Exploring the Different Parts of Animal and Plant Cells with a Worksheet
Animal and plant cells are the fundamental building blocks of life, and yet many students have difficulty understanding the different components of these cells. This worksheet is designed to help students gain a better understanding of the different parts of animal and plant cells.
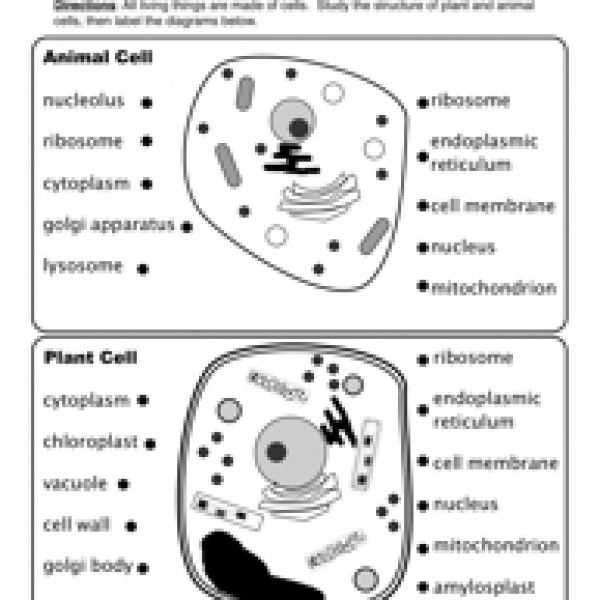
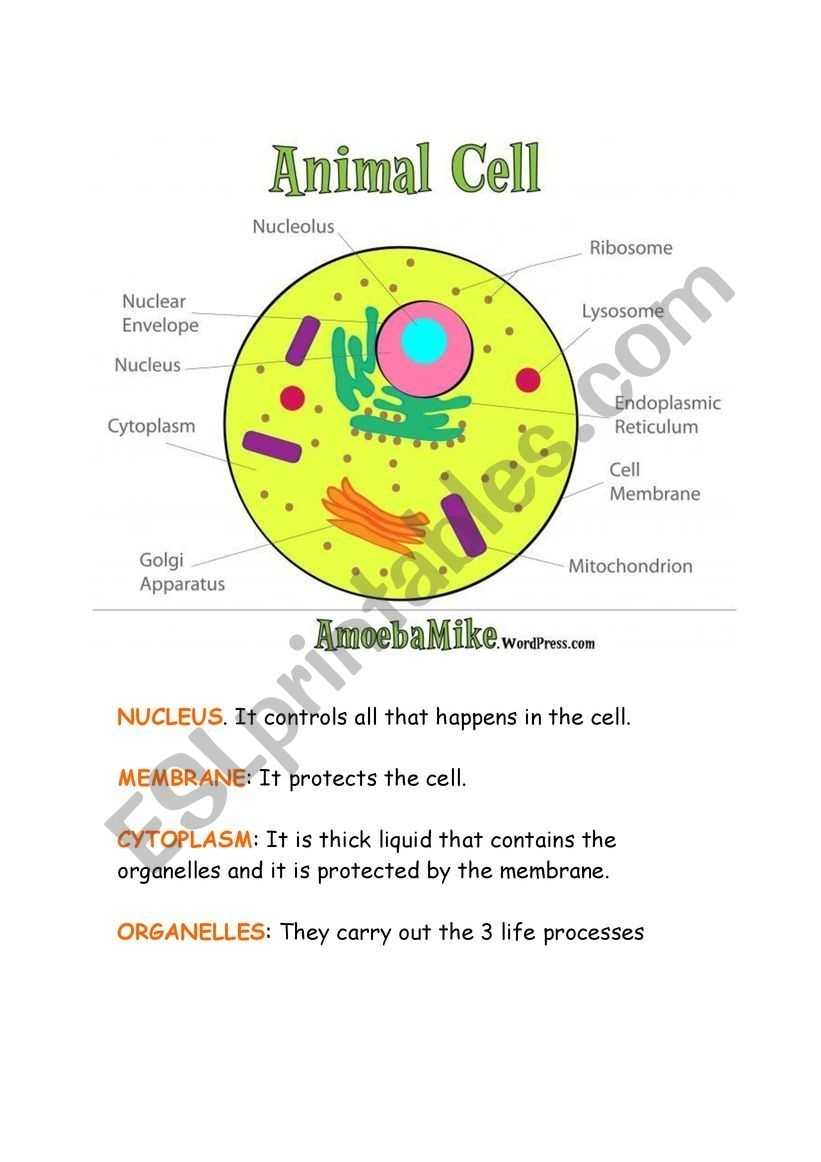
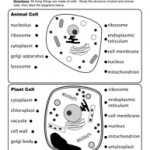
The first part of the worksheet asks students to identify the major components of an animal cell, including the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, lysosomes, and mitochondria. Students should be able to describe the functions of each component and list the organelles or structures associated with it.
