Exploring Angular and Linear Velocity: What is it and How to Calculate it?
Angular velocity and linear velocity are two different concepts in physics, but they are related. Angular velocity is the rate at which an object is turning and is usually measured in revolutions per minute (RPM). It can also be measured in radians per second (rad/s). Linear velocity is the rate at which an object is moving in a straight line, and is typically measured in meters per second (m/s).
In order to calculate angular velocity, one must first determine the number of revolutions per minute that the object is making. This can be done by counting the number of times the object is turning around in a certain amount of time. The angular velocity can then be calculated by dividing the number of revolutions by the amount of time it took to make those revolutions.
To calculate linear velocity, one must first determine the distance that the object is traveling in a certain amount of time. The linear velocity can then be calculated by dividing the distance by the amount of time.
[toc]
Both angular and linear velocity are important concepts in physics, and understanding how to calculate them is essential for anyone studying the subject. By understanding how to calculate these velocities, one can begin to further explore the laws of motion and gain a better understanding of how objects interact with each other in the physical world.
How to Utilize the Angular and Linear Velocity Worksheet for Problem Solving
The Angular and Linear Velocity Worksheet is an invaluable tool for problem solving. It can be used to analyze motion in two dimensions, allowing problem solvers to accurately measure angles and distances in order to determine velocities. The worksheet is divided into two parts: the angular velocity section and the linear velocity section.
In the angular velocity section, problem solvers must first identify the angle between two points. This angle will tell them the angular velocity for their problem. Once the angle is determined, the problem solver must then calculate the angular velocity using the formula provided. This formula is written as the angle change divided by the time interval.
In the linear velocity section, problem solvers must first identify the distance between two points. This distance will tell them the linear velocity for their problem. Once the distance is determined, the problem solver must then calculate the linear velocity using the formula provided. This formula is written as the distance divided by the time interval.
When combined, the angular and linear velocities provide the total velocity of an object. This total velocity gives problem solvers the information they need to determine the speed and direction of an object.
By utilizing the Angular and Linear Velocity Worksheet, problem solvers can quickly and accurately solve problems involving motion in two dimensions. This worksheet is an essential tool for anyone looking to gain a better understanding of motion.
The Benefits of Understanding Angular and Linear Velocity for Everyday Tasks
Linear velocity and angular velocity are terms often used in physics and engineering, but they can also be beneficial in everyday tasks. Understanding the concepts of linear velocity and angular velocity can provide a greater understanding of the world and the physical processes that occur around us.
Linear velocity is the speed of an object in a straight line and is expressed in units of length per unit time, such as meters per second. Linear velocity is determined by dividing the distance traveled by the time it took to travel that distance. Linear velocity can be used in everyday tasks to measure the speed at which an object is moving in a straight line, such as a car or a runner.
Angular velocity is the speed at which an object is rotating around a fixed point and is expressed in units of angle per unit time, such as revolutions per minute. Angular velocity can be used to measure the speed at which an object is rotating, such as the speed of a spinning top or a fan blade. Understanding angular velocity can provide insight into how objects rotate and the forces that influence their rotation.
Understanding linear velocity and angular velocity can help to better understand the physical processes that occur around us. For example, the concepts of linear velocity and angular velocity can be used to explain how a car accelerates and how a fan blade moves. Additionally, understanding linear velocity and angular velocity can be useful when performing everyday tasks such as measuring the speed of a car or measuring the speed at which a fan rotates.
In conclusion, understanding linear velocity and angular velocity can provide a greater understanding of the physical processes around us and be useful when performing everyday tasks. By understanding these concepts, we can gain insight into the physics of the world and better understand the forces that govern the motion of objects.
