Exploring Cell Structure and Function Through a Worksheet Activity
Cell structure and function is an important topic in biology, and a worksheet activity is a great way to explore this topic. Through such an activity, students can gain a better understanding of how the different parts of a cell interact to create a functioning organism.
The first step in designing a worksheet activity is to identify the desired learning outcomes. For example, the objective might be for students to understand the role of the cell membrane and its components, or the structure of the nucleus and its function in the cell. Once the goals of the activity have been identified, the worksheet can be designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
The worksheet should include questions and activities that will help students understand the material. It should also provide visuals to help students visualize the concepts. For example, diagrams of the different parts of the cell and their functions, or a chart showing the various molecules that make up the cell membrane. Additionally, the worksheet should contain questions that will help test students’ knowledge of the material.
[toc]
Finally, the worksheet should include an assessment section so that students can gauge their understanding of the material. This could include multiple-choice or essay questions that test the student’s knowledge of the subject. The assessment should be tailored to the learning objectives of the worksheet so that the student can understand how well they have grasped the concepts.
By providing students with a worksheet activity to explore cell structure and function, they can gain a better understanding of this important topic. Through engaging questions and activities, visuals, and assessments, students can gain an in-depth knowledge of cell structure and function.
Understanding the Role of Proteins in Cell Structure and Function
Proteins play an integral role in the structure and function of cells. Proteins are large molecules composed of amino acids, and they function as building blocks for cells – forming the basis of organs, tissues, and membranes in the body. Proteins are also responsible for the regulation of biochemical reactions and metabolism, as well as transporting molecules and signals throughout the body.
Protein molecules can be divided into two main categories: globular proteins, which are spherical in shape, and fibrous proteins, which are elongated and rod-like. Globular proteins are usually found in the cytoplasm of cells and play a role in enzymatic reactions, cellular signaling, and the transport of molecules. Examples of globular proteins include enzymes, antibodies, and certain hormones. Fibrous proteins, on the other hand, are located in the cell membrane and function as structural elements. Examples of fibrous proteins include collagen, elastin, and keratin.
Proteins also play a role in the process of cell division. In the cell division process, proteins are responsible for reorganizing the chromosomes in the nucleus, replicating DNA, and forming the spindle fibers that attach to the chromosomes and pull them apart during division.
In addition to these functions, proteins also play a role in regulating gene expression. Proteins are capable of binding to DNA and controlling which genes are expressed and which are not. This process is essential for normal cellular functioning and is responsible for the differentiation of cells into specialized types.
Overall, proteins are essential for the structure and function of cells. They provide the physical structure of cells and organs, while also regulating biochemical processes, cell division, and gene expression. Without proteins, life as we know it would be impossible.
Examining the Relationship between Cell Structure and Cell Function
Cell structure and cell function are intimately related, and it is essential to understand how they interact in order to understand the life processes of a cell. Both cell structure and cell function are fundamental to the life of a living organism, since it is the cells that make up the tissues and organs of the organism.
