Exploring Box and Whisker Plots: A Step-by-Step Guide to Using Worksheets
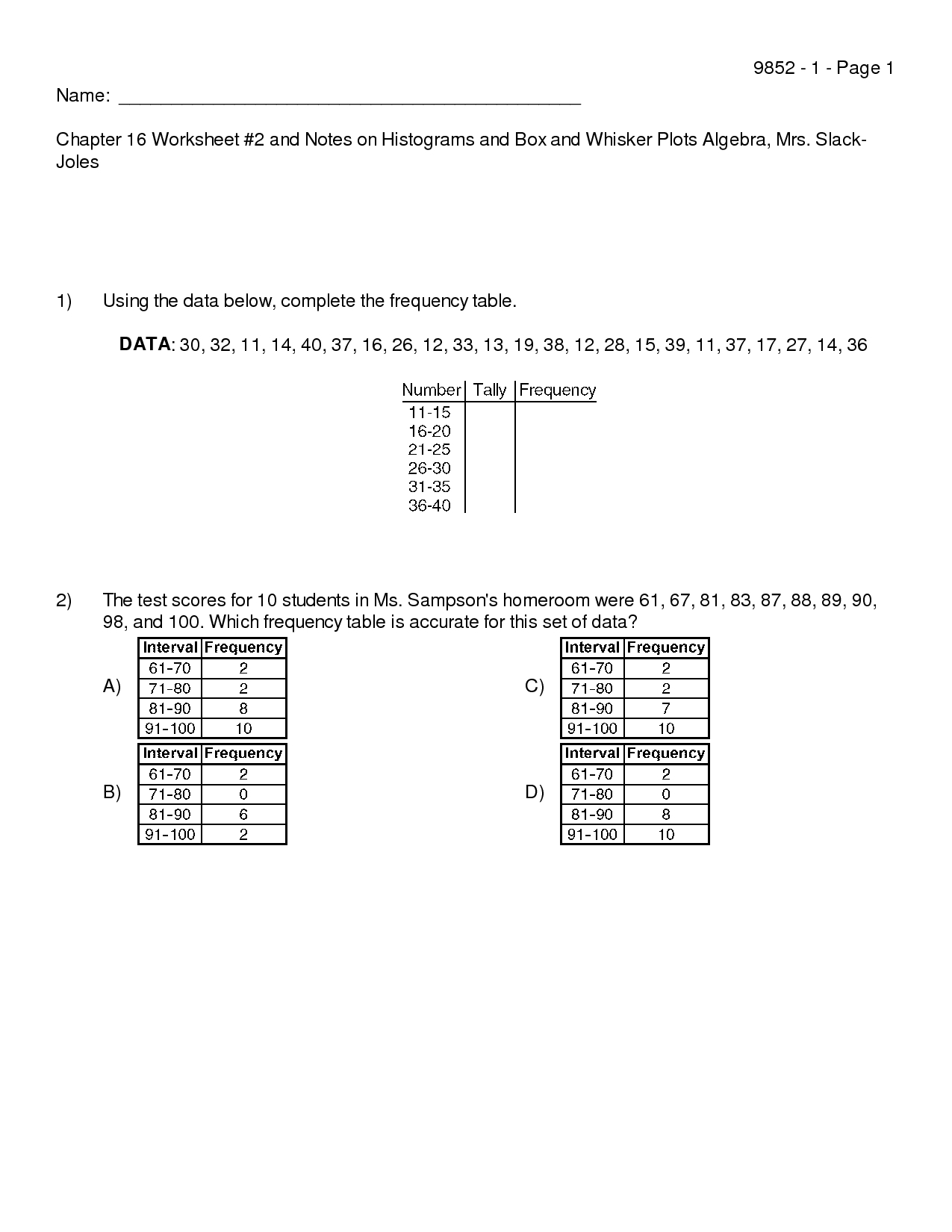
Box and whisker plots are a powerful tool used to summarize and explore data. They provide a visual representation of quantitative data and can help identify potential outliers or clusters in the data. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of using worksheets to create box and whisker plots.