Introducing Angular and Linear Velocity Worksheet to High School Physics Classes
Introducing Angular and Linear Velocity to High School Physics Classes
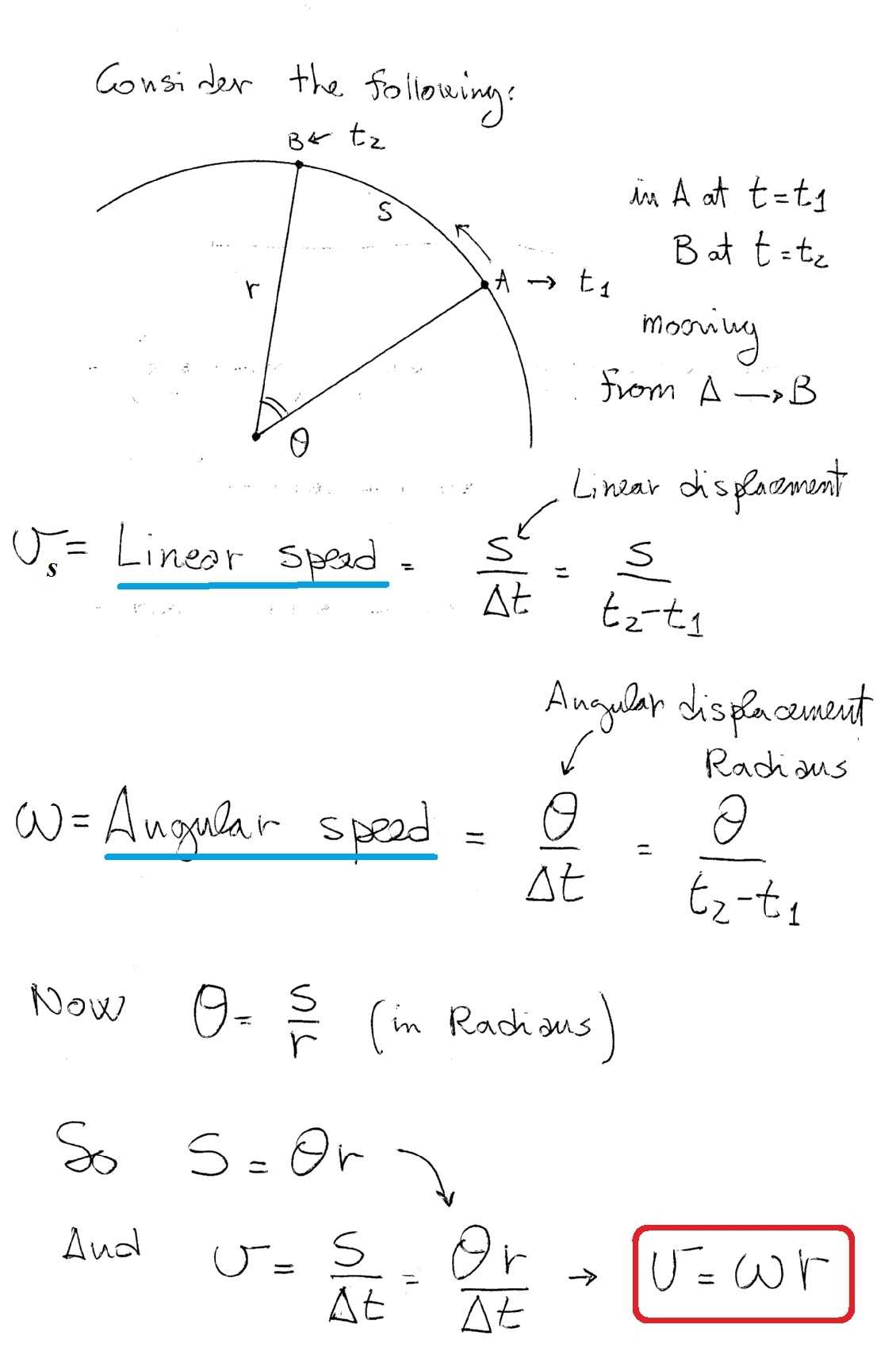
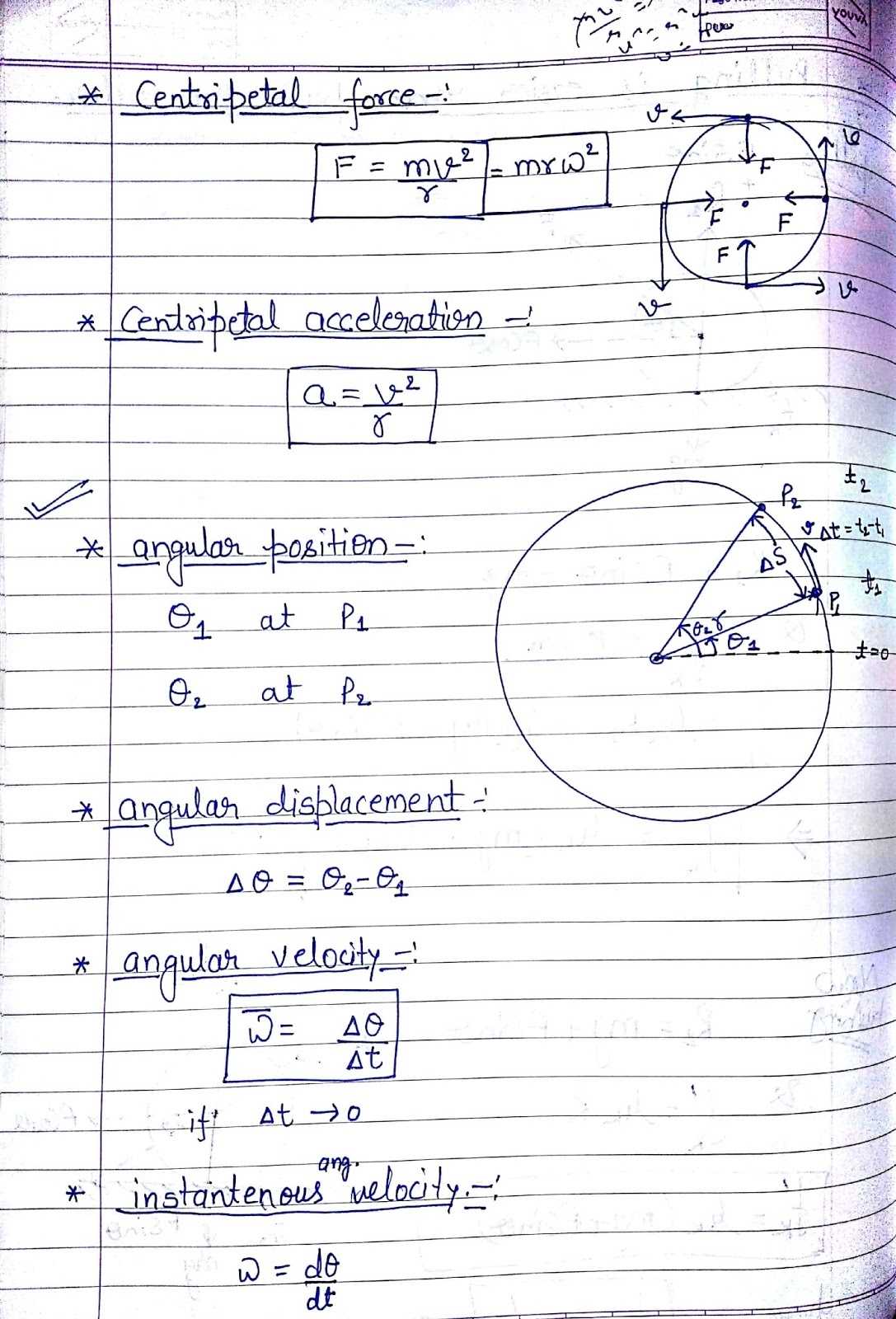
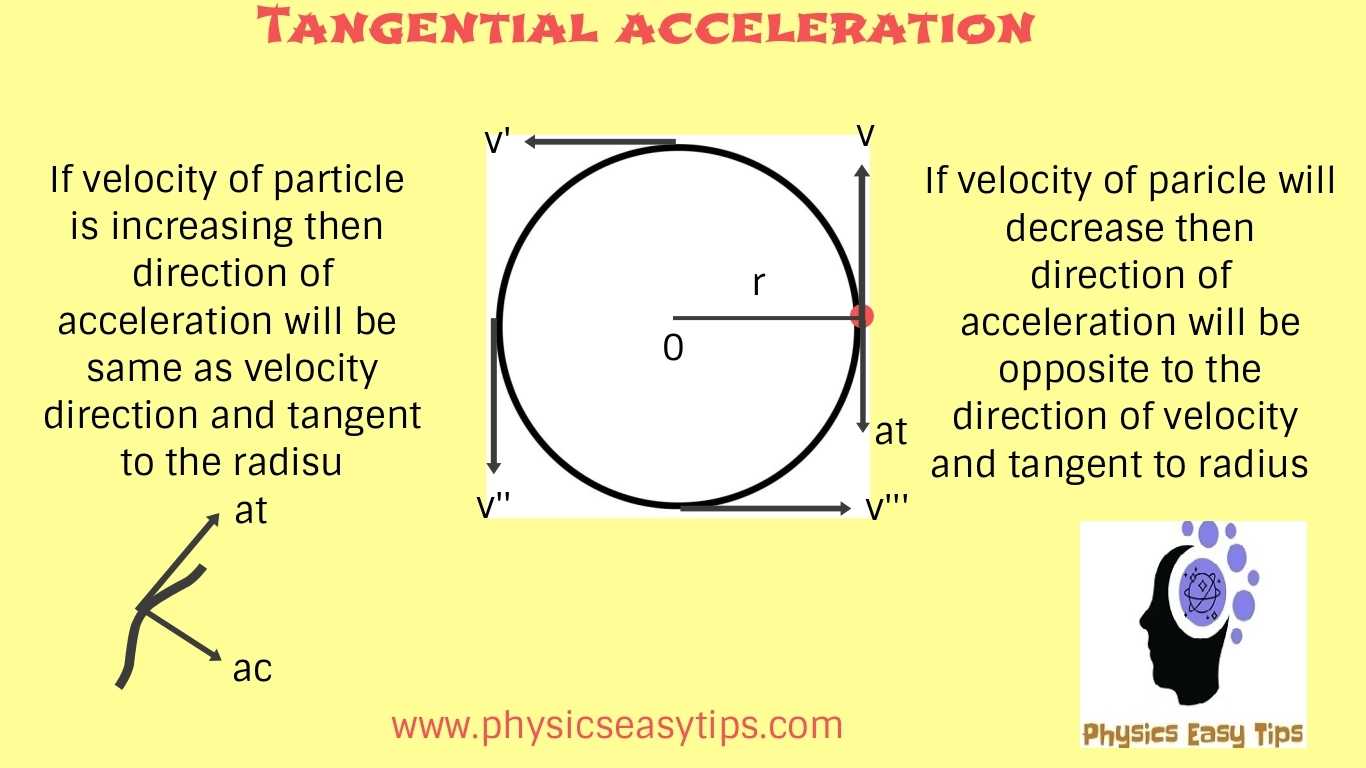
Angular velocity and linear velocity are two key concepts in physics that can help students develop an understanding of the laws of motion. Angular velocity is the rate of change of angular displacement per unit of time, measured in radians per second (rad/s). Linear velocity is the rate of change of an object’s position in a specific direction, and is measured in meters per second (m/s).
In high school physics classes, students will benefit from understanding and applying the concepts of angular and linear velocity. By learning about these concepts, students can gain a better understanding of the principles of motion and velocity, including how they relate to acceleration and force. In addition, they can learn how to calculate various components of angular and linear velocity.