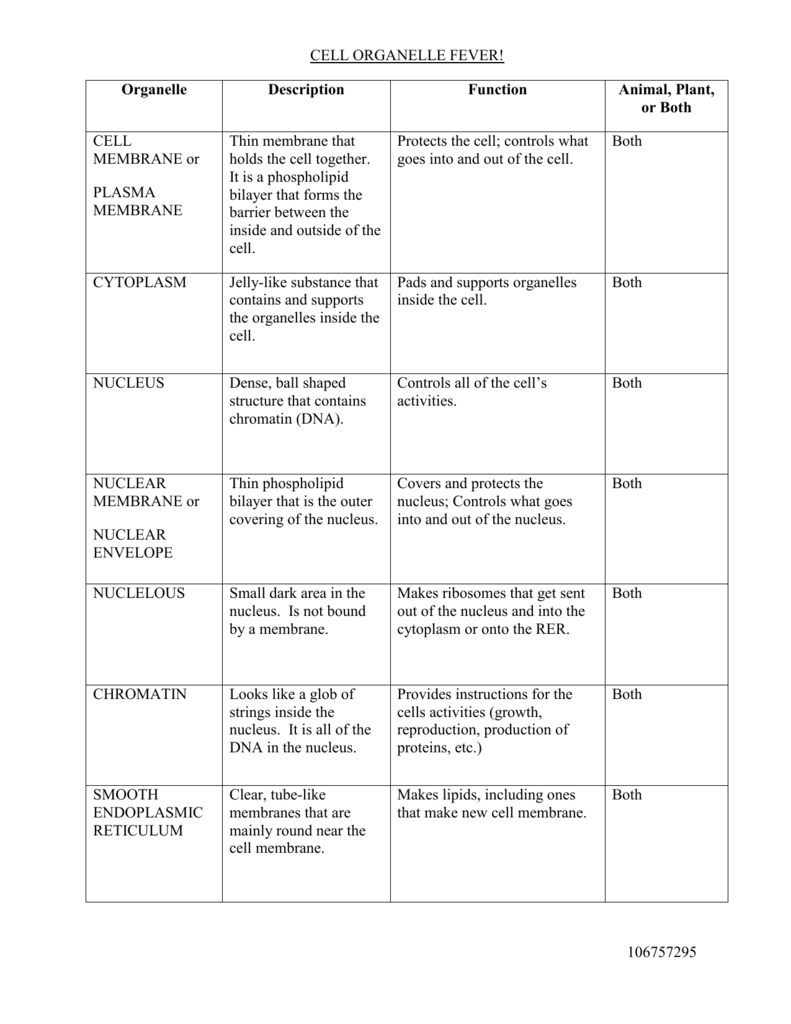
The cell is composed of a variety of components, most of which are essential for the function of the cell. These components include the plasma membrane, which acts as a barrier between the cell and the outside environment; the cytoplasm, which consists of the organelles and other structures within the cell; and the nucleus, which contains the genetic material of the cell.
Each of these components has a specific role in the cell’s function. The plasma membrane acts as a barrier to keep out unwanted substances and to regulate what enters and leaves the cell. The cytoplasm contains the organelles and other structures that are responsible for the cell’s basic functions, such as producing energy and synthesizing proteins. The nucleus contains the genetic material, which is responsible for the cell’s identity and helps it to respond to its environment.
In addition to the components of the cell, the structure of the cell also plays an important role in its function. The shape of the cell is important for its ability to move and to interact with its environment. The size of the cell is also important, since larger cells can contain more organelles and other structures that allow them to perform more complex tasks.
The relationship between cell structure and cell function is complex and dynamic. The structure of a cell affects its function, and changes in the structure can also affect the function of the cell. Therefore, it is essential to understand the relationship between cell structure and cell function in order to understand the life processes of a cell.
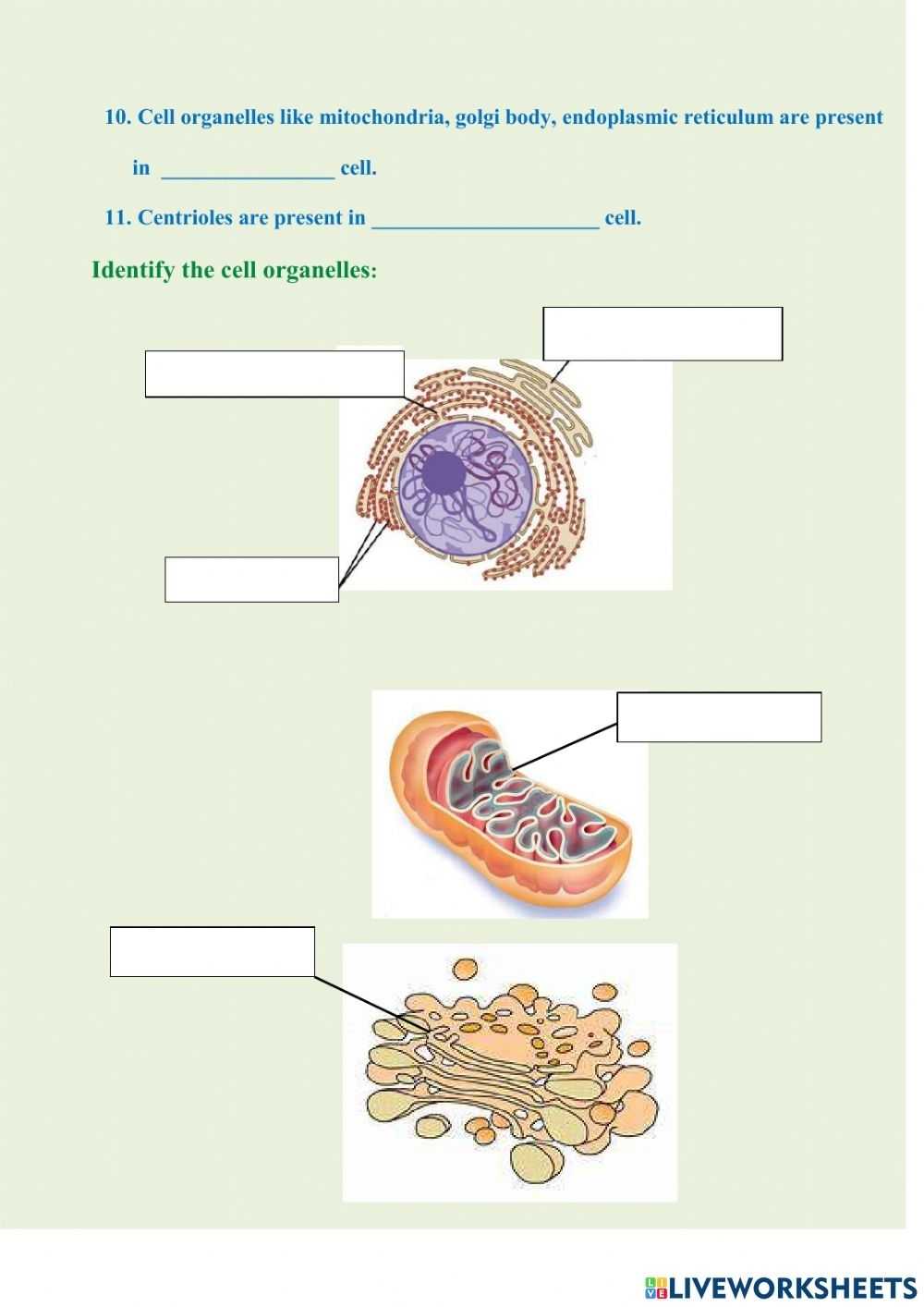
Exploring the Interdependence of Organelles in Cell Structure and Function
The cell is an essential biological unit, essential for the functioning of living organisms. Cells are composed of a variety of organelles, which are subcellular structures that perform specific functions within the cell. These organelles have evolved to form a complex, yet interdependent system that allows the cell to function efficiently.