The second part of the worksheet focuses on the components of a plant cell. Students should be able to identify the cell wall, central vacuole, chloroplasts, and other organelles. Again, students should be able to explain the functions of each component and list the structures associated with it.
[toc]
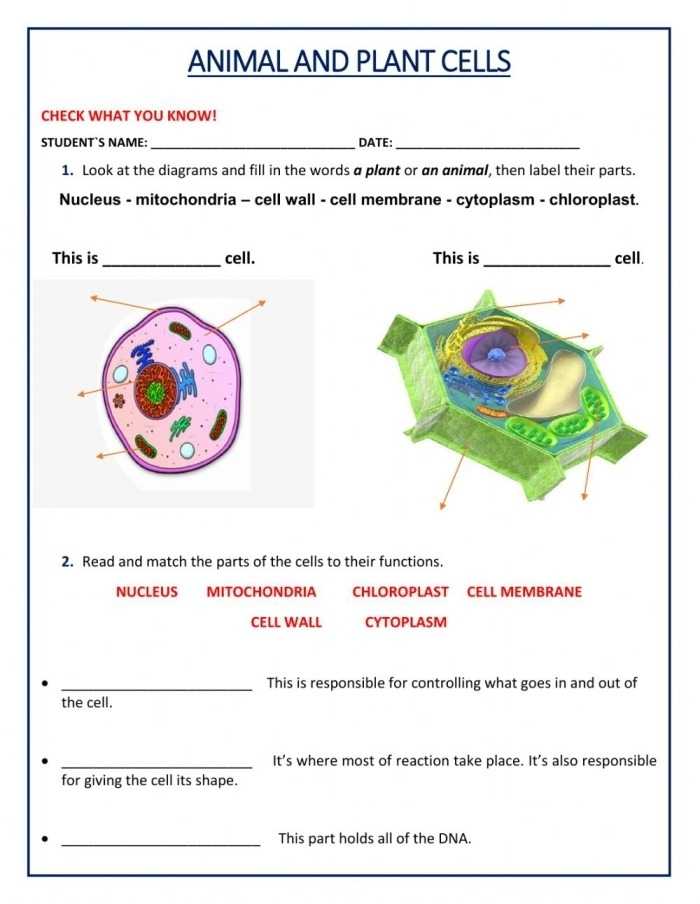
The third part of the worksheet asks students to compare and contrast the components of animal and plant cells. For example, they should be able to compare the cell wall and cell membrane, or the nucleus and chloroplasts.