Teachers can introduce these concepts by having students analyze real-world examples in which angular and linear velocity are used. For example, students can analyze the motion of a spinning wheel or a car moving in a straight line. They can also calculate the angular and linear velocity of an object, such as a ball rolling down a hill.
In addition to these activities, teachers can also provide students with interactive simulations or videos of real-world examples in which angular and linear velocity are used. This will help them visualize the concepts and understand how they apply to the physical world.
By introducing angular and linear velocity to high school physics classes, students will be able to gain a better understanding of the principles of motion and velocity. They will also be able to apply these concepts to real-world examples, analyze them, and calculate various components of angular and linear velocity.
Conclusion
The Angular and Linear Velocity Worksheet has provided an excellent way to understand the concepts of angular and linear velocity. It has allowed students to practice their calculations and gain a better understanding of the relationship between the two. By working through the worksheet, students have gained a better appreciation of the relationship between angular and linear velocity, and can now apply the concepts in real-world situations.
[addtoany]

![[Expert Verified] Derive Relation Between Linear Velocity And Angular For Angular And Linear Velocity Worksheet](https://worksheet1.wp-json.my.id/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/expert-verified-derive-relation-between-linear-velocity-and-angular-for-angular-and-linear-velocity-worksheet.jpg)



![[Expert Verified] Derive Relation Between Linear Velocity And Angular For Angular And Linear Velocity Worksheet](https://worksheet1.wp-json.my.id/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/expert-verified-derive-relation-between-linear-velocity-and-angular-for-angular-and-linear-velocity-worksheet-150x150.jpg)