Exploring the Basics of Acid and Base Chemistry with an Interactive Worksheet
Acid and base chemistry is an essential topic for any student of chemistry. It is also an area of chemistry that can be difficult to understand. This interactive worksheet will provide a comprehensive overview of the basics of acid and base chemistry, helping students gain a better understanding of the key concepts.
The worksheet begins by introducing the definition of an acid and a base. It then explains how acids and bases interact with each other, including how the pH scale is used to measure acidity and basicity. The worksheet then moves on to explain the key characteristics of acids and bases, such as the Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis definitions, and how they are classified. Examples of different types of acids and bases are provided to illustrate the concepts.
Next, the worksheet provides an overview of the different reactions involving acids and bases, including the acid-base reaction, neutralization, and precipitation. It also explains the role of catalysts in acid-base reactions, as well as the importance of buffers.
[toc]
Finally, the worksheet provides an overview of the various laboratory tests used to identify acids and bases, including the indicator, titration, and spectrophotometric tests. The worksheet also includes a set of practice problems to help students apply the concepts they have learned.
This interactive worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the basics of acid and base chemistry. By working through the worksheet, students will gain a better understanding of the key concepts and be able to apply them to practical problems.
Understanding Acid and Base Reactions with a Hands-On Worksheet Exercise
Acid-base reactions are an important part of understanding how chemistry works. With a hands-on worksheet exercise, students can gain a better understanding of how these reactions take place.
The first step in this exercise is to provide each student with a worksheet that outlines the steps for completing the exercise. The worksheet should include a diagram of the acid-base reaction, a list of the materials needed for the experiment, and instructions for completing the experiment.
Once the worksheet is distributed, the students will need to gather the materials for the experiment. These materials usually include an acid and a base, such as vinegar and baking soda. The students will also require materials to measure the acid and base, such as measuring spoons, a graduated cylinder, and graduated beakers.
After the materials are gathered, the students can begin the experiment. The first step is to measure out equal amounts of the acid and base. These measurements should be noted on the worksheet, so that the results can be compared later.
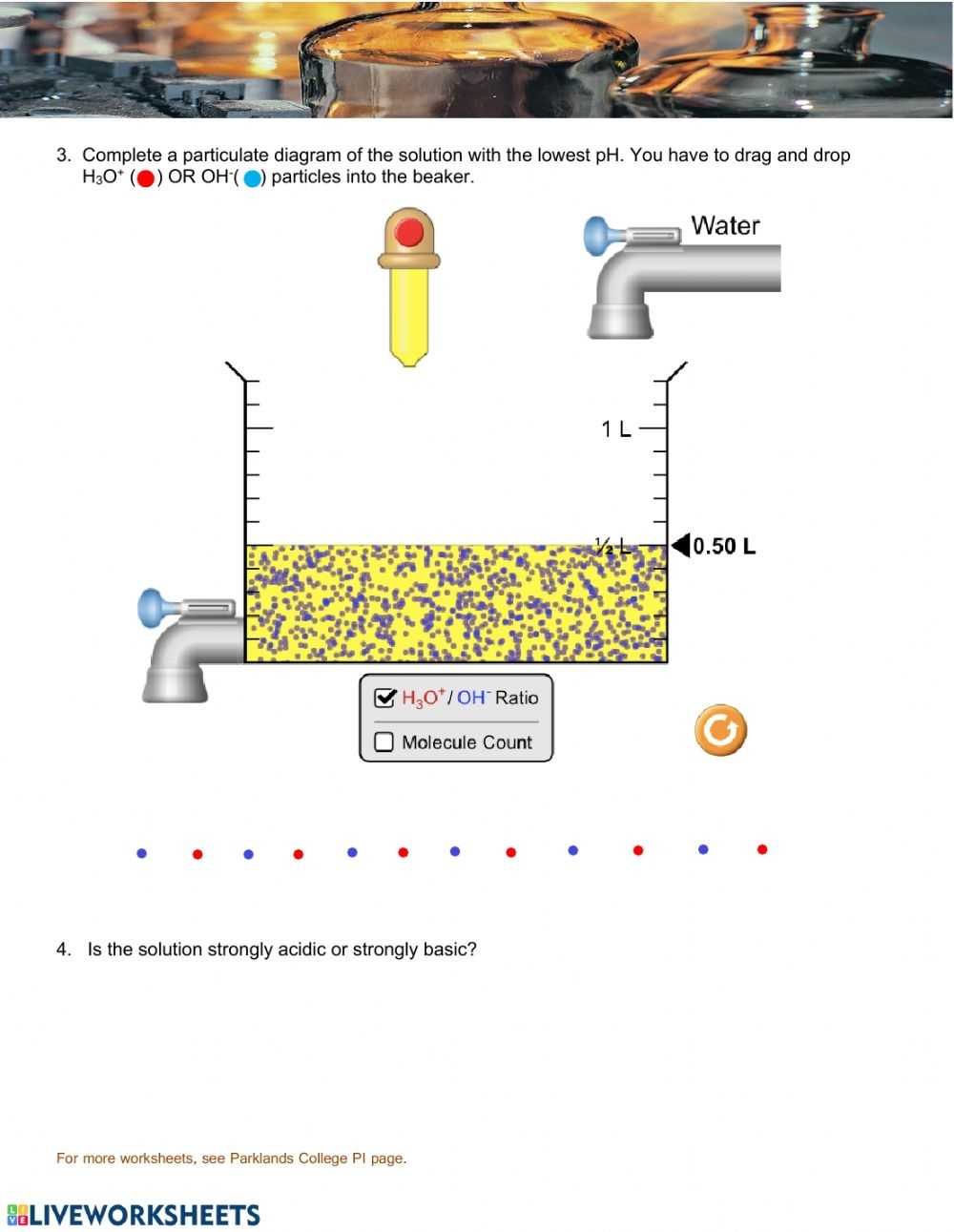
Next, the students will combine the acid and base in the graduated beaker. As the reaction takes place, the students should observe the changes that occur. The students should also measure the temperature of the reaction, as well as the pH level of the mixture.
Finally, the students should calculate the amount of energy that was released during the reaction, and they should record this on their worksheet. This can help them to understand the different types of energy released during different acid-base reactions.