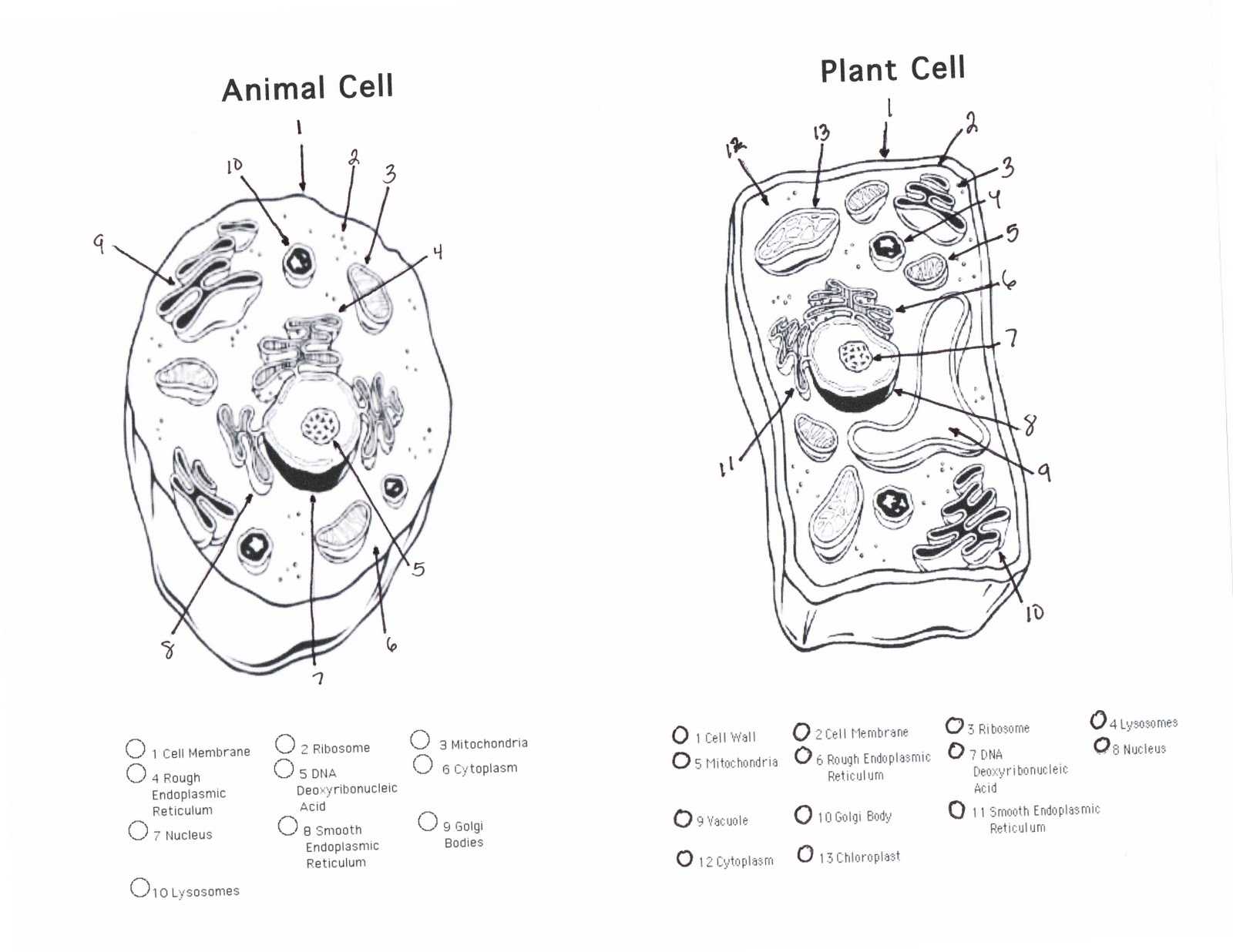
The fourth part of the worksheet requires students to draw a diagram of an animal or plant cell, labeling the different components. This will help them visualize the components and better understand their functions.
By completing this worksheet, students should be able to gain a better understanding of the different parts of animal and plant cells and their functions. This will help them to better understand the process of cell division and the role of cells in the body.
Exploring the Similarities and Differences Between Animal and Plant Cells with a Worksheet
Animal and Plant Cells Worksheet
This worksheet will explore the similarities and differences between animal and plant cells. By completing this worksheet, you will gain an understanding of the distinct structures and functions of each type of cell.
Similarities
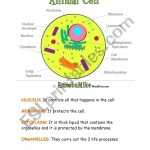
Both animal and plant cells contain a nucleus, which houses the cell’s genetic material. The nucleus is surrounded by a membrane that controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell. Both types of cells also have cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like substance that contains the cell’s organelles. Additionally, both animal and plant cells contain mitochondria, which are responsible for generating energy for the cell.
