Exploring the Different Types of Cell Transport and How They Influence 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers
Cell transport is a vital process that allows cells to move substances in and out of their membrane. This process is essential for many cell functions, including nutrient uptake, waste removal, and even communication with other cells. There are several different types of cell transport, each of which has a unique purpose and affects how cells interact with their environment.
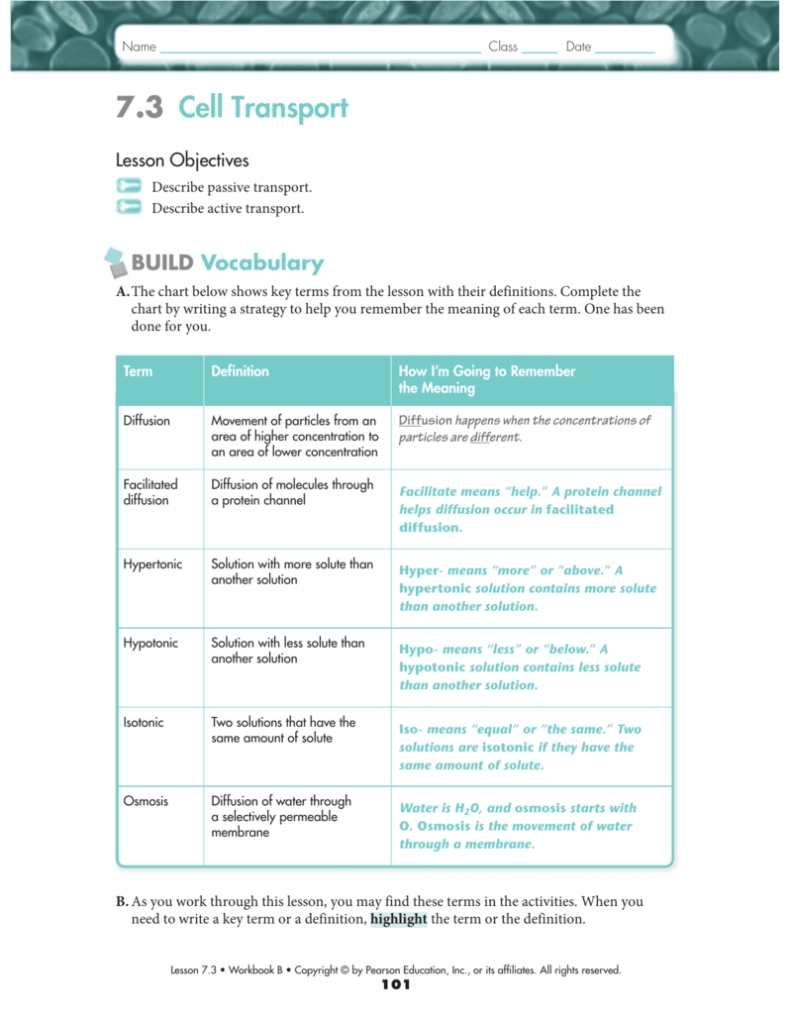
The first type of cell transport is passive transport. This process does not require energy and is used for the movement of molecules across the cell membrane. This type of transport is divided into two main categories: diffusion and osmosis. Diffusion is the process of molecules moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Osmosis is a process of water molecules moving from an area of low solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. Both processes are important for cells to maintain homeostasis.
The second type of cell transport is active transport. Unlike passive transport, this process requires energy to move molecules against the concentration gradient. This type of transport is used to move substances into the cell and can be divided into two categories: endocytosis and exocytosis. Endocytosis is the process of substances being engulfed by the cell membrane and moved inside the cell. Exocytosis is the process of substances being released from the cell membrane and moved outside the cell. Both processes are essential for cells to obtain the necessary nutrients and to remove waste.
[toc]
The third type of cell transport is facilitated diffusion. This process requires the help of proteins to move molecules across the cell membrane. This type of transport is used to move molecules that are too large or too polar to move across the cell membrane by passive transport.
Each of these types of cell transport has a unique purpose and affects how cells interact with their environment. By understanding the different types of cell transport, one can gain a better understanding of how cells interact with their environment and how they maintain homeostasis.
Using 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers to Understand the Consequences of Different Transport Processes
The 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers provide a comprehensive overview of the various transport processes that occur within a cell. These transport processes are critical for the health of the cell and the organism. Understanding the consequences of different transport processes is essential for understanding the functioning of the cell and the organism.