By completing this hands-on worksheet exercise, students can gain a better understanding of how acid-base reactions work. Through this exercise, students can learn about the different types of reactions that can occur, as well as the energy that is released during an acid-base reaction.
Balancing Chemical Equations Involving Acids and Bases Using a Worksheet Approach
Balancing chemical equations involving acids and bases can be a challenging task. However, by utilizing a worksheet approach, learners can become comfortable with this important concept.
Step 1: First, learners should identify the reactants and products involved in the equation. This includes acids, bases, and other chemicals. For example, if the equation is HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O, the reactants are HCl (an acid) and NaOH (a base). The products are NaCl (a salt) and H2O (water).
Step 2: The next step is to assign each reactant and product a coefficient. A coefficient is a number used to represent a molecule of a chemical. In the equation above, HCl is assigned a coefficient of 1, NaOH is assigned a coefficient of 1, NaCl is assigned a coefficient of 1, and H2O is assigned a coefficient of 2.
Step 3: The third step is to write the equation on the worksheet. Learners should be sure to include the coefficients in their equation.
Step 4: The fourth step is to balance the equation. This can be done by adjusting the coefficients until the number of atoms of each element on each side of the equation is the same. In the example above, the equation can be balanced by changing the coefficient of H2O from 2 to 1. The balanced equation is now HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O.
Step 5: Finally, learners can check their work by counting the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation. If the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides, the equation is balanced.
By following the steps outlined above, learners can easily balance equations involving acids and bases. This worksheet approach is an effective way to learn this important concept.
Conclusion
The Acid and Base Worksheet has provided an informative and engaging way for students to learn about the properties of common acids and bases. Through the use of the worksheet, students have been able to learn the definitions of common acids and bases, recognize the indicators used to test for them, and understand the differences between strong acids, weak acids, and strong bases. The worksheet has also provided a hands-on experience by allowing students to create neutralization reactions and test for pH. With this information, students will be able to better understand and apply the concepts of acids and bases in their everyday lives.
[addtoany]



![89 [Pdf] Pdf Worksheet Acids Bases Free Printable Download Docx Zip With Acid And Base Worksheet](https://worksheet1.wp-json.my.id/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/89-pdf-pdf-worksheet-acids-bases-free-printable-download-docx-zip-with-acid-and-base-worksheet.jpg)



![89 [Pdf] Pdf Worksheet Acids Bases Free Printable Download Docx Zip With Acid And Base Worksheet](https://worksheet1.wp-json.my.id/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/89-pdf-pdf-worksheet-acids-bases-free-printable-download-docx-zip-with-acid-and-base-worksheet-150x150.jpg)