Step 1: Prepare the Data
Before you can create a box and whisker plot, you must first prepare your data. This means organizing your data into a format that can be used to construct the plot. Start by gathering the data you want to visualize and writing it down in a worksheet. Make sure the data is sorted in numerical order, from smallest to largest.
Step 2: Calculate the Median
Now that the data is organized, calculate the median. The median is the middle value of the data set. To find it, add up the two middle numbers and divide by two. This is the median value.
[toc]
Step 3: Calculate the Quartiles
Quartiles divide the data set into four equal parts. Start by finding the lower quartile (Q1). This is the median value of the lower half of the data set. To find it, find the median value of the lower half of the data set. Then, find the upper quartile (Q3). This is the median value of the upper half of the data set.
Step 4: Calculate the Interquartile Range
The interquartile range (IQR) is the difference between the upper and lower quartiles. To find it, subtract the lower quartile (Q1) from the upper quartile (Q3).
Step 5: Calculate the Inner Fences
The inner fences are the two values that can be used to identify potential outliers. To find them, subtract 1.5 times the IQR from the lower quartile (Q1) and add 1.5 times the IQR to the upper quartile (Q3).
Step 6: Calculate the Outer Fences
The outer fences are the two values that can be used to identify extreme outliers. To find them, subtract 3 times the IQR from the lower quartile (Q1) and add 3 times the IQR to the upper quartile (Q3).
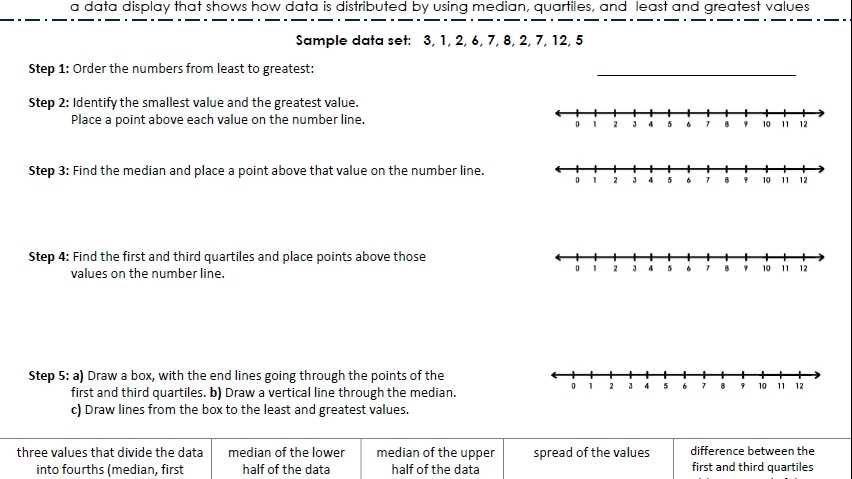
Step 7: Construct the Box and Whisker Plot
Now that all the values have been calculated, it’s time to construct the box and whisker plot. Start by drawing a horizontal number line with the lower quartile (Q1), median, and upper quartile (Q3) marked. Next, draw a box around the lower quartile (Q1), median, and upper quartile (Q3). Finally, draw a line from the lower quartile (Q1) to the lower inner fence. Then draw a line from the upper quartile (Q3) to the upper inner fence. This will complete your box and whisker plot.
By following these steps, you can use worksheets to create box and whisker plots and explore your data. This type of visualization can help you identify potential outliers or clusters in the data and draw conclusions about the data set.