Active transport is a process of cellular transport that requires energy. This process is used to move molecules across the cell membrane, against the concentration gradient. This type of transport is vital for the health of the cell, as it allows the cell to maintain its internal environment. When active transport is disrupted, the cell cannot effectively maintain its internal environment, which can lead to a decrease in cell health.
Facilitated diffusion is a process of cellular transport that does not require energy. This process is used to move molecules across the cell membrane, along the concentration gradient. This type of transport helps to maintain the balance of the cell’s internal environment by allowing molecules to move across the cell membrane without expending energy. When facilitated diffusion is disrupted, the cell may be unable to maintain its internal environment, leading to a decrease in cell health.
Endocytosis is a process of cellular transport that involves the engulfment of molecules into the cell. This process is used to move large molecules across the cell membrane, and to obtain nutrients from the environment. Endocytosis requires energy and can lead to a decrease in cell health if it is disrupted.
Exocytosis is a process of cellular transport that involves the release of molecules from the cell. This process is used to move large molecules out of the cell and to expel waste products from the cell. Exocytosis requires energy and can lead to a decrease in cell health if it is disrupted.
The 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers provide an overview of the various transport processes that occur within a cell. Understanding the consequences of different transport processes can help to ensure that the cell and the organism remain healthy. By understanding the consequences of these processes, it is possible to identify and address any disruptions that may arise.
Analyzing the Driving Forces Behind Cellular Transport: A Guide to 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers
Cellular transport is a complex process that involves the movement of molecules and ions across the cell membrane. It is essential for the survival of all living organisms, as it is responsible for the exchange of nutrients, waste products, and other molecules between the cell and its environment. Understanding the mechanisms that drive cellular transport can provide valuable insight into the structure and function of cells.
This guide provides an overview of the seven major driving forces behind cellular transport, along with a 3-cell transport worksheet to help you understand the concept.
The seven major driving forces behind cellular transport include: diffusion, osmosis, active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis, vesicular transport, and facilitated diffusion. Each of these forces is responsible for moving molecules and ions across the cell membrane.
Diffusion is the movement of molecules and ions from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This process occurs without the input of energy and is the most fundamental way in which molecules move. Osmosis is a type of diffusion in which water molecules move across a semi-permeable membrane in response to a difference in osmotic pressure.
Active transport is the movement of molecules and ions against a concentration gradient, which requires energy input. Endocytosis is the process of a cell taking in substances from its environment by forming a small pocket or vesicle around the material and then engulfing it. Exocytosis is the opposite of endocytosis and involves the release of materials from the cell.
Vesicular transport is the movement of molecules and ions within a cell by means of vesicles. These vesicles are small, membrane-bound structures that are capable of carrying materials across the cell membrane. Facilitated diffusion is the movement of molecules and ions across the cell membrane with the help of specific proteins.
The 3-cell transport worksheet provides an opportunity to practice solving problems related to the seven major driving forces behind cellular transport. The worksheet includes questions on each of the forces and corresponding diagrams that help illustrate the concept. Answers are provided at the end of the worksheet.
By understanding the driving forces behind cellular transport, you can gain greater insight into the structure and function of cells. This guide, along with the 3-cell transport worksheet, can help you gain a better understanding of the concept.
Investigating the Different Modes of Cell Transport and Their Impact on 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers
Cell transport is the process by which molecules, ions and other substances move in and out of cells. It is a fundamental process of life and is essential for maintaining homeostasis. There are two main modes of cell transport: passive and active transport.
Passive transport is the movement of substances across the cell membrane that does not require energy from the cell. It occurs through diffusion, osmosis and facilitated diffusion. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Facilitated diffusion is the movement of molecules through proteins in the cell membrane.
Active transport is the movement of substances across the cell membrane that requires energy from the cell. It occurs through endocytosis, exocytosis and active transport. Endocytosis is the process by which the cell takes in large molecules or particles by forming an invagination in the cell membrane. Exocytosis is the process by which the cell releases large molecules or particles by expelling them through the cell membrane. Active transport is the process by which molecules are transported across the cell membrane against the concentration gradient, using energy from the cell.
The impact of these modes of cell transport on the cell is significant. Passive transport is important for maintaining homeostasis as it enables the cell to take in nutrients and expel waste. Active transport is important for maintaining the cell’s ion balance and for transporting molecules such as glucose across the cell membrane. Both forms of transport are essential for the function of the cell and for sustaining life.