The nucleus is the largest organelle in the cell and is responsible for storing the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. This genetic material is essential for the cell to reproduce and to regulate its metabolic processes. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope, which is composed of two lipid bilayers that separate the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an organelle composed of a network of interconnected tubules and sacs. The ER is responsible for the synthesis of proteins and lipids, as well as the modification and transport of these molecules. The ER is also involved in the storage of calcium ions, which are essential for many cellular processes.
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle composed of flattened sacs that are involved in the modification, packaging, and transport of proteins and lipids. The Golgi apparatus is also responsible for the production of lysosomes and glycosomes, which are organelles involved in the digestion of foreign substances and intracellular waste.
The mitochondria are organelles that are involved in the production of energy for the cell. Mitochondria contain their own DNA and are often referred to as the “powerhouse” of the cell. They are responsible for the production of ATP, which is the energy currency of the cell.
The cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments and microtubules that provide structure and support to the cell. The cytoskeleton also helps to organize organelles within the cell and is involved in cell movement.
The lysosomes are organelles that contain hydrolytic enzymes, which are responsible for the digestion and breakdown of foreign substances and intracellular waste.
The chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that are involved in photosynthesis. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy and converts it into chemical energy.
The interdependence of these organelles is essential for the functioning of the cell. Without one organelle, the cell would not be able to perform its necessary functions. Each organelle is specialized to perform a certain function, and together they form a complex system that allows the cell to function efficiently.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cell Structure and Function Worksheet is a great way to help students gain an understanding of the basic components of a cell and how they work together to maintain life. It provides an interactive and visual way to explore the structure and function of a cell, helping students to develop a better understanding of the living world around them.
[addtoany]