Utilizing Box and Whisker Plot Worksheets to Identify Outliers
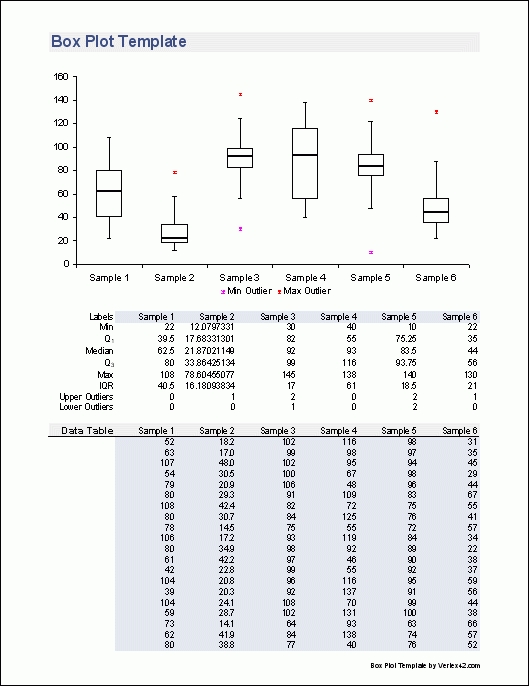
Box and whisker plot worksheets can be used to identify outliers in a data set. These worksheets are composed of a five-number summary that divides the data into four parts, forming a box and whisker plot. The five-number summary consists of the minimum, the first quartile, the median, the third quartile, and the maximum. The box itself is composed of the first and third quartiles, with the median in the middle. The whiskers are composed of the minimum and maximum values.
Outliers are values that fall outside of the range of the whiskers. When a data set contains outliers, it is important to identify and understand their effect on the data. Box and whisker plot worksheets are useful for identifying outliers because they provide a visual representation of the data that makes it easy to spot any values that are outside the range of the whiskers.
When using a box and whisker plot worksheet to identify outliers, it is important to look for any values that are significantly higher or lower than the rest of the data. In addition, it is important to look for any values that are significantly higher or lower than the quartiles and the median of the data set. If any of these values are present, they can be classified as outliers.
Once outliers have been identified, it is important to analyze their effect on the data set. For example, if the outliers are significantly higher than the median and quartiles, they may be skewing the data in a certain direction. It is important to consider the impact of these outliers on the overall results of the data before coming to any conclusions.
Overall, box and whisker plot worksheets are an effective tool for identifying outliers in a data set. By providing a visual representation of the data, these worksheets make it easy to spot any values that are significantly higher or lower than the rest of the data. Once outliers have been identified, it is important to analyze their effect on the data set and consider the implications before coming to any conclusions.
A Comprehensive Guide to Interpreting Data Using Box and Whisker Plot Worksheets
A box and whisker plot worksheet is a useful tool for visualizing and interpreting data. It is a type of graph that helps to display the distribution of a set of data points by using quartiles, or the division of the data into four equal parts. This type of worksheet can be an invaluable tool for data analysis and interpretation.
To begin, it is important to understand the components of a box and whisker plot worksheet. A box and whisker plot consists of a rectangular box with lines extending from the edges of the box. The box is divided into four equal parts, or quartiles, with a vertical line extending from the center of the box. This line is known as the median. The two quartiles on the left of the median are referred to as the lower quartile and the two quartiles on the right side of the median are referred to as the upper quartile. The whiskers extend from the end of the box to the highest and lowest values in the data set.
To interpret data using a box and whisker plot worksheet, it is important to look at the median, the quartiles, and the whiskers. The median is the middle value in the data set and is used to represent the “middle” of the data. The quartiles represent the division of the data into four equal parts, with the median being the middle value. The whiskers represent the highest and lowest values in the data set.
Using this information, it is possible to interpret the data in a box and whisker plot worksheet. For example, if the median is higher than the lower quartile, it indicates that the data is skewed to the right, or that the majority of the data is higher than the median. Similarly, if the median is lower than the upper quartile, it indicates that the data is skewed to the left, or that the majority of the data is lower than the median. Additionally, the whiskers can be used to determine the range of values in the data set, as they indicate the highest and lowest values.
In conclusion, a box and whisker plot worksheet is a useful tool for visualizing and interpreting data. It is composed of a rectangular box with lines extending from the edges of the box, a vertical line representing the median, and whiskers extending from the end of the box to the highest and lowest values in the data set. By looking at the median, quartiles, and whiskers, it is possible to interpret the data in the worksheet and gain valuable insights into the data.
Conclusion
The Box And Whisker Plot Worksheet is a great tool for visualizing data in different ways, and can be used to identify patterns in data. It is a very useful tool for understanding the spread of data, and can help to identify outliers in a dataset. This worksheet can also be used to compare different datasets and identify relationships between different variables. Overall, the Box And Whisker Plot Worksheet is a very useful tool for understanding data.
[addtoany]