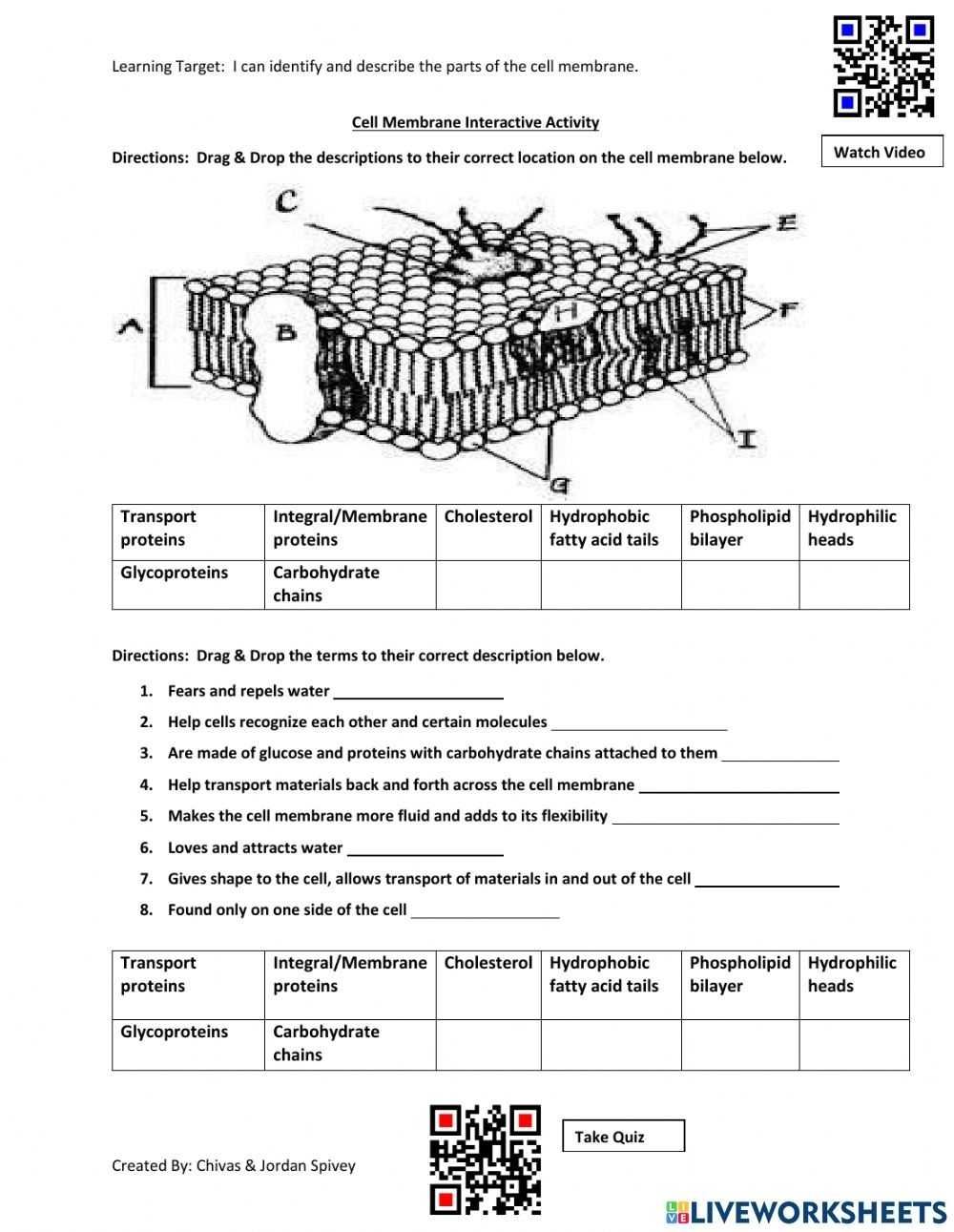
The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, which is composed of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. The phospholipids form a hydrophobic barrier, preventing the passage of polar molecules into the cell. This barrier is made up of two layers, one of which has hydrophobic tails and the other has hydrophilic heads. The proteins embedded in the membrane act as gatekeepers, allowing certain molecules or ions to pass through by forming channels or pumps.
In addition to the hydrophobic barrier, the cell membrane also contains carbohydrates, which are attached to the surface of the membrane. These carbohydrates give the cell a specific identity, allowing it to be recognized by other cells. The carbohydrates also act as receptors, allowing the cell to bind with other molecules and ions.
Cellular transport is a complex process that is affected by the structure and function of the cell membrane. To better understand this process, it is important to answer the following questions related to cellular transport:
1. How do molecules and ions move across the cell membrane?
Molecules and ions are able to move across the cell membrane through a process called passive transport. This involves the movement of molecules and ions through channels and pumps, which are created by proteins embedded in the membrane. Additionally, molecules and ions can move across the cell membrane through facilitated diffusion, which is a process in which a specific molecule binds to a receptor on the cell membrane and is then allowed to enter or exit the cell.
2. How does the hydrophobic barrier affect the movement of molecules and ions?
The hydrophobic barrier prevents the passage of polar molecules into the cell, as the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids repel these molecules. This means that non-polar molecules, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, are able to freely move across the membrane, while polar molecules, such as glucose and amino acids, must be transported through channels or pumps.
3. What role do carbohydrates play in cellular transport?
Carbohydrates attached to the surface of the cell membrane act as receptors, allowing the cell to bind with other molecules and ions. Additionally, carbohydrates give the cell a specific identity, allowing it to be recognized by other cells. This is important for cellular processes such as cell-to-cell communication, immune response, and cell recognition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cellular Transport Worksheet Answers provide a great way for students to understand and apply the concepts of cellular transport. The worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the processes involved and allows students to practice different types of problems to help them better understand the material. The worksheet answers are also useful for instructors to use as a starting point for creating their own lessons and activities.
[addtoany]