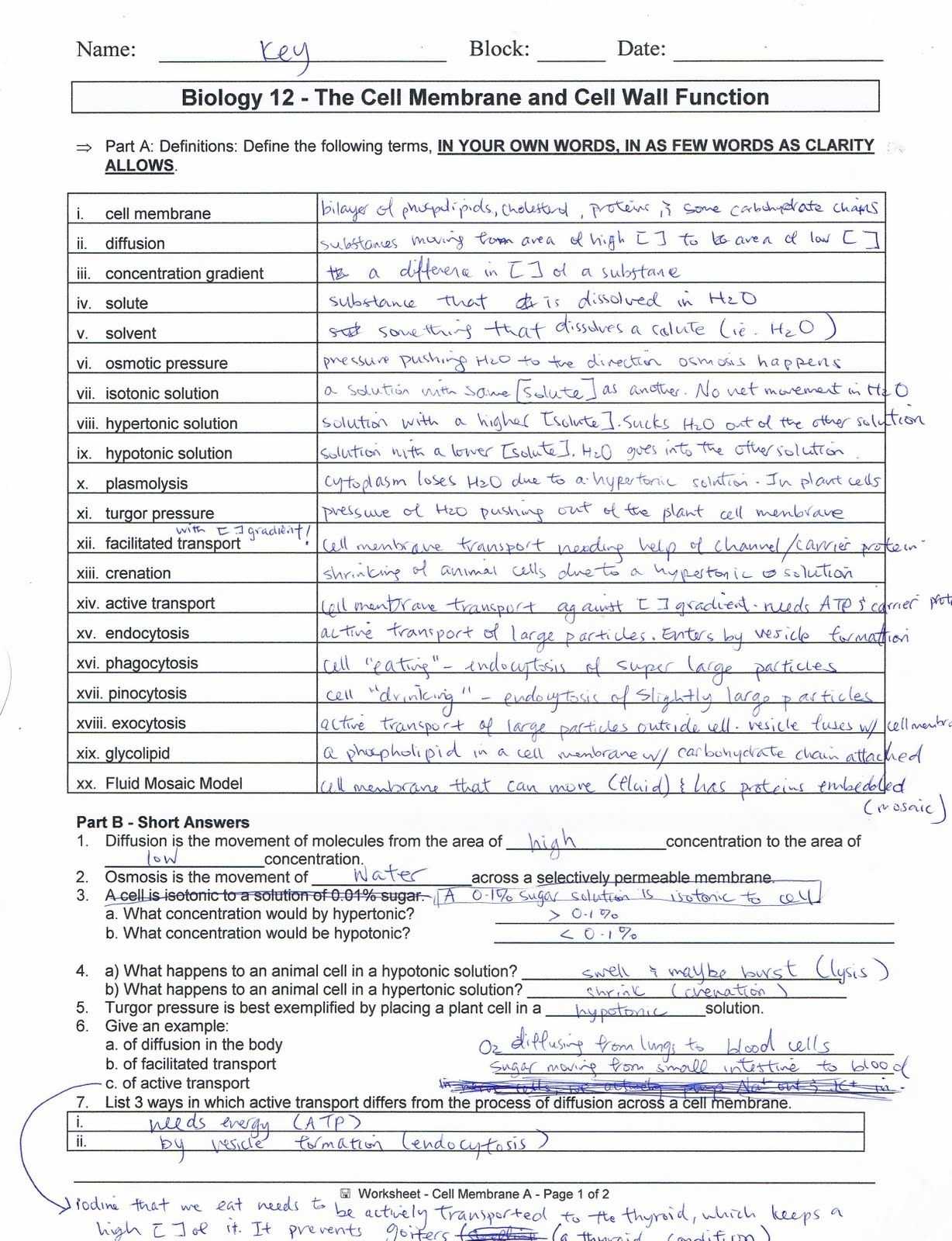
Exploring Osmosis: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Cell Membrane and Tonicity Worksheets
Osmosis is a process that occurs in all living cells, and it is essential for the proper functioning of the cell. Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane, such as the cell membrane, in order to equalize the concentration of dissolved solutes on either side of the membrane. Understanding osmosis and its associated concepts, such as tonicity, is essential for anyone studying biology or biochemistry.
This guide is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of osmosis and tonicity, and to provide worksheets to help reinforce the concepts. It begins with a discussion of the basic principles of osmosis, including tonicity and the different types of solutions that can exist. Then, the guide goes into detail about how osmosis works, and how different solutions interact with the cell membrane. Finally, the guide concludes with a series of worksheets designed to help students practice and apply the concepts of osmosis and tonicity.
By following this guide, students will gain a greater understanding of osmosis and its associated concepts, and will be better prepared for further study in biology or biochemistry. Osmosis and tonicity are complex concepts, but with practice and dedication, students can gain a solid understanding of these topics.