Exploring the Role of Membranes in Cell Transport and Its Effect on 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers
The role of membranes in cell transport is crucial for the maintenance of homeostasis in organisms. Membranes act as a barrier that separates the inside of the cell from its external environment. They also act as gateways that allow certain molecules to enter and exit the cell while preventing the passage of others. In this way, they regulate the movement of molecules into and out of the cell, thus enabling the cell to achieve a balanced internal environment.
The primary function of membranes is to regulate the transport of molecules between the inside and the outside of the cell. This is accomplished through a process known as selective permeability. Selective permeability is a mechanism whereby certain molecules are allowed to enter or exit the cell while other molecules are prevented from entering or exiting. This selective permeability is achieved through the presence of integral proteins, which act like locks or gates that are selectively opened and closed depending on the type of molecule. These integral proteins allow certain molecules to cross the membrane while preventing the passage of others.
The selective permeability of a membrane is also responsible for the movement of molecules within the cell itself. This process is known as passive transport and it involves the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This process occurs without any input of energy from the cell.
Finally, membranes also play a role in active transport. Active transport is a process in which molecules are moved from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. This process requires the input of energy from the cell and it is usually mediated by integral proteins known as transporters. Transporters can move molecules across the membrane in either direction depending on the concentration gradient.
In summary, membranes are essential for the proper functioning of cells. They act as a barrier that separates the inside of the cell from its external environment while regulating the transport of molecules into and out of the cell. They also enable the movement of molecules within the cell itself, both passively and actively. As such, understanding the role of membranes in cell transport is essential for understanding the mechanism by which cells maintain homeostasis and ensure their proper functioning.
Examining Passive and Active Cell Transport and Their Implications on 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers
Passive and active cell transport are two processes which are integral to the functioning of biological cells. Passive cell transport is a movement of particles across a cell membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, without the need for energy expenditure. This process relies on the concentration gradient of the molecules and does not require any energy on the part of the cell. Passive transport includes diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
Active cell transport, on the other hand, requires the expenditure of energy by the cell in order to move particles across the membrane. Active transport involves the use of proteins to move molecules against the concentration gradient. This type of transport is necessary for cells to maintain the correct concentrations of ions and other molecules within their internal environment.
The implications of passive and active cell transport on 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers can be seen in the way in which they affect the concentration gradient of molecules within the cell. By allowing molecules to move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration, passive transport serves to maintain the concentration gradient within the cell. Active transport, on the other hand, is necessary for the cell to maintain its internal environment, as it allows molecules to move against the concentration gradient.
In conclusion, passive and active cell transport are both necessary processes for the maintenance of cellular function. Passive transport enables the maintenance of the concentration gradient of molecules within the cell, while active transport allows for the movement of molecules against the concentration gradient in order to maintain the cell’s internal environment. Both processes are essential for the functioning of cells, and their implications on 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers are evident in the way in which they both affect the concentration gradient of molecules.
Applying 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers to Model Organisms and Their Transport Mechanisms
Model organisms are used by researchers to study the mechanisms of cell transport. In particular, the use of 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers offers information on the various transport mechanisms that are used by animals and plants.
In plants, the transport of ions, molecules, and other substances are conducted by passive and active mechanisms. Passive mechanisms rely on the concentration gradient of the substance, while active mechanisms require the cell to expend energy to move the substance across the membrane. Examples of passive mechanisms include diffusion and osmosis, while active mechanisms include active transport and endocytosis.
Animals also possess a variety of transport mechanisms, including diffusion and active transport. However, animals also possess unique transport mechanisms such as pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Pinocytosis is a process in which small particles are taken into the cell by the formation of small vesicles. On the other hand, receptor-mediated endocytosis involves the binding of specific molecules to receptors that are located on the cell surface. These receptors then form vesicles to transport the molecules inside the cell.
The 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers provides a comprehensive overview of the various transport mechanisms used by plants and animals. Through this worksheet, researchers can gain a better understanding of the various mechanisms and determine which transport processes are best suited for their model organism.
Conclusion
The 7 3 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers provide a comprehensive overview of the different types of cell transport mechanisms and their functions. From active and passive transport to endocytosis and exocytosis, the worksheet provides a clear and detailed explanation of each mechanism. By understanding the different types of cell transport, students can better understand the processes of how cells move materials and compounds within the cell.
[addtoany]