Differences
One of the primary differences between animal and plant cells is that plant cells contain a cell wall, which provides structure and protection for the cell. The cell wall is composed of cellulose, while animal cells do not have cell walls. Additionally, plant cells contain chloroplasts, which are responsible for capturing energy from sunlight to produce food through photosynthesis. Animal cells do not contain chloroplasts. Plant cells also contain large, central vacuoles, which are fluid-filled structures that provide support and regulate the cell’s environment. Animal cells do not have vacuoles.
In summary, there are a number of similarities and differences between animal and plant cells. By completing this worksheet, you now have a better understanding of the distinct structures and functions of each type of cell.
Using a Worksheet to Compare Animal and Plant Cells
The comparison of animal and plant cells is an important area of study in the field of biology. To better understand the differences between these two types of cells, a worksheet can be used to compare their various characteristics.
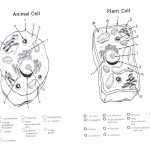
One of the primary distinctions between animal and plant cells is their structure. Animal cells are typically spherical or cylindrical in shape, while plant cells are rectangular or cube-shaped. Plant cells are usually larger in size than animal cells and contain cell walls, a feature not found in animal cells. Plant cells also contain chloroplasts, which are organelles that contain chlorophyll and are responsible for the process of photosynthesis. Animal cells, on the other hand, are typically smaller than plant cells and contain vacuoles, which are organelles that store and release water and other substances.
The cell membranes of animal and plant cells also differ. Animal cells have a semi-permeable cell membrane that regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. Plant cells, however, have a rigid cell wall that allows water and other substances to diffuse in and out of the cell, but does not allow the movement of large molecules.
The worksheet can also be used to compare the organelles within animal and plant cells. Animal cells contain centrioles, lysosomes, and cilia, while plant cells contain chloroplasts, a large central vacuole, and a cell wall. Additionally, animal cells contain mitochondria, while plant cells contain plastids.
By using a worksheet to compare animal and plant cells, students can gain a better understanding of the differences between the two types of cells and how they function. By examining the structure, cell membranes, and organelles of both types of cells, students can gain a more in-depth understanding of the cellular processes that maintain life.
Investigating the Structures of Animal and Plant Cells with a Worksheet
Cellular biology is the scientific study of the structures and functions of cells. Animal and plant cells are the most commonly studied types of cells. In this worksheet, we will investigate the structures of both animal and plant cells.
Animal cells are typically smaller than plant cells. They possess a cell membrane, which serves as the cell’s barrier from the outside environment. Inside the cell, there are organelles, which are specialized structures that carry out specific functions. Two of the most important organelles are the nucleus and the mitochondria. The nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing DNA and other genetic material. The mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for producing energy for the cell to use. Animal cells also contain numerous other organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
Plant cells are slightly larger than animal cells and are composed of several distinct parts. The most notable feature of a plant cell is the cell wall, which provides protection and support to the cell. Additionally, plant cells possess a large central vacuole, which is filled with water and other materials. This vacuole helps regulate the cell’s osmotic pressure. The nucleus and mitochondria are also present in plant cells, similar to animal cells. Other organelles, such as chloroplasts and endoplasmic reticulum, are found in plant cells but not in animal cells. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, which is the process of converting light energy into chemical energy.
In conclusion, animal and plant cells are both made up of numerous structures that are essential for their function. Animal cells possess a cell membrane, nucleus, and mitochondria, along with other organelles. Plant cells contain a cell wall, large central vacuole, and chloroplasts, in addition to organelles found in animal cells. By understanding the structures of these cells, we can gain a better appreciation of how they work.
Conclusion
The Animal and Plant Cells Worksheet provides an excellent opportunity for students to explore the differences and similarities between these two types of cells. Through the completion of this worksheet, students gain a better understanding of how cells function and the differences between animal and plant cells. Moreover, students gain an appreciation of the important role that cells play in the lives of both plants and animals.
[addtoany]