[toc]
Unraveling the Mysteries of Cell Membrane and Tonicity: A Step-By-Step Tutorial
This tutorial aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the fundamentals of cell membrane and tonicity. Through this step-by-step guide, readers will gain a better understanding of how cell membranes and tonicity work and how they interact with each other.
First, let’s discuss the basics of cell membranes. A cell membrane is a thin, semi-permeable barrier that surrounds the entire cell and controls the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. It is composed of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates and acts as a gatekeeper for the cell, allowing only certain molecules to pass through.
Next, let’s discuss tonicity. Tonicity is the ability of a solution to cause a cell to swell or shrink based on the difference in solute concentration of the solution and the cell. A hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration than the cell, causing the cell to shrink, while a hypotonic solution has a lower solute concentration than the cell, causing the cell to swell.
Now, let’s talk about how cell membranes and tonicity interact. When a cell is placed in an isotonic solution, the solute concentration of the solution is equal to the solute concentration of the cell. As a result, the cell membrane remains fairly stable and no water is exchanged between the solution and the cell.
However, when a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the solute concentration of the solution is greater than the solute concentration of the cell. This causes water to quickly leave the cell, shrinking the cell in size. In contrast, when a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, the solute concentration of the solution is lower than the solute concentration of the cell. This causes water to quickly enter the cell, resulting in an increase in the cell’s size.
Finally, let’s discuss how cells can adapt to changes in tonicity. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, it can adapt by increasing the permeability of its cell membrane. This allows for water to enter the cell, reducing the difference in solute concentration between the cell and the solution. Similarly, when a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, it can adapt by decreasing the permeability of its cell membrane. This prevents water from entering the cell, reducing the difference in solute concentration between the cell and the solution.
Through this tutorial, readers should now have a better understanding of the fundamentals of cell membrane and tonicity and how they interact with each other. With this knowledge, readers can gain a deeper insight into how cells can adapt to different environmental conditions.
How to Design an Effective Cell Membrane and Tonicity Worksheet
Instructions
1. Begin by introducing the concepts of cell membranes and tonicity in a brief but comprehensive overview. Explain the role of a cell membrane in the cell and how it allows for the transport of materials in and out of a cell. Explain tonicity as it relates to the movement of water through a cell membrane.
2. Provide an example of a cell membrane and explain how it is composed and how it functions. Include diagrams or pictures if available.
3. Create an activity or worksheet that requires students to apply their understanding of cell membranes and tonicity. Begin by introducing a scenario that requires the student to analyze how water will move in and out of a cell based on the tonicity of the solution. Ask questions that require students to explain the role of the cell membrane in the movement of water and the role of tonicity in this process.
4. Provide the students with examples of hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic solutions and ask them to predict the movement of water in and out of the cell based on the tonicity of each solution.
5. Include a section that allows students to draw or diagram their predictions and explain why they believe water will move in and out of the cell as they have predicted.
6. Include an answer key that provides the correct answers to the questions posed in the worksheet.
7. Review the worksheet and make any necessary changes or additions before providing it to the students.
Analyzing the Impact of Cell Membrane and Tonicity Worksheets on Student Learning Outcomes
Cell membrane and tonicity are two important concepts in biology. As such, these two topics are often taught in classrooms as part of a larger biology curriculum. Worksheets are a valuable tool for assessing student learning outcomes in these topics. This paper will analyze the impact of cell membrane and tonicity worksheets on student learning outcomes.
First, it is important to consider the benefits of using worksheets to assess student learning outcomes. Worksheets are a simple and effective way to gauge student understanding of the topics. They are also easily administered and provide an immediate overview of student performance. Additionally, worksheets can be reused and modified, making them a cost-effective teaching tool.
The use of cell membrane and tonicity worksheets can result in improved student understanding of the concepts. This is because worksheets provide a structured approach to learning, allowing students to practice and assess their knowledge. By focusing on specific topics, students can focus on the key concepts and gain a better understanding of the material.
Worksheets can also be used to assess student progress over time. By monitoring student performance on the worksheets, teachers can identify areas of strength and weakness and adjust their teaching strategies accordingly. This allows teachers to focus on areas of improvement and provide targeted instruction.
Finally, worksheets can be used to encourage student engagement. By providing students with a set of questions, worksheets can encourage students to ask questions and participate in class discussions. This helps to foster a more interactive learning environment, which can improve student learning outcomes.
Overall, worksheets can be an effective way to assess student learning outcomes in cell membrane and tonicity topics. By providing structure and encouraging student engagement, worksheets can help to improve student understanding of the concepts. As such, worksheets can be a valuable teaching tool for teachers when teaching these topics.
Conclusion
The cell membrane and tonicity worksheet was a great way to learn more about the structure and function of the cell membrane and tonicity. It provided an in-depth look into the different components of the cell membrane and how they interact with one another to maintain the cell’s tonicity. This worksheet also highlighted the importance of osmosis and its role in maintaining the cell’s homeostasis. Through the activities, students were able to gain a better understanding of how the cell membrane works and how tonicity can affect a cell’s environment.
[addtoany]